Flashcards on The Thorax: Respiratory System, Upper Respiratory Tract, created by Anam Ijaaz on 21/02/2015.
Pinned to
44
2
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Anam Ijaaz
almost 10 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Anam Ijaaz
almost 10 years ago
|
|


Describe the structure of the trachea
Why is the space within the upper respiratory tract termed 'dead space'?
Which parts of the upper respiratory tract contain smooth muscle?
What is a URTI, and what usually causes it?
What does the upper respiratory tract refer to?
Why can a URTI spread to the ears?
Name the three parts of the pharynx
What are the consequences of viral URTIs?
Name the epithelium which lines the upper part of the respiratory tract (nasal cavities to bronchi)?
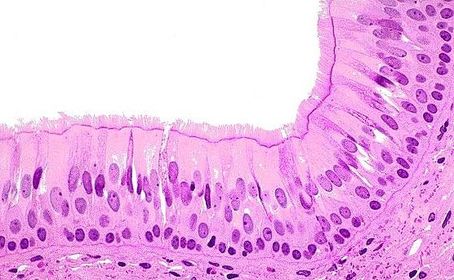
What are goblet cells, and what is the advantage of them being present within the respiratory epithelium of the upper tract?
Apart from goblet cells, what other cells lining the URT aid protection of the airway by trapping foreign particles?
What are vibrissae?
What do serous glands secrete?
Why are the cilia known as the 'mucocilary escalator'?
If viruses and bacteria manage to bypass the upper respiratory tract protective mechanisms and reach the alveoli, how are they dealth with?
Which immune cells secrete a substance which can cause restriction of the airways?
What are the paranasal sinuses, and how many are there?
Name the paranasal sinuses.
The paranasal sinuses are present at birth, true or false?
List the 5 functions of the paranasal sinus.
Describe the position of the frontal sinus
Describe the position of the maxillary sinuses.
Describe the position of the ethmoid sinuses
Describe the position of the sphenoidal sinuses.
What is sinusitis?
What is the consequence of sinusitis?
How are sinus disorders treated?
From where the the nerve fibres of the lung (pulmonary plexus) arise from?
Visceral pain in the thorax is transmitted through sympathetic nerves arising from where on the spinal cord?
Give examples of EFFERENT fibres of the pulmonary plexus
Give examples of AFFERENT fibres of the pulmonary plexus
What is referred to as the 'cough center'?
What initiates the cough reflex?
What 3 changes occur in the thorax in inspiration during the cough reflex?
When the lungs are fully stretched and ready to recoil (height of inspiration) during the cough reflex, what happens next?
The causes of coughing have been divided into two categories; name these.
What is extrinsic irritation?
Give the most common examples of intrinsic irritation
Give the most common examples of extrinsic irritation
What acts as the sphincter of the airway, and name the muscle involved?
What happens to the epiglottis during swallowing?
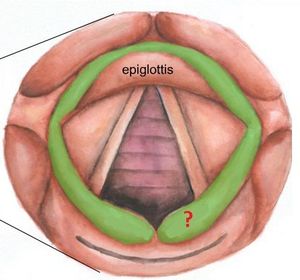
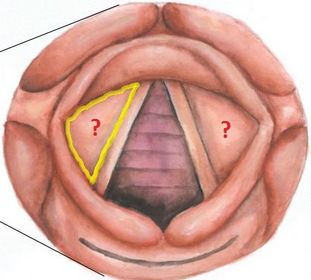
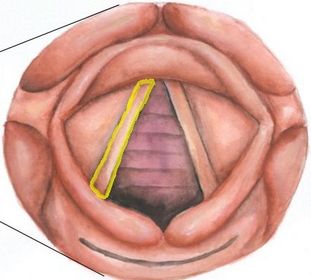
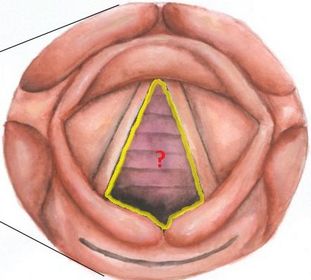
What prevents fluid from entering the airways?
Why are vocal fords readily identifiable with a laryngoscope?
What is the glottis?
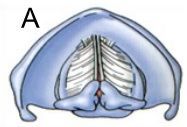
Complete closure of the glottis, shown above, happens when you
1) Speak
2) Cough
3) Breathe
4) Whisper
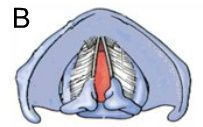
The partial separation of the vocal cords and arytenoid cartilages, shown above, happens when you
1) Speak
2) Cough
3) Breathe
4) Whisper
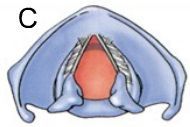
Complete separation/abduction of the vocal cords and arytenoid catilages, shown above, happens when you
1) Speak
2) Cough
3) Breathe
4) Whisper
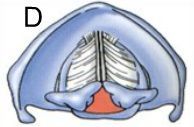
Movement of the vocal cords towards the midline, and abduction/separation of the arytenoid cartilages, shown above, happens when you
1) Speak
2) Cough
3) Breathe
4) Whisper
In what circumstance would an emergency laryngotomy be required?
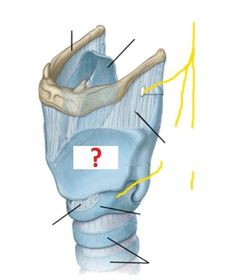
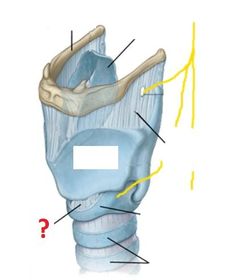
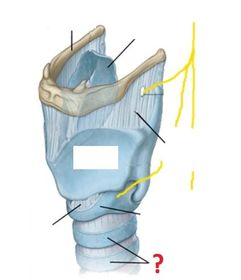
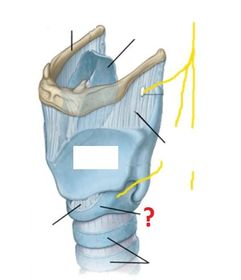
What is a laryngotomy?
How is a laryngotomy carried out?
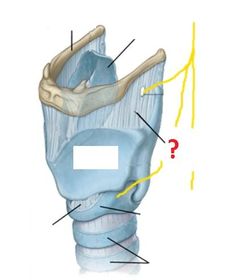
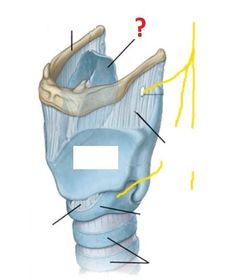
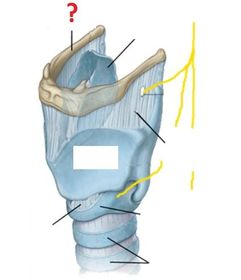
Which arteries supply the larynx? (hint: same as those which supply the thyroid gland)
Venous drainage of the larynx is into which veins?
The mucosal lining of the larynx ABOVE the vocal cords is innervated by which nerves?
The mucosal lining of the larynx BELOW the vocal cords is innervated by which nerves?
The motor supply to the larynx (except the cricothyroid muscle) is entirely from which nerves?
The motor supply to the cricothyroid muscle is by which nerves?
Describe the course of the recurrent laryngeal nerves.
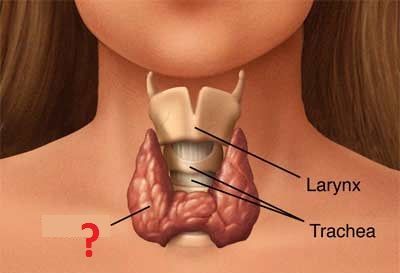
The trachea is composed of C-shapes rings of which type of cartilage?
Which muscle can modify the diameter of the trachea?
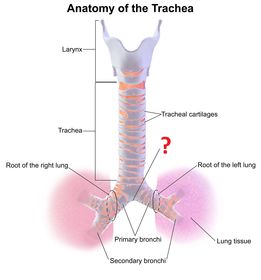
Why is an inhaled objected more likely to enter the right bronchus than the left bronchus?
From where on the vertebrae does the trachea extend from and to?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards