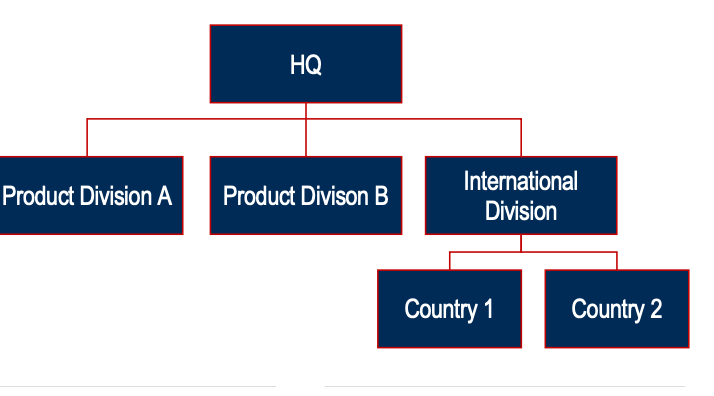
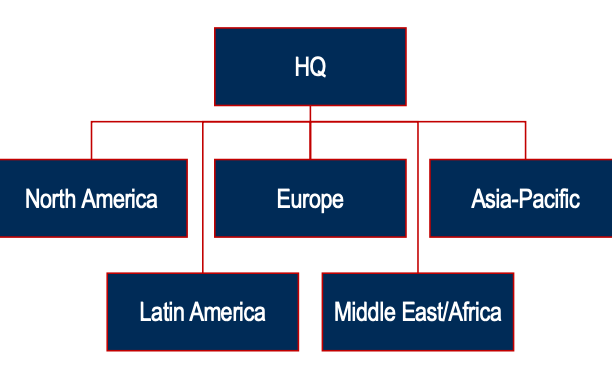
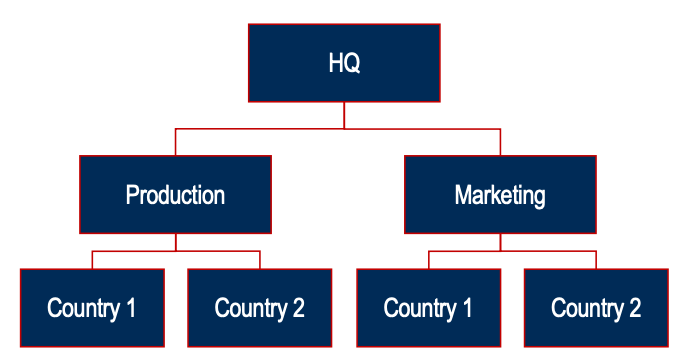
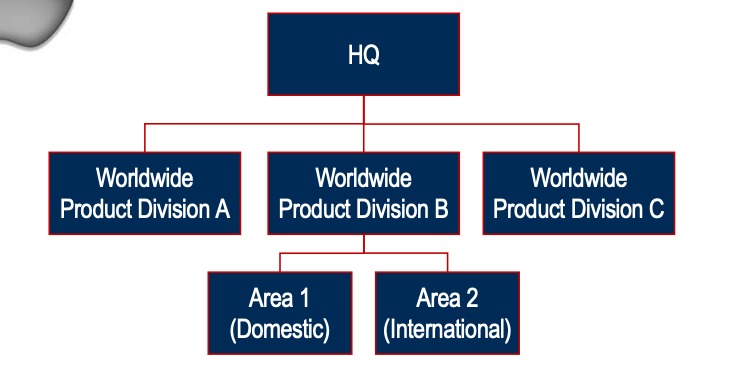
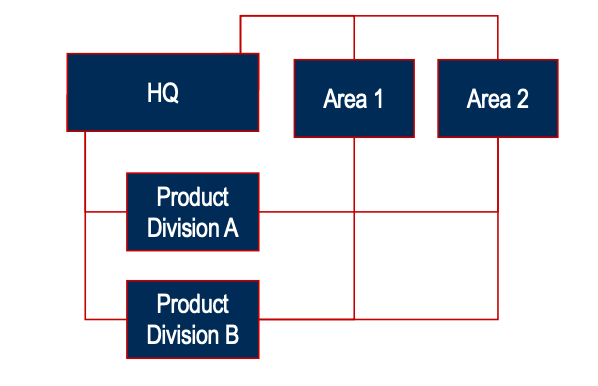
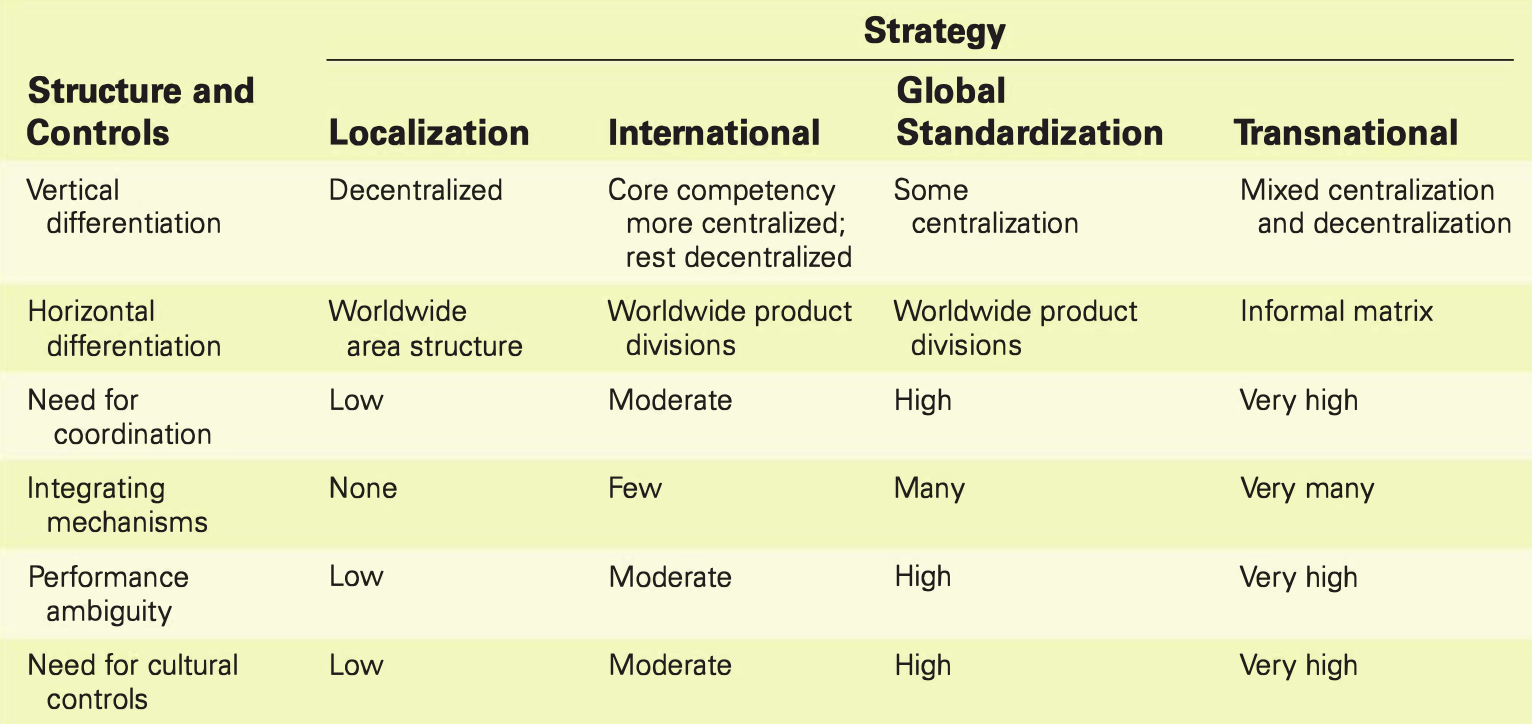
Wirtschaftswissenschaft Karteikarten am International Strategic MGMT_Part1, erstellt von Nora Mahrer am 27/09/2019.
Angeheftet an
270
0
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von Nora Mahrer
vor mehr als 5 Jahre
|
|
Schließen