Flashcards on Cell injury & adaptations: Flash cards dr.brahma, created by Pooja Acharya on 20/02/2020.
Pinned to
55
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Pooja Acharya
almost 5 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Pooja Acharya
almost 5 years ago
|
|

Define pathogenesis
A normal cell experiences stress. What outcomes may arise from this stress?
What are the 4 types of cellular adaptation?
Define Hypertrophy
- What type of cells utlize this adaptive mechanism?
- what occurs during this adaptation?
What causes a cell to undergo hypertrophy?
If giving examples, are they pathological or physiological?
Define Hyperplasia
- what type of cells are capable of this?
Name 6 causes for atrophy
What are the 2 mechanisms of atrophy
Define metaplasia
In chronic gastric reflux what adaptation is expected to occur?
Cellular swelling is a morphology of reversible cell injury, what is the mechanism___________?
What are the morphological features of reversible cell injury?
What is the morphology of necrosis?
What are the 6 patterns of tissue necrosis?
Define coagulative necrosis.
- what are key features of this form of necrosis?
Define liquefactive necrosis
- what are key features of this necrotic form?
- what structures undergo this form of necrosis?
What is caseous necrosis?
What is a common disease that this necrosis occurs in?
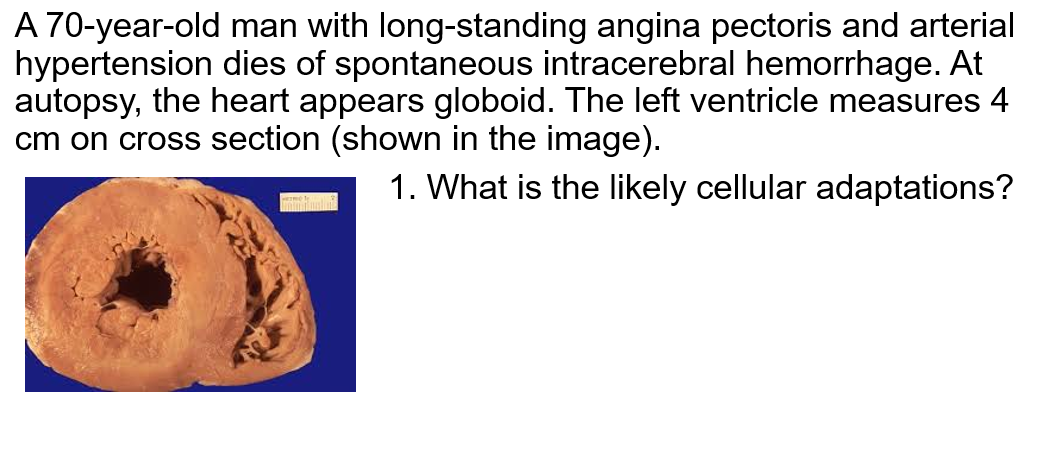

Concentric hypertrophy of the Heart is seen in _____________
Complication of endometrial hyperplasia__________
Streak ovaries in Turner syndrome is an example of_____________
Lipofuscin residual bodies in the cytoplasm would represent? _______
Cancer cachexia is due to an increased secretion of which cytokine___________
Mechanism of Metaplasia_________
What is fat necrosis?
- what mechanism allows for fat necrosis to occur?
What is fibrinoid necrosis?
What are the principal targets and biochemical mechanisms of cell injury? (4)
What consequences occur when cell injury leads to an increased calcium influx? (5
How do phagosomes create free radicals, what enzyme helps with this process and what purpose does this mechanism serve?
What is ischemia reperfusion injury? Explain pathophysiological mechanisms responsible.
What are the for pathologies of intracelluar accumulations
What are the two typesof lipid accumulations that occur intracellularly? What are their etiologies?
Give 2 examples of endogenous pigments
Proapoptotic factors __________
Anti-apoptotic factors
Killing of virus infected cells by cytotoxic T-Cells_______________
Accumulation of misfolded proteins due to ER stress is an example of________________
Ink dot nucleus(pyknosis) and eosinophilic cytoplasm with intact cell membrane on light microscopy, this feature suggest_______
Mutations of bcl-2 can lead to ___________
Mention special stains used to diagnose various intracellular accumulations>

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards