Close

What were some early philosophical arguments for the roots of human psychology (i.e., arguments of Plato, Aristotle, & Descartes)?
Who was Wilhelm Wundt? What is Structuralism?
Who was William James? What is Functionalism?
Who was Sigmund Freud? Psychoanalytic theory and the importance of the unconscious.
What is Behaviorism? Who were the three key contributors to this perspective?
What was the Humanistic perspective? Proponents?
What are some of the basic characteristics of science that we discussed in class (e.g., non-dogmatic, falsifiability, etc.)?
What were the three types of descriptive study we discussed in class(1)?
What were the three types of descriptive study we discussed in class(2)?
What were the three types of descriptive study we discussed in class(3)?
difference between a sample and a population. Why is representative sampling important?
What is the correlation coefficient? What does the sign (+/-) indicate? What does the number value indicate?
Can correlational research allow us to determine cause-effect relationships? Why or why not? What is the third variable problem?
Independent Variables
Confounding Variable
Dependent Variable
Experiment
Control Group
Random Assignment
Population
Random Sample
Scatterplot
Regression Toward the mean
What is the genome?
DNA?
Genes
Nucleotides/Bases?
What’s the significance of the human FOXP2 gene?
What is Huntington’s Disease and what causes it (at both the genetic and neurological level)?
What is behavior genetics?
What are some of the major findings of twin and adoption studies regarding psychological traits such as intelligence and personality?
What happens when rats are raised in impoverished vs. enriched environments?
Provide some examples of how experience can alter our brains.
How can chronic stress accelerate the aging process? How can stress-reduction techniques counteract this process?
Based on the study mentioned in class, how does the interaction of genes and early experiences lead to individual differences in violence and criminal behavior later in life?
What are the major prenatal stages of development? (PT. 1)
What are the major prenatal stages of development? (PT. 2)
What are teratogens? What biological mechanism may minimize teratogen exposure in early pregnancy?
What is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder?
Describe the different temperamental styles and research regarding their consistency across childhood.
What is attachment?
What did Harry Harlow’s experiments with monkeys show us about the mechanisms of attachment?
What are the findings regarding attachment in orphans(1)What are the different attachment styles? How are these typically assessed??
What are the findings regarding attachment in orphans(2)What are the different attachment styles? How are these typically assessed??
Explain how maternal care (low-licking vs. high-licking) in rats can lead to long-term changes in genetic expression and brain functioning in rat pups raised by these mothers?
Who are John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth?
How does early attachment affect our later social experiences?
Be familiar with the diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder(1).
Be familiar with the diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder(2).
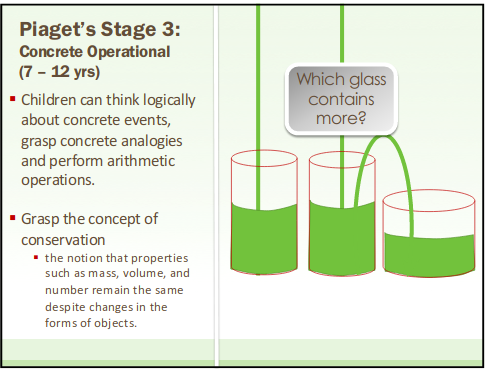
Who is Jean Piaget?
What is a schema? What is assimilation and accommodation?

Know the basic anatomy of a neuron.
What are sensory-, motor-, and interneurons?
What are mirror neurons?
What is the resting potential? What are the roles of sodium and potassium ions during this period?
What is an action potential? Where does the action potential take place (i.e., which part of the neuron)? What are the roles of sodium and potassium ions during this period?
What is hyperpolarization, depolarization, and repolarization?
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
Describe the process of propagation of the action potential down the axon? How does myelin impact this process?
What is the distinction between gray and white matter?
What is a synapse?
Describe the process of how one neuron (the presynaptic neuron) communicates with its neighboring neuron (the postsynaptic neuron).
Explain the difference between excitatory vs. inhibitory transmission.
What is a neurotransmitter? Know the different neurotransmitters we covered in class and their associated functions.
What is reuptake and enzyme deactivation?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards