Flashcards on Chemistry 1A - Products from rocks, created by mariamdarwish on 19/05/2015.
Pinned to
48
1
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by mariamdarwish
over 9 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by mariamdarwish
over 9 years ago
|
|

Chemistry 1A
Products from rocks
Atoms and elements
Number of protons equals number of electrons
Atoms have no charge overall, they're all neutral
The charge on the electrons is the same size as the charge on the protons
The number of protons always equals the number of electrons in an atom
If some electrons are added or removed, the atom becomes charged and is then an ion
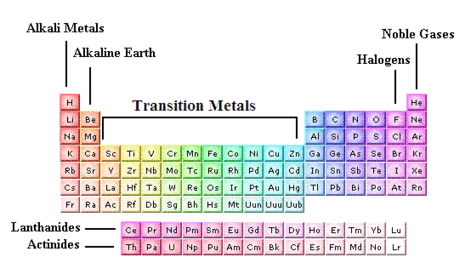
The Periodic Table
The periodic table puts elements with similar properties together and they form columns. (groups)
All of the elements in a group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
For example - Group 1 are all metals that react the same way and Group 0 are noble gases
Electron Shells
Working out the electronic structure
Compounds
The metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions and the non metal atoms gain electrons to form negative ions. The opposite charges (positive & negative) of the ions mean they're strongly attached yo each other. This is IONIC BONDING
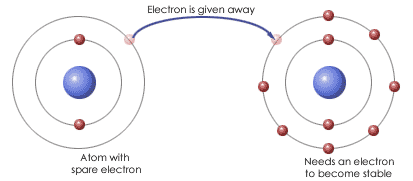
The properties of a compound are different from the properties of the original elements. For example -
Iron (shiny magnetic metal) and sulfur (yellow powder) react, the compound formed (iron sulfide) is a dull, grey solid lump and doesn't behave like iron or sulfur.
A formula shows what atoms are in a compound
CO2 is a compound formed from a chemical reaction between carbon and oxygen. It contains 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms
BALANCING EQUATIONS
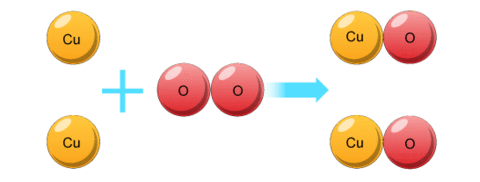
Balanced symbol equations show the atoms at the start and at the end, and how they're arranged.
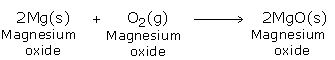
BALANCING THE EQUATION, MATCH THEM UP ONE BY ONE
There must always be the same number of atoms on both sides
You balance the equation by putting the numbers in front of the formulas where needed
METHOD -
Balance one type of atom at a time -
1) Find an element that doesn't balance and write in a number to try and sort it out
2) It may create another imbalance, if so just write in another number
3) Carry on chasing unbalanced elements and it 'll sort itself out
USING LIMESTONE
When magnesium, copper, zinc and sodium carbonates are heated, they decompose in the same way
E.g -
Magnesium carbonate → magnesium oxide + carbon dioxide
Calcium oxide reacts with water to produce calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide is an alkali which can be used to neutralise acidic soil in fields. Powdered limestone can be used for this too but the advantage of calcium hydroxide is that it works faster
Powdered limeston is heated in a kiln with powdered clay to make cement. Cement can be mixed with sand and water to make mortar. Mortar is used to stick bricks together.
You can mix cement with water and aggregate (water and gravel) to make concrete
ADVANTAGES OF LIMESTONE -
Limestone provides things that people want (houses, roads)
Limestone products are used to neutralise acidic soil.
The quarry and associated businesses provide jobs and bring money in to the local economy
GETTING METALS FROM ROCKS
A metal can be extracted from it's ore chemically, by reduction or by electrolysis.
Some ores may have to be concentrated before the metal is extracted. This involves getting rid of the unwanted rock material
Electrolysis can also be used to purify the metal
The position of the metal in the reactivity series determines whether it can be extracted by reduction with carbon.
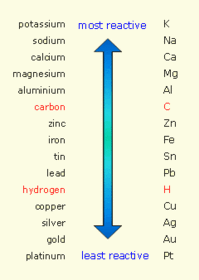
Metals that are more reactive than carbon have to be extracted using electrolysis of molten compounds (e.g - aluminium)
However the process is much more expensive than reduction because it uses lots of energy
Electrolysis is the breaking down of a substance using electricity
It requires a liquid to conduct the electricity, called the electrolyte
Electrolytes are usually metal salt solutions made from the ore or molten metal oxides
The electrolytes has free ions that conduct electricity
Electrons are taken away by the positive anode and given away by the negative cathode
You can extract copper from a solution using a displacement reaction
More reactive metals react vigorously than less reactive metals
If you put a reactive metal into a solution of dissolved metal compound, the reactive metal will replace the less reactive metal in the compound
New methods to extract copper are bioleaching and phytomining -
BIOLEACHING -
This uses bacteria to seperate copper from copper sulfide. The bacteria get energy from the bond between copper and sulfur separating out the copper from the ore in the process. The leachate (solution produced by the process) contains copper, which can be extracted
IMPACTS OF EXTRACTING METALS
Metal extraction can be bad for the environment
People have to balance the social, economic and environmental effects of mining the ores. Most of the issues are the same as quarrying limestone
Recycling metals is important -
Mining and extracting metals takes lots of energy (comes from fossil fuels)
Fossil fuels are running out so we need to conserve them. Burning them also leads to acid rain, global dimming and climate change
PROPERTIES OF METALS
A metal's properties decide how it's best used
COPPER is a good conductor of electricity, so it's ideal for electrical wiring. It's hard and strong but can be bent. It doesn't react with water
Different metals are useful for different things. E.g - for an aeroplane, you'd want a light metal that is strong but can be bent into shape like aluminium
ALLOYS
Most of the pure iron is converted into steel - an alloy. Steels are formed by adding small amounts of carbon and sometimes other metals to the iron
FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION OF CRUDE OIL
Crude oil is split into separate groups of hydrocarbons
The fractionating column works continuously with heated crude oil piped in at the bottom. The vaporised oil rises up the column and the various fractions are constantly tapped off at the different levels where they condense
PROPERTIES AND USES OF CRUDE OIL
THE BASIC TRENDS -
The shorter the molecules, the more runny the hydrocarbon is
The shorter the molecules, the more volatile they are (turn into gas at a lower temp)
The shorter the molecules, the more flammable the hydrocarbon is
USING CRUDE OIL AS A FUEL
Crude oils also provides raw materials for making various chemicals, including plastics.
Alternatives to using crude oil fractions as fuel are possible e.g - electricity can be generated by nuclear power or wind power. There are ethanol powered cars and solar energy can be used to heat water
ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen are oxidised so that carbon dioxide and water vapour are released into the atmosphere. Energy (heat) is also produced
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Sulfur dioxide is one of the gases that causes acid rain.
When the sulfur dioxide mixes with clouds, it forms dilute sulfuric acid. This then falls as acid rain
In the same way, oxides of nitrogen cause acid rain by forming dilute nitric acid
The benefits of electricity and travel have to be balanced against the environmental impacts
Governments have recognised the importance of this and international agreements have been put in place to reduce emissions of air pollutants (sulfur dioxide)
Increasing carbon dioxide causes climate change
The level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing because of the large amounts of fossil fuels burnt
This causes global warming
Global warming is a type of climate change and causes other types of climate change (flooding due to the polar ice caps melting)
Renewable alternative fuels
ETHANOL - Produced from plant material so it's known as biofuel. Made by fermentation of plants and can be used to power cars. Often mixed with petrol to make a better fuel
BIO-DIESEL - Another type of biofuel. Can be produced from vegetable oils (rapeseed, soybean) Bio-diesel can be mixed with ordinary diesel fuel and used to run a diesel engine
HYDROGEN GAS - Used to power vehicles. You get the hydrogen from the electrolysis of water. There's plenty of water but it takes electrical energy to split it up. This energy comes from a renewable source (solar)

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards