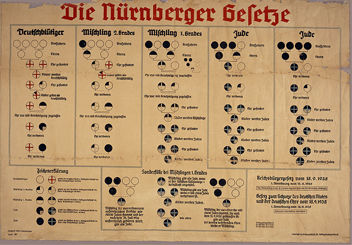
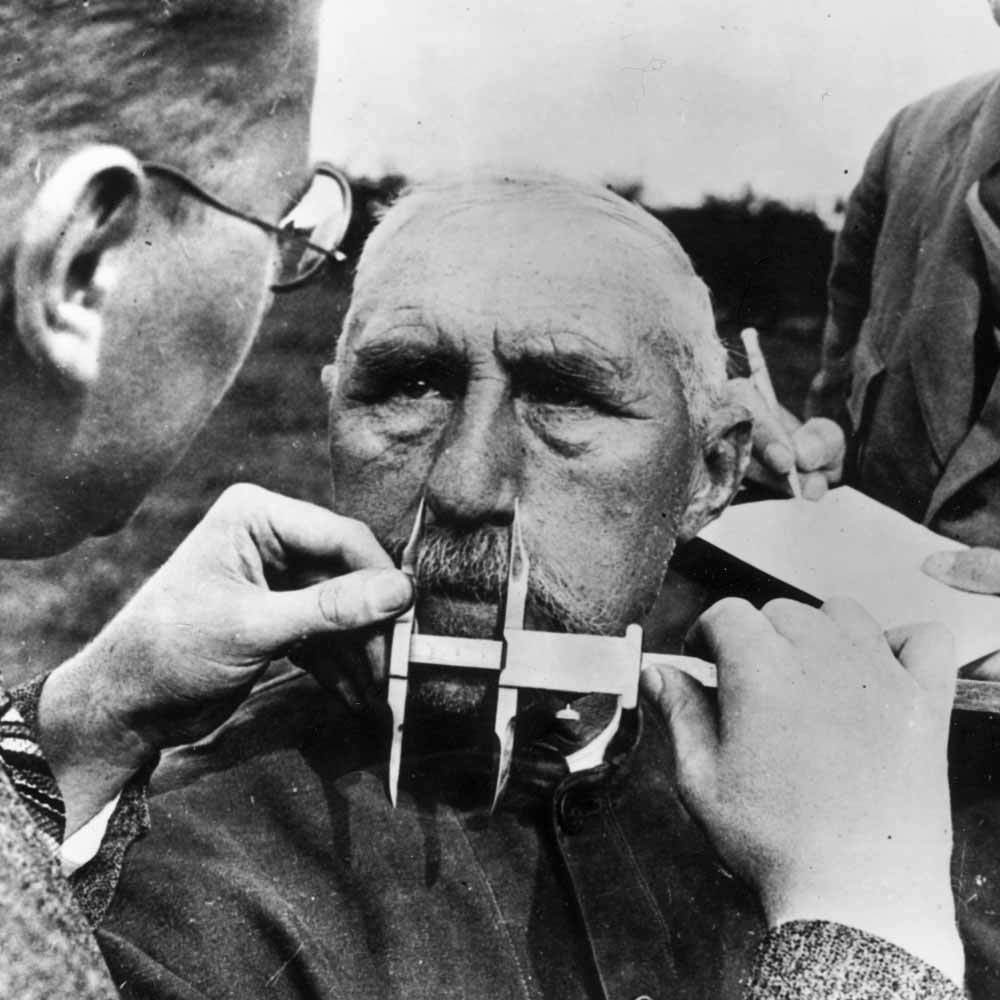
A set of Flashcards detailing key events from the unification of Germany to the start of WWII
Pinned to
10
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Nathan Chan
over 6 years ago
|
|
|
|
Copied by Nathan Chan
over 6 years ago
|
|
Close