
physical needs such as sleep and hunger
private; unobservable

the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
1. description
2. explanation
3. prediction
4. influence
an educated guess about some phenomenon
research

using psychological principles to solve more immediate problems

In 1879 he opened the first psychology laboratory in Germany; "father of psychology"

the concept that the mind and body are separate and distinct
our mind is a blank slate that the environment (aka experience) writes upon; John Locke

being interested in the basic elements of human experience
self-observation to collect information about the mind
taught the first class in psychology at Harvard University in 1875

study how animals and people adapt to their environments
declared that the "most fit" humans were those with high intelligence

the debate about the extent to which our behavior is inborn (innate) or learned through experience
perception is more than the sum of its parts
a physician who practiced in Vienna until 1938; more interested in the unconscious mind

a method for indirectly studying unconscious processes
a female pioneer in psychology (1863-1930)

Russion physiologist (1849-1936); studied conditioned reflexes provoked by stimuli

psychologists who stress investigating observable behavior
(1878-1958) psychology should concern itself only with the observable facts of behavior; all behavior, even apparently instinctive behavior, is the result of conditioning and occurs because the appropriate stimulus is present in the environment

describe human nature as evolving and self-directed; does not view humans as being controlled by the events in the environment or by unconscious forces. instead, the environment and other forces simply serve as a background to our own internal growth
a specialty of medicine

help people deal with personal problems; they normally work in offices, mental hospitals, and prisons
work in their own private office, in schools, or industrial firms, advising and assisting people with their problems
employed by business firms and government agencies; study and develop methods to boost production, improve working conditions, place applicants in jobs for which they are best suited, train people, and reduce accidents
African-American psychologist who conducted the White/Black Doll Experiment for the Brown vs. Board of Education court case

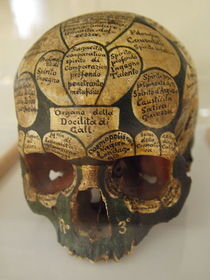
science of skull bumps
to be objective; listening and interpreting the associations
psychoanalytic theory, a desire for sexual involvement with the parent of the opposite sex and a concomitant sense of rivalry with the parent of the same sex; a crucial stage in the normal developmental process; Sigmund Freud
His theory: operant conditioning; “the behavior is followed by a consequence, and the nature of the consequence modifies the organisms tendency to repeat the behavior in the future.”

a slip of the tongue where a person says what they're actually thinking about at the time

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards