Close

Physics - P2
Nuclear Power: Advantages - No Co2, no carbon monoxide, quantity of waste is small, low fuel costs, local economy could benefit from the many jobs created.
Nuclear Waste: Medium Level Waste - About 20 % of the total waste, from cladding of fuel rods & radioactive sludge. can be contained in stainless steel drums and monitored areas about ground.
Alpha - Helium nucleus, particle made up of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
Beta - High energy electron.
Gamma - High frequency electromagnetic radiation.
Uses of radiation: Radiotherapy, gamma rays, x-rays, steralisation of medical equiptement, [reserving food, controlling the thickness of paper, smoke detectors.
Nuclear Fusion: Joining together of 2 (or more) nuclei go form a larger atomic nuclei. It takes a huge amount of heat and energy to force the nuclei to fuse. More energy is produced by fusion than fission.
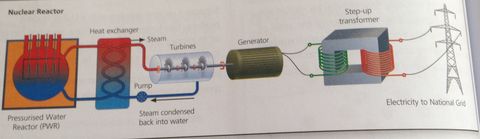
Nuclear Reactors: (picture on back) reactor inside steel pressure vessel, surrounded by thick concrete to absorb radiation. Heat is carried away by boiled water to produce steam that drives turbines, steam cools to produce water which is returned to be re-heated.
Chain reactions: Uncontrolled - An enormous amount of energy & radiation is released, neutrons bombard pure uranium nuclei.
This forms an atomic bomb.
Kinetic energy: The energy an object has because of its movement.
Kinetic energy(J) = 1/2 X Mass(Kg) X Velocity2 (m/s2)
Work: When a force moves and object, work is done on the object, resulting in the transfer of energy where:
Work done (J) = Energy transferred (J)
Power: The rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of energy. The grater the power, the more work done every second.
Power (W) = Work done (J)
Time taken (s)
Crumple zones: Areas of a vehicle that designed to deform & crumple in collision, increasing time interval for change in momentum. This means the force exerted on people in the car will be reduced, so less serious injuries.
Momentum: A measure of the state of movement of an object. It is dependent on 2 things. The mass (Kg) and the velocity (m/s) of an object. Momentum is a vector because velocity is a vector.
Stopping distances: This depends on the thinking and the breaking distance.
Stopping distance = Thinking distance + Breaking distance
The slope of a distance-time graph represents the speed of the object . The steeper the gradient, the greater the speed. The speed can be calculated from the gradient.
*(Picture on back of card)*
Terminal velocity: The constant velocity reached by a falling body when the resultant force is zero.
Unstable nuclei: Found in atoms that disintegrate; they emit radiation.
Protons: A positively charged subatomic particle with nearly the same mass as a neutron.
Neutrons: A neutrally charged subatomic particle with nearly the same mass as a proton.
Earthing: Enables electrons to flow from one object to earth to allow discharge.
Electron: A negatively charged subatomic particle with a very tiny mass.
Daughter nucleus: A nucleus produced by radioactive decay of another another nucleus (the parent).
Control rods: Devices used to control the power of a nuclear reactor.

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards