Close

John Dalton
John Newland
Dmitri Mendeleev
Limitations of Mendeleev's periodic table
Element groups
Reactivity within groups
Group 1 reactivity
Group 7 Reactivity
Metal reaction
Alkali Metals
Properties of alkali metals
Melting and boiling points of alkali metals
Alkaline metals reaction with water
Alkali metals reactions
Transition elements
Physical properties of transition metals
Chemical properties of transition metals
Compounds of transition metals
Group 7- Halogens
Reactions of halogens
Displacement reaction between halogens
Hard Water
How hard water forms
How hard water wastes soap
How scale (limescale) is formed
Advantages of hard water
Removing hardness
Temporary hardness
Permanent hardness
Explaining the effect of heating hard water
Softening water - Using washing soda
Softening water - Using an ion-exchange column
Water treatment - boreholes
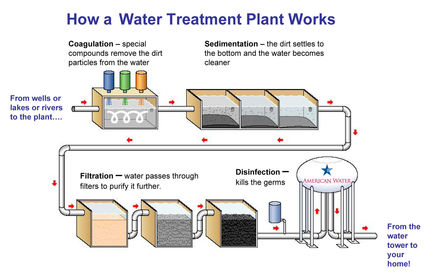
Water treatment - Rivers and reservoirs
Water treatment - Filter jugs
Pure - or just fit to drink?
Water treatment - Rivers and reservoirs - Steps
To soften or not to soften?
Chlorine in water
Fluoride in water
Advantages of fluoridation
Disadvantages of fluoridation of water
Comparing the energy released by fuels
Calculating the energy released
Calculate the energy released per gram or per mol
Simple calorimeter
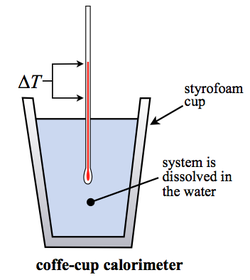
Energy transfers in solutions
Worked example of energy transfer in solutions
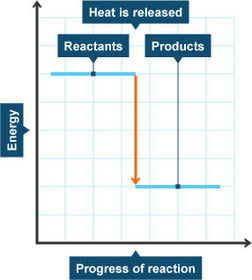
Energy level diagrams
Energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction
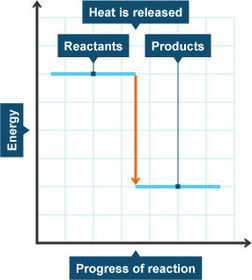
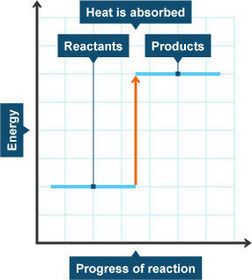
Energy level diagram for endothermic reactions
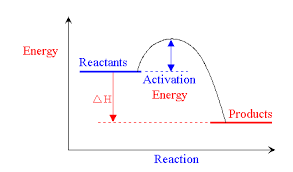
Activation energy and catalysts
Bond breaking and bond making
Making and breaking bonds
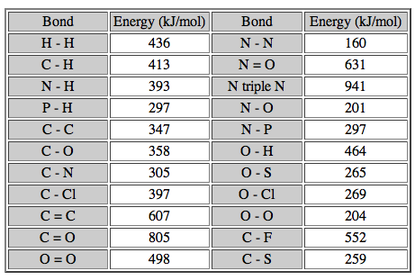
Bond energy
Consequences of burning fuels
Hydrogen powered vehicles
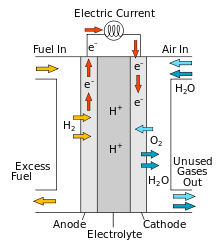
Hydrogen fuel cells
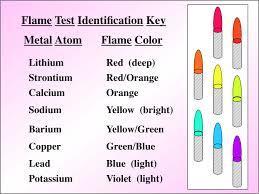
Test for positive ions
Test for positive ions:
Flame test- Though Lithium is crimson, potassium lilac, barium green, calcium red only one that's right is sodium.
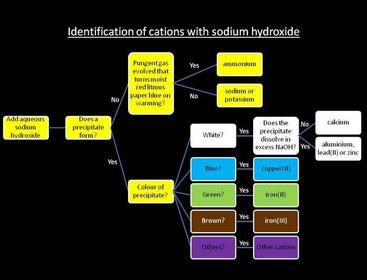
Reactions with sodium hydroxide
Tests for negative ions: Carbonates
Test for negative ions:
Halides (chloride, bromide and iodide)
Test for negative ions:
Sulfates
Titration
Carrying out titration
Carrying out titration 2
Titration calculations: Calculating concentrations
Titration calculation: Calculating concentrations - Example
Titration calculation + Example 3
Titration calculations: Example 3 continued
Titrations Calculations: Example 2
Chemical analysis
Analysis in foresnic science
Analysis in pollution control
Analysis in medicine
Chemical equilibrum
Chemical equilibrium continued
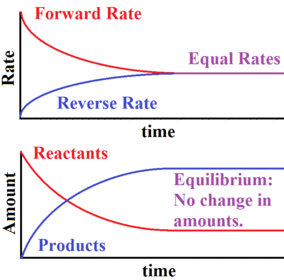
Chemical equilibrium example
Altering conditions: Pressure and equilibrium
Altering conditions: Pressure and equilibrium - Example
Altering conditions: Energy and equilibrium
Altering conditions: Energy and Equilibrium - Example
Making ammonia
The Haber process
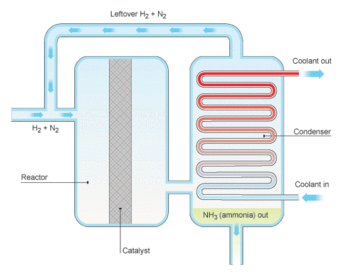
The Haber process continued
Economics of the Haber process - Effect of pressure
Economics of Haber process - Effect of temperature
Economics of Haber process - Effect of catalyst
Structures of alcohols, carboxylic acids and esters
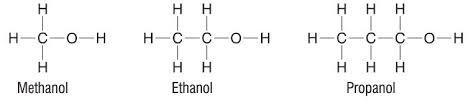
Alcohols
Carboxylic acids
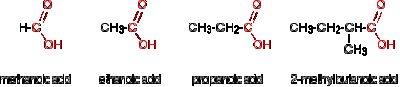
Esters
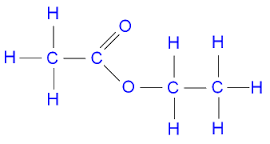
Properties and uses of alcohols
Uses of alcohols: Combustion
Uses of alcohols: Reaction with sodium
Uses of alcohols: Oxidation
Carboxylic acids uses
Why carboxylic acids are called 'weak acids'?
Why carboxylic acids called weak acids - continued
Making esters
Organic issues: Ethanol in drinks
Ethanol in drinks
Ethanol and esters as biofuel

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards