Flashcards on Pharm Exam 1, created by Meghan Childs on 03/02/2015.
Pinned to
24
0
1
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Meghan Childs
almost 10 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Meghan Childs
almost 10 years ago
|
|

What characteristics of a drug affect absorption?
Where are CYP450 enzymes found?
Which CYP450 enzymes metabolizes 50% of prescribed drugs?
How does induction of CYP450 enzymes affect the bioavailability of a drug?
What is the function of P-glycoprotein?
What is the absorption factor of IV drug?
Where does a PO drug go after being absorbed from the stomach?
What is "first pass" metabolism?
What affects first pass metabolism?
How can you minimize/avoid the first pass effect?
What are the possible outcomes of first pass metabolism?
Phase I reactions involve______ and ________ type reactions
What factors affect distribution?
What affects glomerular filtration rate?
Define tubular secretion
What are two important concepts for understanding tubular secretion?
Define tubular reabsorption
What affects tubular reabsorption?
Define first order kinetics
How many half-lives to essentially eliminate a drug?
How many doses to reach steady state?
Define zero order kinetics
Define EC50
Define Kd
How is Kd related to affinity?
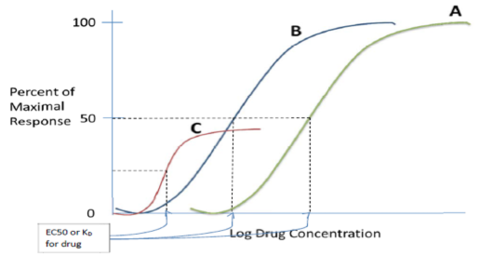
Which curve shows a more potent drug?
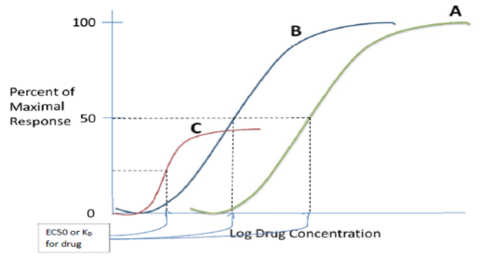
Which is more potent? Drug A or B?
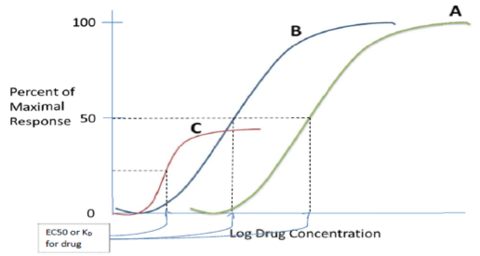
Which drug has the lowest efficacy?
Which curve shows Drug A in the presence of a non-competitive antagonist?
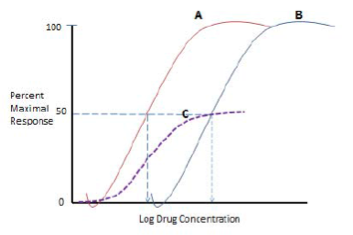
Which curves shows Drug A in the presence of a competitive antagonist?
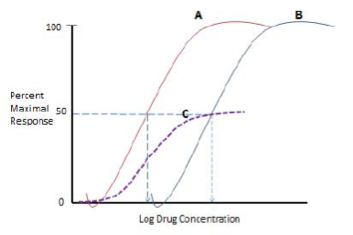
Define ED50
Therapeutic index=
Define additive effect
Define synergistic effect
Define tachyphylaxis
Define down-regulation
Define tolerance
Define dependence
Gastric pH changes:
Premature infants ________
Full term babies___________
In neonates:
Bile formation _____
Pancreatic enzyme production_____
Gastric emptying____
Intestinal motility____
Bowel length____
Effective absorptive surface ____
Infants have a higher volume of distribution for _____-soluble drugs and a lower volume of distribution for _______-soluble drugs
Blood brain barrier is more/less permeable in neonates
Neonates have more/less plasma binding proteins and more/less bilirubin, which competes for plasma binding proteins.
Generally infants have increased/reduced hepatic blood flow and increased/reduced Phase I metabolism.
Infants have decreased/increased glomerular filtration compared to adults.
Rates of tubular secretion and renal reabsorption are generally lower/higher in pediatrics, especially neonates and young infants.
Overall lower/higher rates of elimination in peds lead to increased/decreased response to the drug.
Oral absorption in pregnancy:
o Gastric emptying/intestinal motility?
o Gastric pH?
o CO? affects absorption/metabolism?
Inhalation absorption is ______ in pregnancy due to ______CO and _______ tidal volume.
IM absorption in pregnancy is ______ due to _______ blood flow to muscles.
Plasma volume is _____ during pregnancy, leading to _____ plasma drug concentration.
Pregnancy is a state of ____ albuminemia. Hormones cause ______ protein binding.
Drug metabolism in pregnancy is _____ due to ______ hepatic blood flow and _______ CYP450 enzyme activity.
Excretion in pregnancy is ________.
Characteristics of drugs that are easily transported through the placenta:
lipo/hydrophilic?
high/low molecular weight?
bound/unbound?
long/short half-life?
ionized/unionized?
Pregnancy Category A
Pregnancy Category B
Pregnancy Category C
Pregnancy Category D
Pregnancy Category X
Phase II metabolism involves what type of reaction?
Define side effect
Define adverse event
What are Type A drug reactions?
What are Type B drug reactions?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards