Cue cards for the whole of unit 1 (topic A and B) psychology
Pinned to
109
2
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by lilyquenya
over 9 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by lilyquenya
over 9 years ago
|
|

Define Perception
Retina
Rods
Cones
Optic nerve
Name the biological process of seeing and the psychological process of seeing.
Name the points of the:
- Pupil
- Retina
- Optic Nerve
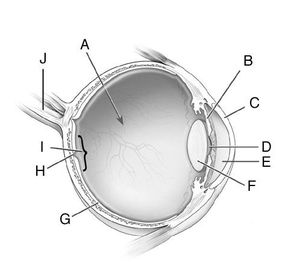
What travels along the optic nerve?
Blindspot
Optic Chiasma
Visual Cortex
What is the job of the visual cortex?
Depth Cues
Monocular depth cues
Binocular depth cues
Size constancy
For size constancy, state the d-u-bs and ne-d-s
Relative size
Texture gradient
Height in the plane
Superimposition
Linear perspective
Stereopsis
Gestalt laws
In the figure-ground relationship, compared to the ground, the figure is...
We tend to group things that are similar, such as in:
Figure-ground
Similarity
Proximity
Continuity
Closure
What are the three types of illusion?
Visual illusion
Fiction
Illusory Contour
Motion after-effect
Colour after-effect
Leeper (1935)
Ambiguous figure
Distortion illusion
Name four distortion illusions
Name the 5 Gestalt laws
Name the 5 monocular depth cues
State the name and type of the illusion
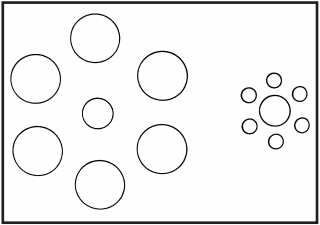
State the name and type of the illusion

State the name and type of the illusion.

State the name and type of the illusion.
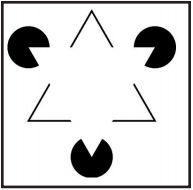
State the name and type of the illusion.
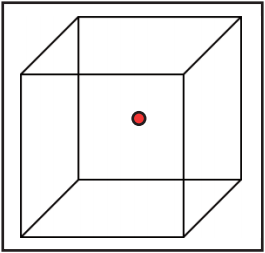
State the name and type of the illusion.

State the name and type of the illusion.
Schema
Perceptual set
Independent variable
Dependent variable
Palmer (1975)
Aim
Bartlett (1932)
Aim
Carmichael et al (1932)
Aim
What was the year of Bartlett?
What was the year of Carmichael et al?
What was the year of Palmer?
Serial reproduction
Repeated reproduction
Palmer (1975)
Conclusion
Bartlett (1932)
Conclusion
Carmichael et al (1932)
Conclusion
Reconstructive memory
Experiment
Experimental (participant) design
Independent groups design
Repeated measures design
Hypothesis
Controls
Mode
Descriptive statistics
Bar chart
Median
Mean
Range
Ethical issues
Informed consent
Right to withdraw
Ethical guidelines
Eyewitness
Allport & Postman (1945)
Boon & Davis (1987)
Tuckey and Brewer (2003)
In terms of Freud's (1900) dream theory, what is repression?
After learning hypnotism, why did Freud come to reject it?
Manifest content
Latent content
Condensation
Displacement
Secondary elaboration
What is the name of Freud's therapy?
What kind of patients did Freud treat?
What is the aim of psychoanalysis?
What are the three unique research methods that are involved in psychoanalysis?
Psychoanalysis
Free association
Slips of the tongue
Dream analysis
Qualitative data
Valid
Generalisable
Subjective
Objective
What makes up the central nervous system (CNS)?
What are the two types of neuron?
What does the central nervous system (CNS) do?
What are the four important features of a neuron?
Label the four important features (cell body, terminal buttons, axon & dendrites) on this neuron.
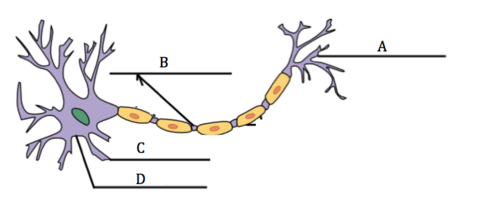
How are brain messages sent using neurons?
Neuron
Axon
Impulse
Neurotransmitter
Synaptic gap
Synaptic transmission
Who is responsible for the activation-synthesis theory of dreaming and what does the theory claim about dreaming?
What is used to measure brain activity during REM sleep?
What happens during REM sleep?
Activation-synthesis model
Random activation
Sensory blockade
Movement inhibition
REM sleep
Synthesis
Aim
Case study
Qualitative data
Quantitative data
Generalisability
Reliability
Subjectivity
Objectivity
Privacy
Confidentiality
Phallic
Oedipus complex
False memory
What are the four categories of sleep disorders?
Insomnia
Hypersomnia
Circadian rhythm disorders
Parasomnias
What are treatments of psychological sleep disorders?
What are primary sleep disorders?
What are secondary sleep disorders?
Narcolepsy

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards