Lipid Metabolism I, II, & III - MED 2017
Angeheftet an
5
0
0
Keine Merkmale angegeben
|
|
Erstellt von Kristina Redd
vor mehr als 7 Jahre
|
|
Schließen
|
|
Erstellt von Kristina Redd
vor mehr als 7 Jahre
|
|

What tissues don't experience FA catabolism?
What type of oxidation does catabolism require?
What is the result of B-oxidation in catabolism?
How much ATP results from acetyl-CoA entering the Krebs cycle?
What are fatty acids stored as in adipose tissue and muscle?
What do FAs bind to when transported in the blood?
What enzyme is used to transfer TF into FA in adipose tissue?
Where are ketone bodies made?
What alcohol is attached to the FAs before being stored as triglycerides?
Breakdown: TG --> FA --> _____ . What is the form of energy?
Most of the body lives on FA oxidation. Glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis occur where?
Where are FAs activated and primed for metabolism?
What enzyme is used to make an activated fatty acid from fatty acid + CoA?
Why does a FA need to be oxidized? Where does the site of this oxidation occur?
How many ATP are required to activate a FA (that happens in the cytosol)?
What molecule carries FA into the mitochondria?
How many carbons in a FA chain does it require to complete B-oxidation and make 2C acetyl-CoA?
What is THE major source of biological energy production during fasting?
What is significant about the B-oxidation of FAs that does not occur in the Krebs Cycle oxidation?
How many ATP result in accumulating 1 FADH2 from the B-oxidation cycle?
How many ATP result in accumulating 1 NADH from the B-oxidation cycle?
How many ATP result in accumulating 1 acetyl-CoA from the B-oxidation cycle?
What cells primarily use FA for energy metabolism?
How is acetyl-CoA exported from the mitochondria to cytoplasm?
What drives FA synthesis?
FA synthesis involves energy-driven (ATP) carboxylation of _____ to _____.
The chemical reversal of B-oxidation is _______.
How are carbon atoms added on FA synthesis?
What is the intermediate for FA synthesis?
Where does FA synthesis occur?
What is the primary co-enzyme for FA synthesis?
How are carbon atoms removed in FA oxidation?
How much energy does it cost for acetyl-CoA to exit the mitochondria as citrate/
What enzyme makes malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA?
What is the rate-limiting enzyme of FA synthesis?
At what point does FA synthesis stop?
How do elongases function?
What do desaturaes do?
What is the "longest reach" when referring to desaturases?
Which three FAs are essential?
For FA synthesis, what are the two allosteric controls?
How many ATP for acetyl-CoA to be exported from the mitochondria?
How many ATP does it require for 7 malonyl-CoA syntheses?
How many ATP is offered by 2 NADPH?
How do you calculate how much ATP is used to make FA from acetyl-CoA to store?
The net energy cost between FA synthesis and FA oxidation is ____ ATP.
What is the general chemical equation to make a triglyceride?
Identify.
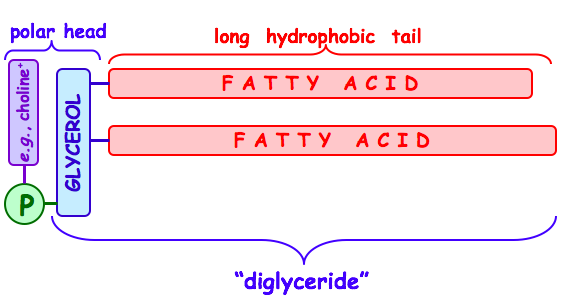
What type of energy activates choline in the biosynthesis of a phospholipid?
What phospholipid is important for lung surfactant that can also cause respiratory distress for premature babies if missing?
What is the energy input required in the synthesis of FAs?
What molecules result from the Krebs Cycle [ox]?
What molecules result from the B-oxidation of FAs?
What is the multi-enzyme complex in cytosol used in FA synthesis?
What is chylomicrons (lymph)?

 Verberge bekannte Karten
Verberge bekannte Karten