Medicine Flashcards on Unit 3 Week 6 & 7 , created by shirou masoodi on 06-04-2018.
Pinned to
33
2
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by shirou masoodi
over 6 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by shirou masoodi
over 6 years ago
|
|

Name 4 Risk factors of CVD (2 Constitutional & 2 non-constitutional)
Outline the formation of a Transitional atheromatous plaque
Describe what causes TIA
Compare a fatty streak to an advanced plaque
Name & describe the 2 methods for formation of complicated plaque
Outline the difference between Stable & Unstable angina
Define and name 2 causes of Prinzmetal angina
Outline the pathogenesis of MI
What is an ST elevated MI?
Which parts of the heart is supplied by
Anterior interventricular artery
Left Circumflex
RCA
Explain the following presentations in MI
1. Chest pain (Left)
2. Sweaty & Clammy
3. Shortness of breath
Outline which investigations should be conducted following STEMI
What is the most optimal management strategy for MI
Why was atenolol prescribed
What is the mechanism of action of Simvastatin.
Mechanism of action of Ramipril
2 Adverse effects of warfarin
Why is aspirin given to chew after MI
How does a AED work?
Give 2 examples of shockable rhythms
What are the 4 primary criteria when analysing ECG
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic HF
Explain the pulmonary presentations of LHF
Outline how chronic lung disease leads to cor pulmonale (What are the clinical manifestations of this?)
Management of HF
Basic management of HF
What is the role of a first responder?
Outline the Self regulatory model of illness
Describe the cognitive and emotional response of the self regulatory model of illness
Give 2 examples of positive consequences of MI
What is the role of cardiac rehabilitation
Define global governance
Give 4 ways governance can achieve equity in health
Compare and contrast the Beveridge model of healthcare to the out of pocket model of healthcare

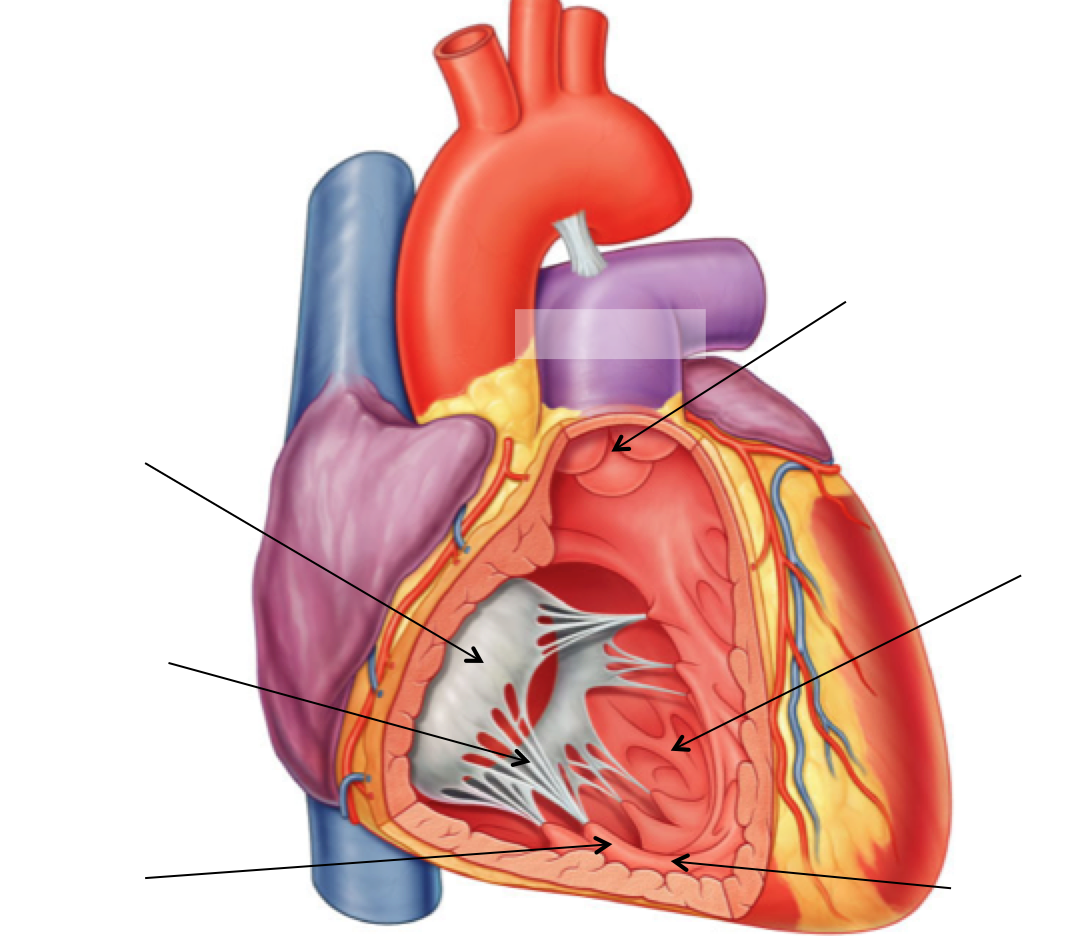
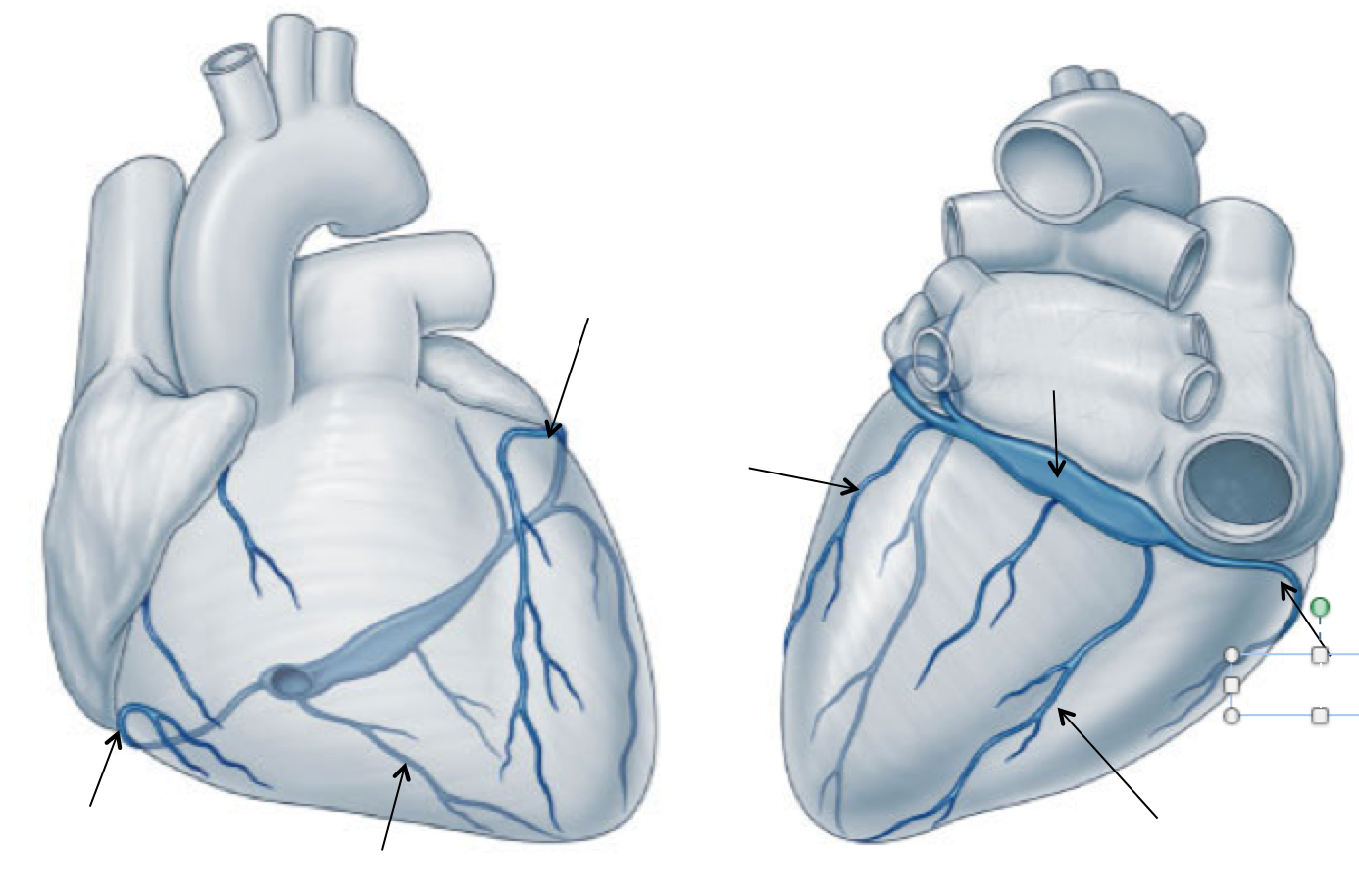
Outline the classification for stage 1, & 3 of hypertension
Name 2 constitutional and 2 non-constitutional risk factors of hypertension
What is the difference between primary and secondary hypertension
Outline how left heart failure is caused by hypertension
Explain how low blood pressure is regulated by the baroreflex
How does the kidney normalise GFR when blood pressure is increased
Give 5 actions of Angiotensin 2
Explain why patients with hypertension would present with proteinuria
Explain the following fundoscopic findings
1. Papilloedema
2. Cotton wool spots
3. Small haemorrhages
What would you expect to happen to serum creatinine and eGFR for a patient with hypertension?
List 4 non-pharmacological interventions for hypertension
Give 2 adverse effects of phenoxymethylbenzamine
a. What class of drug is Clonidine?
b. What is the mechanism of action?
Amy-lee was prescribed the beta-blocker propanolol for hypertension and now finds she often has cold hands and feet. Why might this be?
Why are beta-blockers such as atenolol & bisoprolol contraindicated in diabetics?
Abbie Randall has been suffering from a persistent cough for the past 2 weeks. Upon consultation her GP finds that she has recently started taking Ramipril. Explain Abbie's cough
a. What is the mechanism of action of Amlodipine?
b. In what circumstance would amloppine be the first line treatment for hypertension?
a. what is the mechanism of action of furosemide?
b. Why is the action of diuretics transient?
Identify 3 possible triggers to consultation.
Identify 3 possible barriers to consultation.
Explain the pathological basis of the following presentations in pheochromcytoma:
1. Sweating
2. Nausea & vomitting
3. Hypertension
4. Palpitations

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards