
What are compounds?
what does chemical bonding involve?
What structure is obtained after a chemical bond?
What are formed when ions are transferred?
what ions are formed when atom lose electrons?
What ions are formed when atoms gain electrons?
What charge do group 1 metal ions have?
What charge do group 7 halide ions have?
How are ionic compounds held together?
When are covalent bonds formed?
Give 4 examples of simple covalent molecules?
Give two examples of giant covalent structures.
What is another name for a giant covalent structure?
What is a metal?
What is important about the outer shell electrons in a metal?
Do simple molecules have a high or low melting points and boiling points?
Why are the melting and boiling points low in simple molecules?
Why do simple molecules not conduct electricity?
What is the name for a giant structure?
Do ionic structures have a high or low melting and boiling point?
Why are the melting and boiling points high in ionic structures?
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Why do giant covalent structures have very high melting points?
Why is diamond so hard?
Why is graphite so soft and slippery?
Why does graphite conduct heat and electricity?
Give three uses of fullerenes.
What properties do the delocalised electrons give to metals?
Why can metals be bent and shaped?
How are alloys usually made?
Why are alloys harder than pure metal?
What is special about shape-memory alloys?
What do the properties of polymers depend upon?
What is the difference between thermosoftening and thermosetting polymers?
What size are nanoparticles?
Why are nanoparticles useful to us?
Give 3 examples of how nanoparticles could be used.
What is the relative atomic mass of a proton?
What is the relative atomic mass of an electron?
What does the mass number tell us?
What are isotopes?
What is the relative formula?
What is the relative formula mass of a substance also known as?
Why do we use instrumental methods (such as gas chromatography)to detect elements and compounds?
For what is paper chromatography used?
Give an example of an instrumental method.
What does gas chromatography do?
What does a mass spectorometer do?
What else can the mass spectrometer do?
How do we calculate the % of an element in a compound?
What is the empirical formula of a compound?
Why is it not possible to get the full theoretical amount of product in a reaction?
What is a yield?
How do we calculate the % yield?
what is a reversible reaction?
Give two ways of calculating the rate of a reaction.
When do chemical reactions occur?
What is the minimum amount of energy particles need to react called?
Why does increasing temperature increase the rate?
Why does increasing the pressure increase the rate of a reaction?
Why does increasing concentration increase the rate?
Why does increasing surface area increase the rate of the reaction?
How do we increase the surface area?
What is a catalyst?
Why are catalysts used in industrial processes?
What is the name for a reaction that transfers energy to the surroundings?
What type of reaction does the graph show?
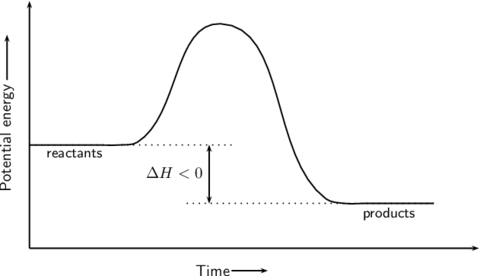
Give 2 examples of exothermic reactions.
Give two uses of exothermic reactions.
What is the name of a reaction that takes in energy from the surroundings?
What type of reaction does the graph show?
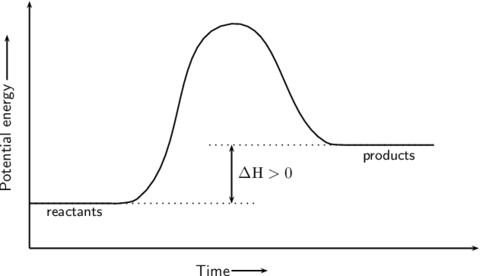
Give an example of an endothermic reaction.
Give a use for endothermic reactions.
What can you say about reversible reaction that is exothermic in one direction?
What does the symbol (s) mean?
What does the symbol (aq) mean?
Give three ways of making salts?
How are insoluble salts made?
What is the name given to metal oxides and hydroxides?
What is the name for soluble hydroxides?
What does the salt depend on?
What salts do we get from hydrochloric acid?
What salts do we get from sulphuric acids?
What salts do we get from nitric acids?
What type of solution is formed when ammonia dissolves in water?
Which salts are made from ammonia?
For what do we use ammonium salts?
Which ions make a solution acidic?
What ions make a solution alkaline?
How do we measure acidity and alkalinity?
What happens during neutralisation reactions?
When are ions free to move?
What is electrolysis?
What is the name for the chemical being broken down?
Where do positive ions move?
What is electroplating?
What happens at the negative electrode?
What happens at the positive electrode (anode)?
What happens if there is a mixture of ions?
How are reactions at the electrodes represented?
How is aluminium manufactured?
What forms at the negative electrode?
At which electrode is oxygen produced?
Why is carbon dioxide produced?
What is produced in the electrolysis of brine?
What do we make from sodium hydroxide?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards