Schließen

G E N E T I C S
- the scientific study of how genes control the characteristics of an organism.

GREGOR MENDEL
- The father of genetics is a late 19th-century scientist and Augustinianfriar. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring.

FEATURES OF INHERITANCE
1.Punnette Square
2.Notation and Diagrams
3.Multiple Gene Interactions
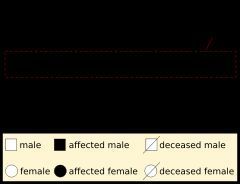
NOTATION AND DIAGRAMS
- Geneticists use diagrams and symbols to describe inheritance. A gene is represented by one or a few letters. Often a "+" symbol is used to mark the usual, non-mutant allele for a gene.
MOLECULAR BASIS FOR INHERITANCE
1.DNA and chromosomes
2.Reproduction
3. Recombination and genetic linkage
Reproduction
Main articles: Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction
When cells divide, their full genome is copied and each daughter cell inherits one copy. This process, called mitosis, is the simplest form of reproduction and is the basis forasexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction can also occur in multicellular organisms, producing offspring that inherit their genome from a single parent. Offspring that are genetically identical to their parents are calledclones.
CONCLUSION :
Genetics play a very large role in the appearance and behavior of all organisms. Genetics are the reason for the inheritance of certain traits such as the white forelock or the bent pinky. Most genetic traits are inherited from the person's biological parents, and some people may have a recessive allele present rather than a dominant one. Just because a trait is "dominant", doesnt mean that it will be the trait thats predominantly common in society. Genetics give people their identity, their own personal imprint that makes them unique. Everyone is different.

 Verberge bekannte Karten
Verberge bekannte Karten