Close

Formulae for calculating Mr, Moles & Mass
Relative atomic mass (Mr)
Explain the meaning of the numbers in the above graphic.

Mass number (Ar)
Mr = Relative formula mass = relative molecular mass
For an isotope, define the numbers in the adjacent graphic
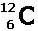
Molecular/formula mass calculation Example:
The diatomic molecules of the elements hydrogen H2 and chlorine Cl2
Molecular/formula mass calculation Example: The compound water H2O
Law of conservation of mass calculation Example:
Magnesium + Oxygen ==> Magnesium oxide
2Mg + O2 ==> 2MgO (atomic masses required: Mg=24 and O=16)
Law of conservation of mass calculation Example:
When limestone (calcium carbonate) is strongly heated, it undergoes thermal decomposition to form lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide gas.
CaCO3 ==> CaO + CO2 (relative atomic masses: Ca = 40, C = 12 and O = 16)
Calculate the mass of calcium oxide and the mass of carbon dioxide formed by decomposing 50 tonnes of calcium carbonate.
Formulae for Hydrochloric Acid, Nitric Acid and Sulphuric Acid
Diatomic molecules of elements
Formuae for Methane and Ammonia
Calculation of % composition Example:
Calculate the % of copper in copper sulphate, CuSO4
Relative atomic masses: Cu = 64, S = 32 and O = 16
Calculate the % of water in hydrated magnesium sulphate MgSO4.7H2O
Relative atomic masses: Mg = 24, S = 32, O = 16 and H = 1
The empirical formula of a compound is?
Empirical formula calculation Example:
The empirical formula of a lead oxide.
It is found that 207g of lead combined with oxygen to form 239g of a lead oxide.
Work out the formula of the lead oxide. (Relative atomic masses: Pb = 207 and O = 16)
Empirical formula calculation Example: The analysis of sodium sulphate, calculating its empirical formula from the % composition by mass. On analysis, the salt sodium sulfate was found to contain 32.4% sodium, 22.5% sulphur and 45.1% oxygen (atomic masses: Na = 23, S = 32 and O = 16

The formulae to calculate Molarity (concentration) of a solution
The formulae to calculate Moles and Volume of a gas.

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards