iNFO FROM: Psychology Frontiers and Applications by Passer
Angeheftet an
17
1
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von Susannah Mackenz
vor etwa 10 Jahre
|
|
Schließen
|
|
Erstellt von Susannah Mackenz
vor etwa 10 Jahre
|
|

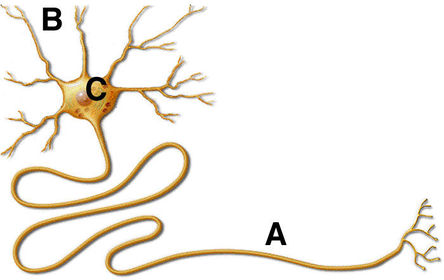
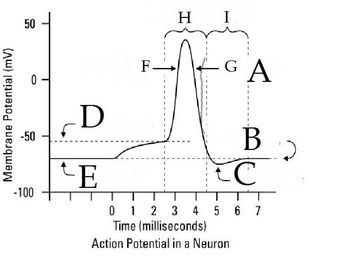
What does this image represent?
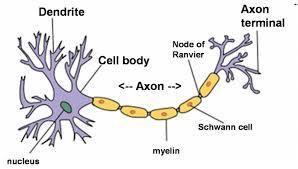
What is a neuron?
What does C represent?
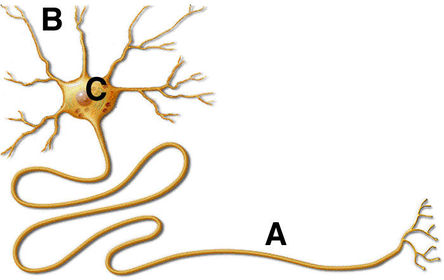
What does B represent?
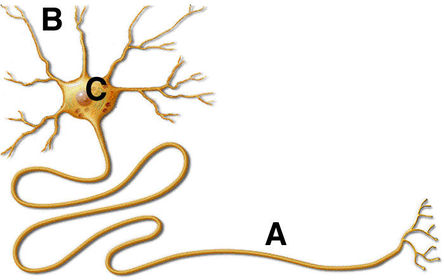
What does A represent?
The branchlike fibres that are like antennas that collect messages from neighbouring neurons and send them to the cell body are called?
Here neighbouring information from other neurons is collected and processed.
This conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body and to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
-Surround the neurons and hold them in place
- Manufacture nutrient chemicals that the neurons need
- Form the myelin sheath around some axons
- Absorb toxins and waste materials that might damage neurons.
Surround neurons and hold them in place
Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need
Form myelin sheath around some axons
Absorb toxins and waste materials
Fatty insulating layer some neurons have
Gaps in the myelin sheath that allows impulses to jump, and speeds up transmission
Protect(s) the brain from toxins
Nerve activation has how many basic steps?
What are the steps for basic nerve activation?
What is depolarization and when does it occur?
Reversal in the membrane's voltage, from -70mV to +40mV (inside).
The change in polarization in a neuron membrane that leads to a neural impulse
The interior of the cell is negative. The exterior of the cell is positive. There is a high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell (in the liquid) and chloride ions (outside cell in the liquid). Negatively charged protein ions (A-) and + potassium ions are inside the neuron.
The inside of the cell is positive; outside, negative.
Sodium channels open up; flood into the axon, creating depolarization
Most sodium outside cell; chloride outside cell
Potassium inside cell; negative anion proteins inside cell
Gates closed
Sodium channels open. Sodium floods into axon. K+ channels still closed
Sodium channels close; potassium channels open
What is the voltage of the refractory period?
Membrane cannot generate another action potential.
All-or-none law
-50 mV
Graded potentials
Action potential travels down the axon like a burning fuse
High conduction speeds generated from jumping of action potential from node to node
High conduction speeds generated from jumping of action potential from node to node
Satiago Ramon Y cajal
Otto Loewi
Gap from the axon terminal of one neuron to the dendrites of another
True or false: electrical impulses through a wire are faster than impulses through an axon
Damage to the myelin sheath can cause
When the immune system attacks the Myelin Sheath; impulses are slowed down
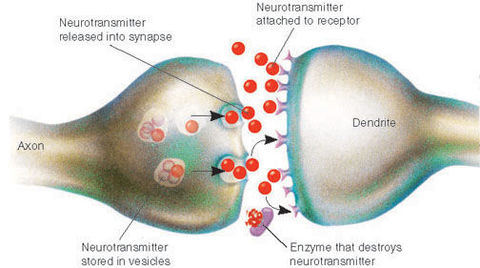
Chemicals that carry messages across the synapse
That excite other neurons OR inhibit their firing
______Molecules stored within these _______chambers, within the axon terminal
When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, the axon terminal releases ________ into the place between the end of the sending neuron( _______) and the membrane of the receiving neuron (______). The space is called _______.
When neurotransmitters cross the synaptic space, they bind to ______ which are?
Space between the pre-synapse and post-synapse?
Neurotransmitter activity moves from synthesis to deactivation. What is this process?
_________ of neurotransmitter --> storage in ______--> Release into ______--> _________to receptor sites --> Deactivation through _______ or breakdown
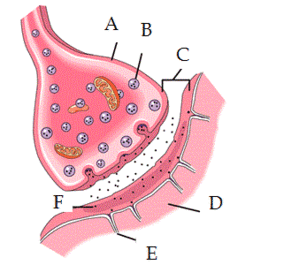
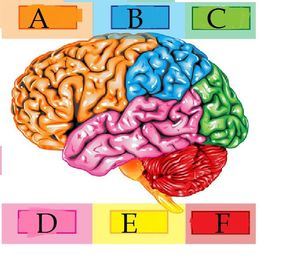
What do A, B, C REPRESENT?
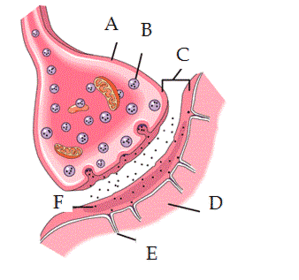
What do D, E, F represent?
Neurotransmitters that create depolarization
TRasnmitters that create hyperpolarization
Excitatory--> Depolarizes membrane--> _____likelihood of action potential
Inhibitory--> Hyperpolarizes membrane--> _______likelihood of action potential
Transmitters are reabsorbed into the pre-synapse
Depression: undersupply
Stress and panic disorders: oversupply
Inhibitory and excitatory at various sites
Involved in learning, memory, wakefulness and eating
Glutamate
GABA
ACh
Dopamine
Serotonin
Endorphins
What does this represent?
What does this chart visualize?
The brain and spinal cord comprise what component of the nervous system?
Label the following components of the brain
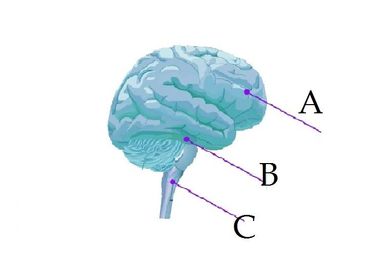
Label the following
Label the graph
Two major branches of the nervous system
The hindbrain is composed of the ______ and ______
The nervous system is composed of the _____ and the ______.
The peripheral NS is composed of the ______ and the _______.
The somatic system is a part of the _______nervous system. Its function is?
The autonomic system is part of ______. Its functions are?
The two branches of the autonomic system are?
The somatic system
The autonomic system is involved in?
Compare sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Function of the sympathetic system?
Parasympathetic system
________ and _______ work together to ensure our body is at a state of equilibrium (homeostasis); coordinated sequence of these activities
Connects spinal cord and brain
Most nerves enter and leave the CNS through the ______ _______.
______ _______ are fast responses that involve the senses and the spinal cord (not the brain).
Grey matter is surrounded by white (myelinated) matter; this structure cross-section forms an "H". the neurons are protected by back bone vertebrae.
The most active energy consumer of all your organs
Rate of energy metabolism relatively constant throughout the day/night and even increases slightly as you sleep. 2% of body weight; 20 % oxygen consumption at rest.
_________tests measure verbal and non-verbal behaviours affected by areas of brain damage. Used in clinical evaluations of people who may have suffered BD through disease or accidents.
Specific nervous tissue is destroyed by chemicals, electricity, cold or heat; this produces brain damage (lesions).
Or can surgically remove areas and study the consequences.
Or can be stimulated--producing opposite effects--through electricity or chemicals. This can be constant if an electrode is implanted.
PARTS AND FUNCTIONS OF THE BRAIN
LOBES AND FUNCTIONS OF BRAIN STUDY
LEFT AND RIGHT HEMISPHERES OF BRAIN
BRAIN SCANS
NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND FUNCTIONS

 Verberge bekannte Karten
Verberge bekannte Karten