Close

What is the general name for a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction?
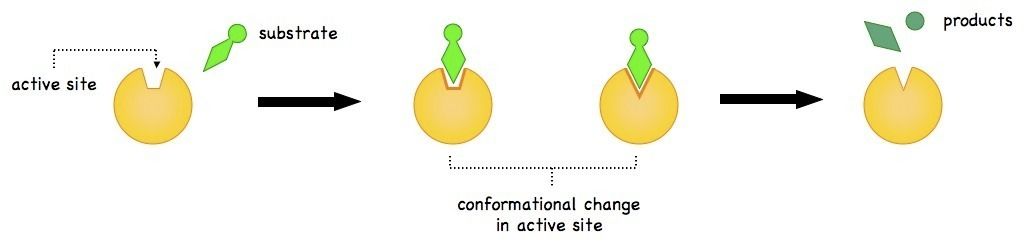
Explain the scheme:
What is the collective name of all the chemical reactions that occur within an organism?
Give 2 ways by which enzymes can lower activation energy
What do the variables mean in the equation
G = H - TS
Draw a graph showing how substrate concentration can affect the rate of reaction
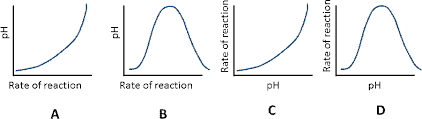
Which graph shows the effect of pH on enzyme activity?
How do we call non-protein helpers for catalytic activity?
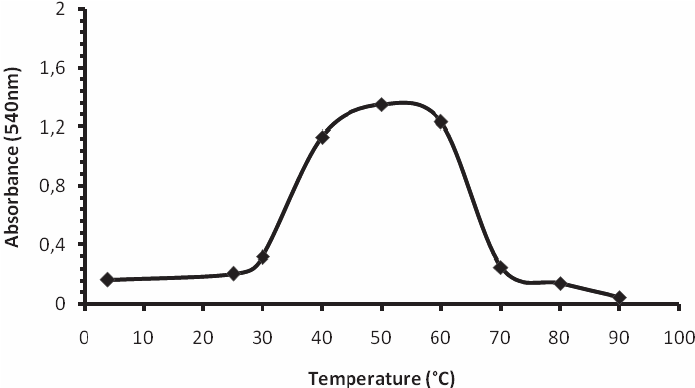
Estimate the optimal temperature for the enzyme X represented below:
What is a coenzyme? Give one example
All cofactors are coenzymes, but not all coenzymes are cofactors. Do you agree?
Illustrate the process of energy coupling
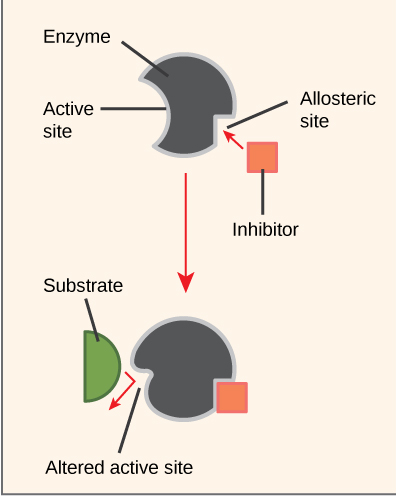
Name and explain the type of enzyme inhibition illustrated by the figure:
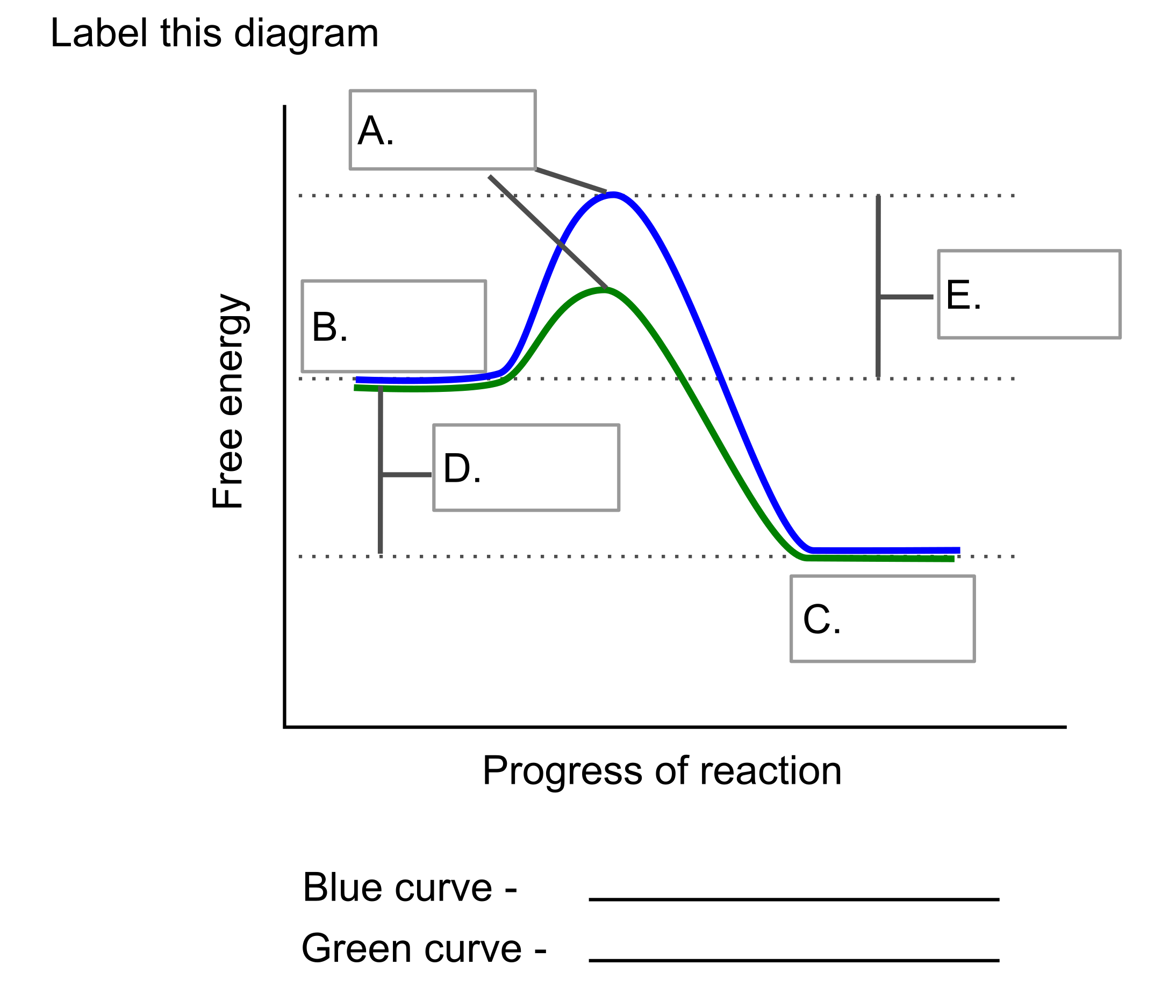
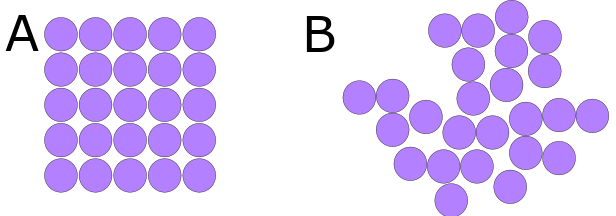
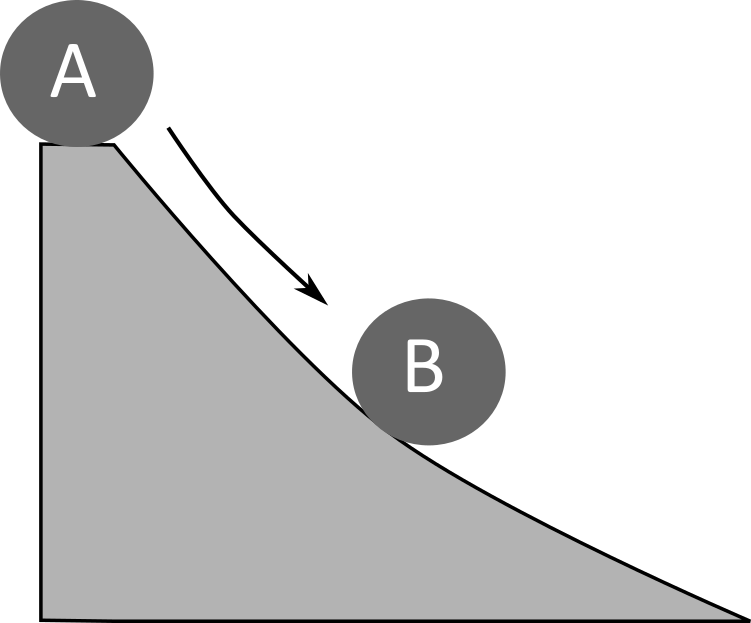
Which state has higher entropy?
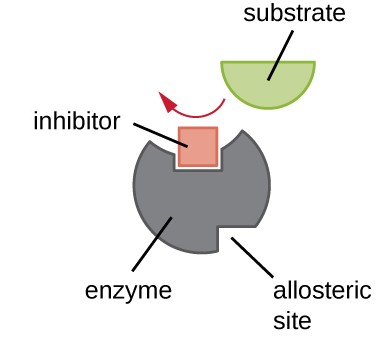
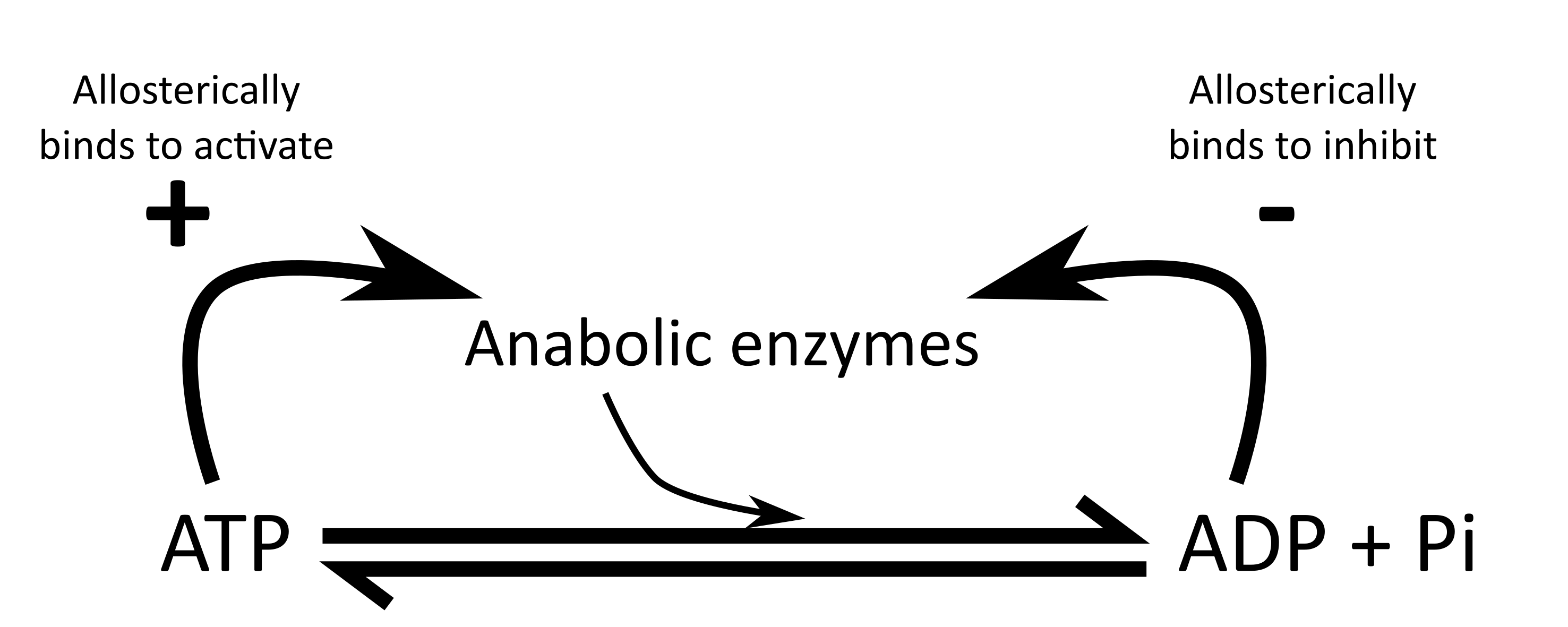
Illustrate the process of feedback inhibition
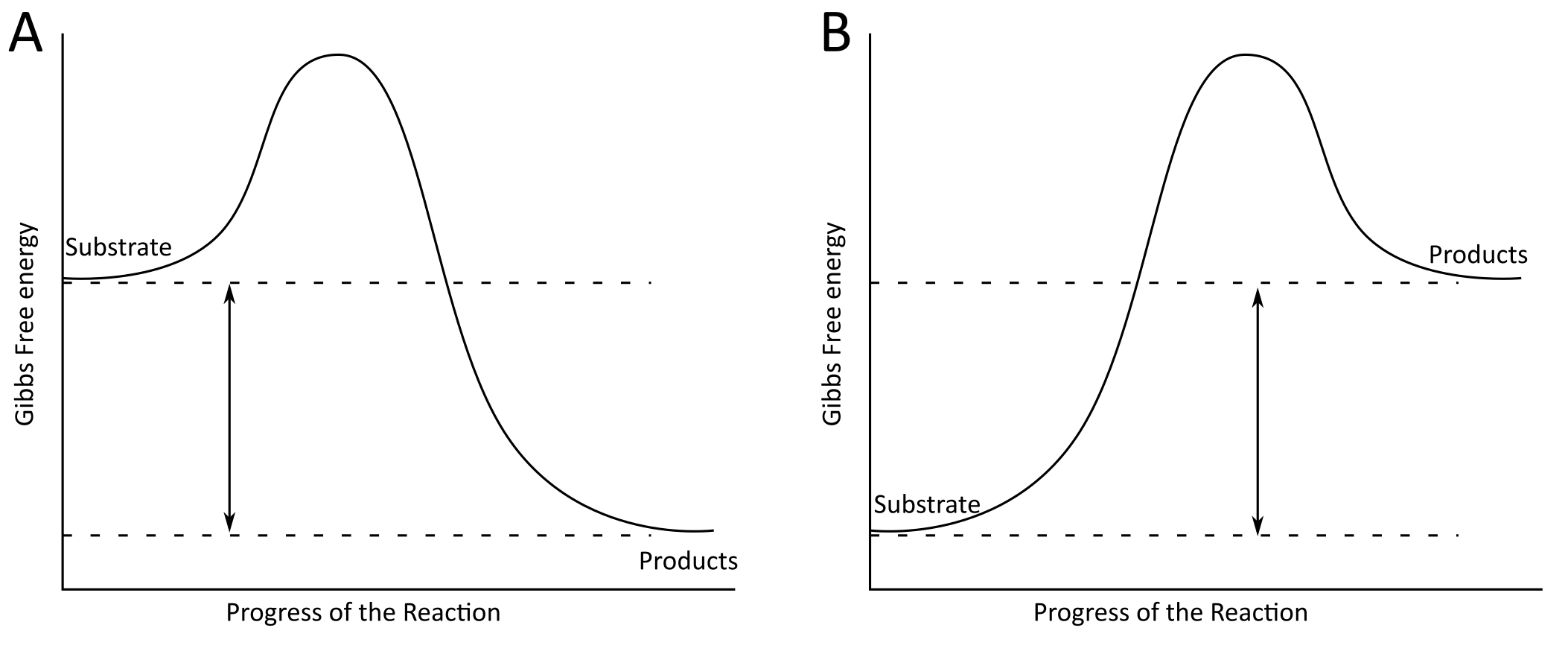
Which graph represents an endergonic reaction?
Name and explain the process illustrated by the figure
Which direction represents an anabolic reaction?
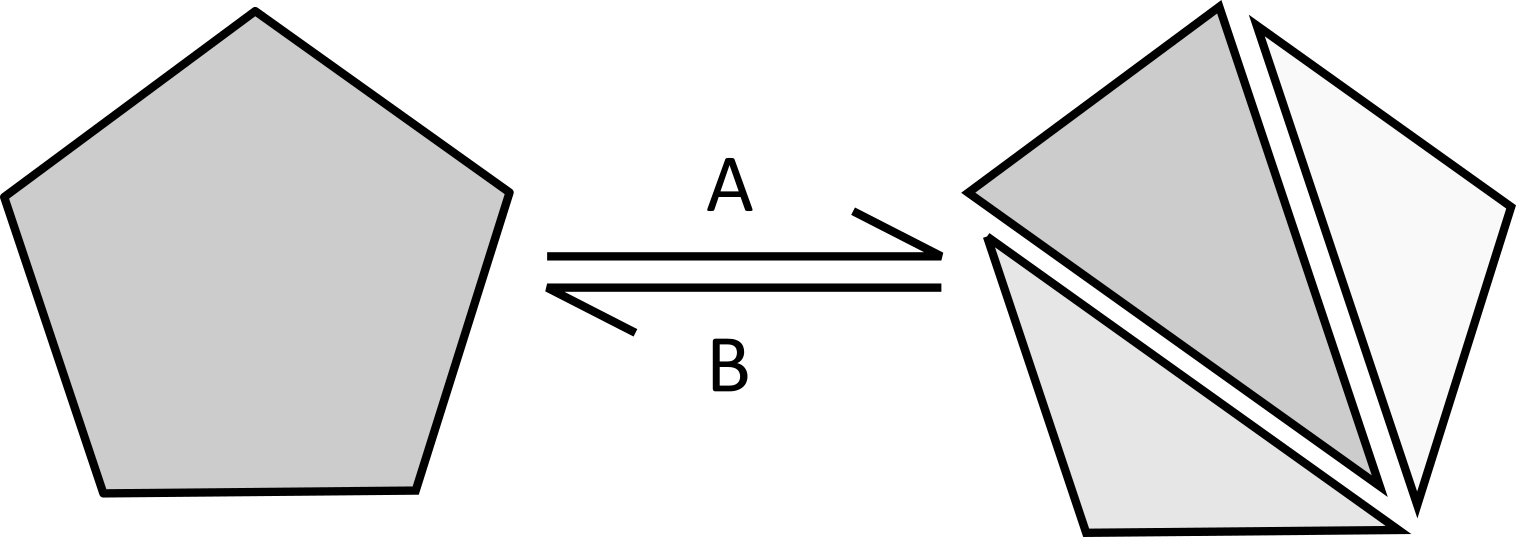
Which state has the highest kinetic energy? And potential energy?
Name the form of allosteric regulation in which binding of one substrate molecule to a multisubunit enzyme triggers shape change in all subunits
Explain the scheme:

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards