
Waves can transfer __________ and information without a net __________ of the medium through which they travel.
They involve ____________ (oscillations) of some sort.
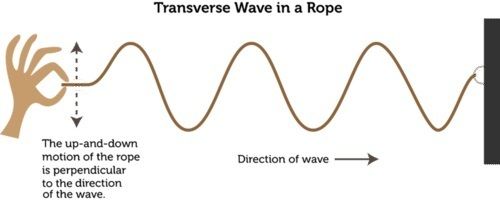
In transverse waves, the ___________________ (oscillations) are __________________ (at right angles) to the ________________ of energy transfer.
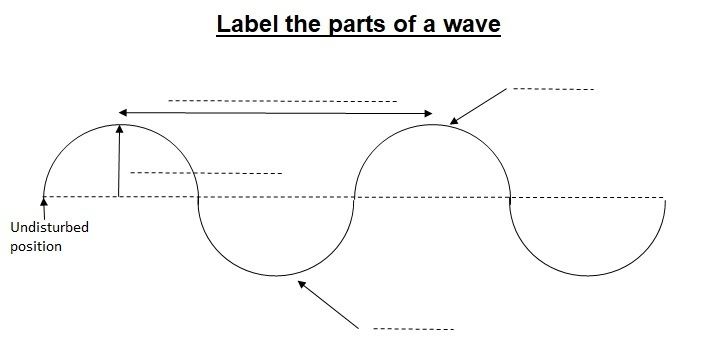
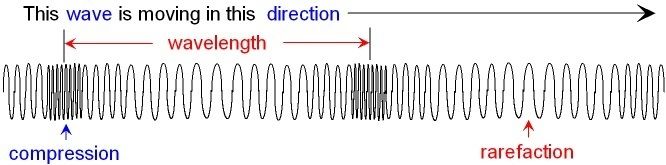
What is wavelength?
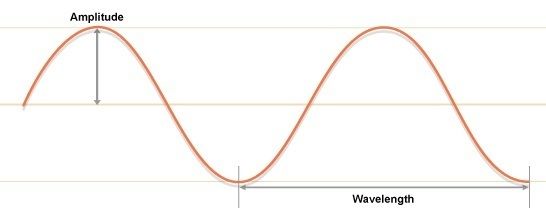
What is amplitude?

What is frequency?

wave speed (meters per second) = frequency (Hertz) × wavelength (meters)
Calculate the speed of a wave.sound wave with a wavelength of 0.65 m and a frequency of 512 Hz.
In longitudinal waves, the _________________ (oscillations) are in the ________ direction as the direction of travel.
When waves ____________ off a plane (_____) barrier, the __________ of reflection and the angle of ________________ will be equal.
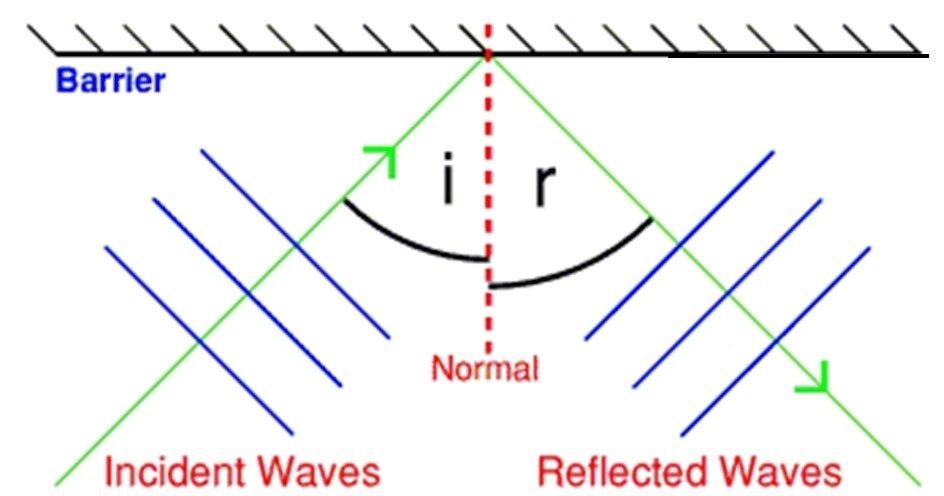
Describe the changes in wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave when it is reflected.

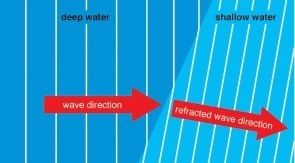
Refraction occurs when water waves pass between deep and __________ water.
The waves slow ______ in shallow water. The _______________ of the waves remain constant and so the ______________ decreases.
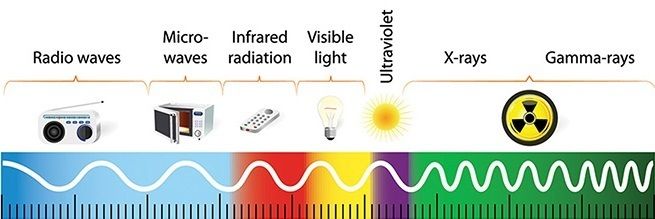
The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of 7 different types of radiation. In order of increasing frequency, these are:
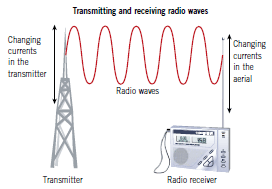
1. Radio waves
2. ________________
3. Infrared
4. ____________ ___________
5. Ultraviolet
6. __-______
7. Gamma
List 3 things that all 7 types of electromagnetic radiation have in common.
Ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma radiation can be described as ionising radiation.
What does ionising radiation mean?

What is a geosynchronous satellite?
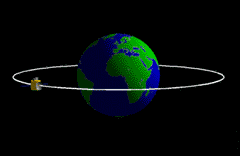
What is a geostationary satellite?
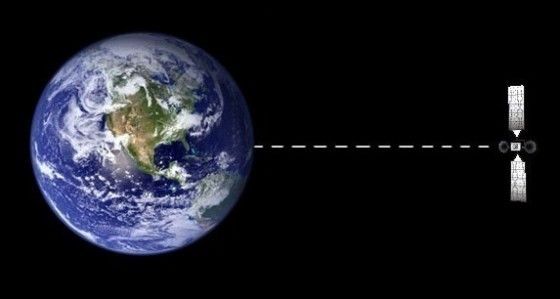
Why do communications satellites need to have a geostationary orbit?

Why do communications satellites use microwave radiation to transmit information?

How long would it take a TV signal reach a satellite dish on your house roof, after the signal has been broadcast from a TV transmitter on Earth to a communication satellite in orbit 36,000 km above the Earth?
(All electromagnetic waves travel at 300,000 km/s in a vacuum)

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards