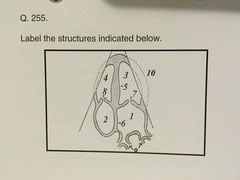
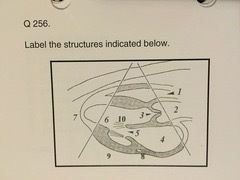
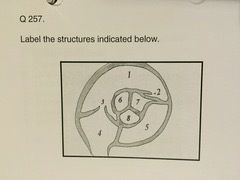
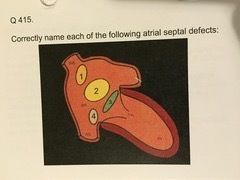
Echocardiography Karteikarten am Echo Final Deck 2, erstellt von Heather Edmonson am 26/10/2018.
Angeheftet an
35
1
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von Heather Edmonson
vor etwa 6 Jahre
|
|
Schließen