Karteikarten am Waves and light , erstellt von laura.scottt am 24/08/2015.
Angeheftet an
53
4
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von laura.scottt
vor mehr als 9 Jahre
|
|
Schließen
|
|
Erstellt von laura.scottt
vor mehr als 9 Jahre
|
|

angle of incidence = angle of reflection
1/di +1/do = 1/f
m = di/do = hi/ho
Concave mirror produces...
Convex mirror always produces...
Concave mirror
O - center
O - c
O - parallel
O - axis
O - centre - under O
Convex mirror
O - parallel - F
O - C
Refraction - bending of light as passes from materials into another
Light travels at different speeds in different mediums
1n2 = C1/C2
In vacuum - no air - n = 1
1n2 = n2/n1
Snells Law
sinθ1/sinθ2 = 1n2
or
sinθ1/sinθ2 = n2/n1
or
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
Total internal reflection
Past the critical angle, all light reflects off the boundary (from dense to less dense medium)
θc = sin-1(n2/n1)
Convex lenses outside focal point
(real and inverted image)
O - P - f
O - C
O - F - P
Convex lenses inside focal point
(virtual and upright image)
P - f
O - c
Concave lenses
(virtual, upright, diminished)
O - P - F
O - C
Waves
V = F λ
Transverse - vibrate at right angles to direction of wave movement
(water waves)
Longitudinal - vibrate in same direction as direction of wave movement
(sound waves)
Pulse of string
Fixed boundary - inverted, same amplitude
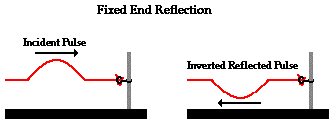
Pulse enters denser/slower medium
Reflected pulse - inverted, smaller amplitude, same wave length
Transmitted pulse - smaller amplitude, shorter wavelength
Pulse enters less dense/ faster medium
Reflected pulse - upright, smaller amplitude, same wavelength
Transmitted pulse - bigger amplitude, longer wavelength
Constructive interference
crest meets crest
trough meets trough
forms double amplitude
Deconstructive interference
crest meets trough (of equal amplitude)
two waves cancel each other out
Waves from point move outwards in circles
waves from a straight line move away in straight lines
Water waves - deep to shallow - shorter wavelength and slower velocity
sinθ1/sinθ1 = V1/V2 = λ1/λ2 = n1/n2
Standing waves - series of incident waves interact. Reflecting wave off closed boundary
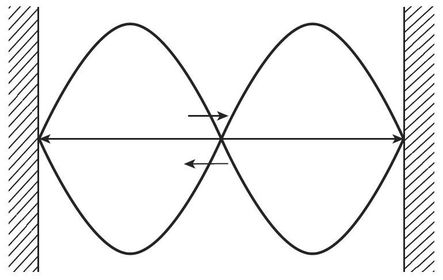
anti node & anti nodal lines = crest + trough
arrive in phase & constructive interference
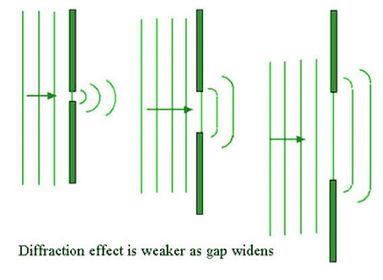
Diffraction - bending of waves around the edges of an object
Diffraction through slit
Wave interference - waves from 2 sources add together to form interference pattern of nodes and antinodes
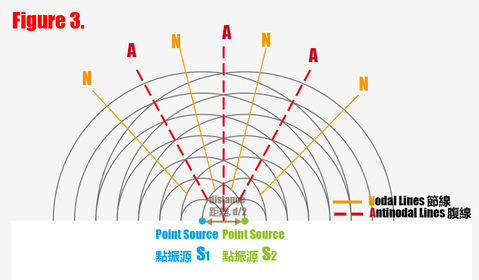
Path difference
difference of the distance a point is away from source 1 and source 2

 Verberge bekannte Karten
Verberge bekannte Karten