Flashcards on Pharmacology, created by Aizza Memon on 21/05/2018.
Pinned to
28
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Aizza Memon
over 6 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Aizza Memon
over 6 years ago
|
|

What is an allergy?
Types of hypersensitivity reactions
Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
examples
Allergic Conjunctivitis
SAC
PAC
Vernal Keratoconjuctivitis
VKC
Atopic Keratoconjuctivitis
AKC
TYPE 1 reaction
2 stages:
1) initial sensitisation
2) subsequent exposure
Histamine receptors
Type 2 and type 3 hypersensitivity
Type 4 hypersensitivity
Giant Papillary Conjuctivitis
Astringent eye washes and drops
Ocular decongestants
Ocular decongestants examples and problems
Antihistamines
Antihistamines
how do they work?
examples
Examples of
dual action antihistamine
and mast cell stabilser
antihistamine problems
Mast cell stabiliser
Mast cell stabiliser examples
Mast cell stabiliser
indications
problems
oral antihistamines
what is inflammation?
stages of inflammation
components of inflammatory response
signs of inflammation
How are chemical mediators synthesised?
Prostaglandins
COX enzymes
NSAIDS- inhibit the PG synthesis
example of topical NSAIDS
Systemic NSAIDs
anti inflammatory action of corticosteroids
SAIDS
TOPICAL SAIDs
topical SAIDS examples
other inflammation measured
pain pathway
ocular pain pathway
Pyresis
Pyresis V hyperthermia
paracetamol
v NSAIDS
Cox enzyme inhibition
Aspirin
ibuprofen
paracetol
drugs and Analgesic activity
painkillers drug safety
Opioid analgesics
Opioids and pain pathway
Codeine
dihydrocodeine
OPIOID ANTAGONISTS
mixed action compounds
general ocular response
sites of ocular infecction
class of micro- organisms
Bacteria characteristics
bacterial resistance
Differentiation of bacteria
Common bacterial causes of infection
Mechanism of action ( bacteria)
penicillions and cepholosporins
Mechanism of action - pencillion
Pencillin use
Bacitracin
Vanomycin
drugs affecting cell membrane permeability
drugs affecting protein synthesis
Aminogylcosides
tetracyclines
chloramphenicol
macrolides
Fusidic ACID
inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
quinolones/ fluoroquinolones
interference with uptake of DNA, rna precursers
propamidine and dibromopropamidine
antibiotics with antimetabolitee activity
Sulpohamides
trimethorpim
optometrist and bacteria management
Acanthamoeba keratitis
treatment of acanthameoba keratitis
viruses
viral replication
virus transcription and translation
viral infections
Herpesvirus infections
virus and infection
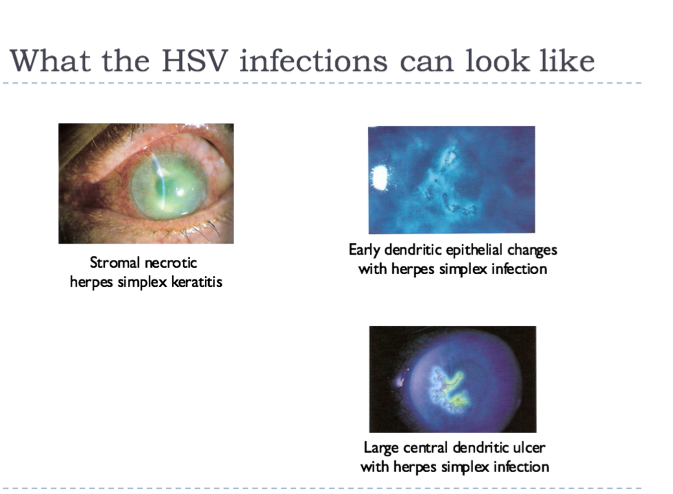
herpes varicella zoster infections
cytomegalovirus
antiviral drugs
mechanism of action - antiviral
anti viral
side effects
drug regime
RNA retroviruses
fungi
fungal infections
fungal keratitis
polyenes
azoles
other antifungals
open angle glaucoma
sites of aqueous humour production and outflow
glaucoma
what do we want for an antiglaucoma treatment
Drugs and mechanism of action
parasympathomimetics?
beta blockers?
alpha 2 agonists?
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
hyperomsotic agents?
prostaglandin analogues?
prostamide analogues?
POM only
management of glaucoma?
NICE GUIDELINES FOR GLAUCOMA
Prostaglandin analogues
prostglandin analogues examaples
prostamide analogue
prostaglandin and prostamide analogues
Beta Blockers
-facts
beta blocker mechanism
beta blockers
- advantages
- disadvantages
beta blockers side effects
normal tension glaucoma
beta blockers for glaucoma
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
mechanism
systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
other CAIs
Sympathomimetics
ALPHA 2 ADRENOCEPTOR
alpha 2 adrenoreceptor agonists examples
parasympathomimetics
future glaucoma medication
how to treat dry eye with no drugs?
level 1 pharamcological approaches
tear substitutes
artificial tears
tear substitutes
POLYMERS
tear film
polymers
HPMC
tear substitutes polymers
HMC
CMC
tear substitutes
lubricants
tear substitute
gels
tear substitutes
ointments
problems associated with tear substitures
Biofilm
viscoelastic preperations
Lipid spray
mucolytics
dry eye alternative approach
anti inflammatory
dry eye alternative approach
ciclosporin A
dry eye alternative approach
Lifitgrast
IL-1 inhibitors
dry eye alternative approach
dry eye alternative approach
tetracylcline
secretagogues
Commonly prescribed drug
statin what are they used for?
warfarin
Aspirin
thyroxine
anti hypertensives
beta blockers
diuretics
calcium channel blockers
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin antagonists
anti asthma drugs
anti diabetic drugs
Adverse Reactions
muscarinic antagonist
Adverse reaction
Anti-dysrhythmics: Amiodorone
Adverse reactions
anti dysrhythmics
DIGOXIN
Adverse reactions
beta blockers
adverse reaction
anti-epileptic drugs
adverse reaction
hormones
adverse reactions
adrenal steroids
adverse reactions
NSAIDS
adverse reaction
anti malarials
adverse reaction
drugs used for erectile dysfunction
types of adverse reactions
type A adverse reactions
biologics definition
SMEs v biologics
why do we use biologics?
antibodies as biologics

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards