Karteikarten am Project management 2, erstellt von Markus Holm am 18/03/2020.
Angeheftet an
62
0
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von Markus Holm
vor mehr als 4 Jahre
|
|
Schließen
|
|
Erstellt von Markus Holm
vor mehr als 4 Jahre
|
|

180. Describe a strategy to get support for coming changes in an organization.
179. What are the four rooms for change?
178. Tonnquist distinguish between “motivators”, “enablers” and “triggers”, which govern the action of personnel, for instance during changes. What do these concepts refer to?
177. What are the 8 steps, which according to Kotter, are required for change projects to succeed?
176. Give 3 examples of tacit knowledge and of explicit knowledge.
175. What is the difference between tacit and explicit knowledge?
174. Draw the knowledge management loop.
173. According to the course book, what is the difference between knowledge and competence?
172. What does the concept “collective memory” stand for?
171. What are reference measures?
170. How can the impact measurement be determined?
169. Why are some projects discontinued? Please three reasons and explain.
168. What are the hidden flaws of project closure?
167. Agile projects have been said to be better at meeting deadlines and budget than projects with detailed schedules, but are they better at meeting quality goals too? Motivate.
166. Which elements should be included in a final report?
165. Explain how a project can be evaluated.
164. According to Tonnquist (2016), administration and management of the results is important in order to secure impact goals. What is the primary goal of an administration and management model?
163. Which activities can facilitate a successful hand-over?
162. Tonnquist (2016) argues that even if the employees know that a change is necessary it might be difficult to execute it, what can be done to facilitate this process?
161. What are the three stages of an individual’s attitude to change?
160. What does project implementation entail?
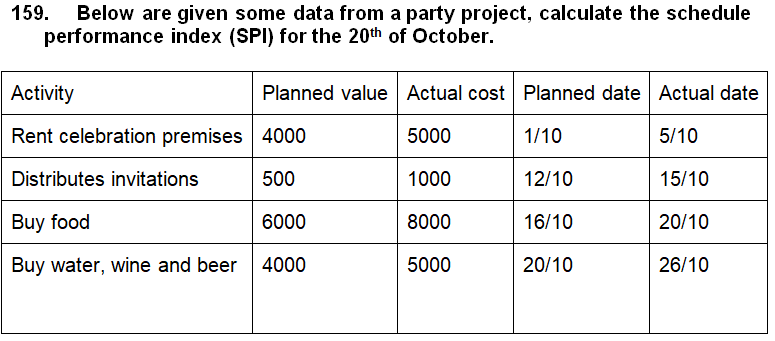
158. Which are the six steps for keeping project cost under control.
157. Name two of the methods for status reports and briefly explain them.
156. What does RACI stand for?
155. Which activities should be performed during execution?
154. Describe three different conflict management styles and their strengths and weaknesses.
153. Which are the steps of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs? What is the logic behind the different levels?
152. Fill in the following table
151. What is situational leadership according to Hersey? Explain
150. What is the Pygmalion effect and how can this be put to use in a project setting?
149. McGregor says that the leader gets the employees that he/she deserves, explain why?
148. What is theory X and Y?
147. Tom Peters have coined the phrase “leadership is attention” what does he mean by that?
146. What are the similarities and differences between being a manager and being a project manager?
145. How is our decision-making affected by different levels of stress?
144. What is self-leadership? What two dimensions are to be balanced?
143. What are the important aspects when receiving feedbacks?
142. What are the important aspects when giving feedback?
141. If others know things about yourself what you are not aware about, what happens from a Johari window perspective?
140. If you tell someone something that you have previously hidden, what happens from a Johari perspective?
139. Draw and explain the Johari window
138. What are the four components of self-awareness
137. What is the purpose of a kick-off? What actions affect the purpose?
136. What is organizational culture and how does it affect a project?
135. What phases are there in group development? What happens in each phase?
134. What is MBTI?
133. What are the four dimensions of DISC? Describe each dimension?
132. According to Tonnquist (2016) quality management consists of quality planning, quality assurance and quality audit.
131. What is the Japanese quality philosophy?
130. Give four examples of risk response strategies. Explain each of them.
129. There are many risks that can be identified in risk planning, and it is often not possible to act upon all of them. What strategy should then be used to choose between risks? Explain.
128. What is risk response planning?
127. Once risks have been identified, what is the next step to be done in the planning?
126. Explain the difference between the mini-risk method and the maxi risk method
125. Tonnquist (2016) gives four examples of risk categories. Name the categories and briefly explain them.
124. Briefly explain the process of risk identification.
123. Tonnquist (2016) distinguish risk from uncertainty. Briefly explain the difference.
122. You are planning a project with 2 different course of action. Course of action A has a 20% probability of yielding revenue of €200 000 and a 80% probability of yielding losses of €40 000. Course of action B is estimated to yield revenue of €40 000, with 40% likelihood, of losses of €10 000 with 60% likelihood. What is the expected value for course of action A? What is the expected value for course of action B?
121. What is the internal rate of return method and how can it be used?
120. What is the net presented value method and how can it be used?
119. What is the pay-back method and how can it be used?
117. Calculate the estimated average value of the following project: The estimate for a project shows that an activity will cost €1 800. Usually the price is €1 700, but it has sometimes been €1 500 and in some cases €2 000.
116. What are the values of Clikely, Cmax, Cmin based on
115. Fill in the following table based on Lichtenberg’s method:
- Cost estimation of uncertainty How can it be calculated? S =
- Estimated average value = Cexpected =
- Estimated maximum value =
- Estimated minimum value =
- Estimated likely value =
114. How can a resource histogram be used during execution?
113. What is a resource histogram and how can it be used during planning?
112. How is the cost for an agile project calculated?
111. How is the cost for a scrum team calculated?
110. Why is the activity plan useful when estimating costs? Explain.
109. How is the financial result calculated?
108. How is the contribution margin calculated?
107. What is a specific cost?
106. What is a specific revenue?
105. What is a contribution estimate and why is it useful?
104. Why does the project triangle play a big role when planning costs? Explain.
103. What is a self-costing estimate?
102. What is the difference between direct and indirect costs?
101. What are the two strategies to estimate costs during the planning phase of a project? Explain.
100. What is the lifecycle cost?
99. What is the difference between project costs and product costs?
98. What are the different basic phases of negotiation process? Describe them.
97. What are the 5 questions that should be answered ahead of procurement.

 Verberge bekannte Karten
Verberge bekannte Karten