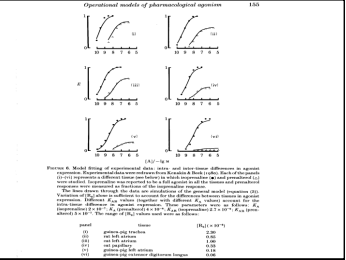
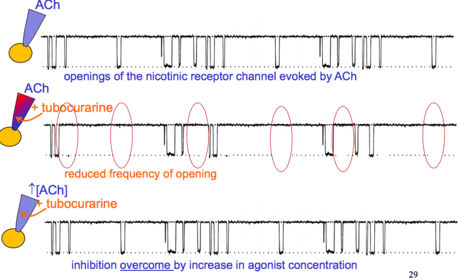
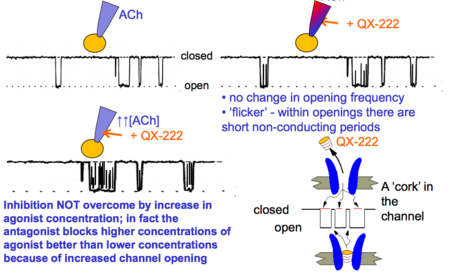
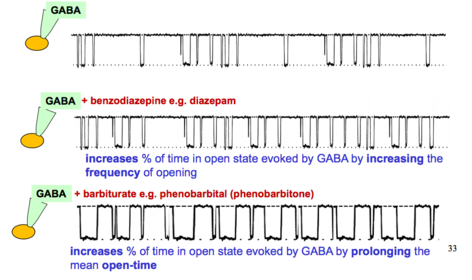
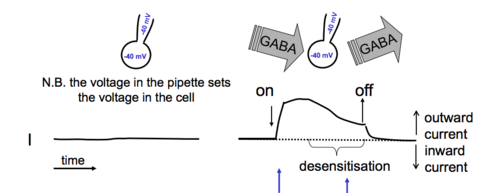
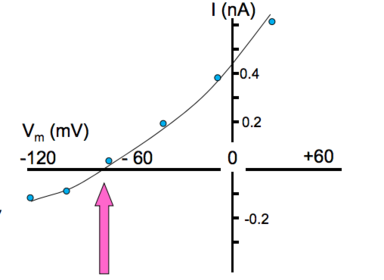
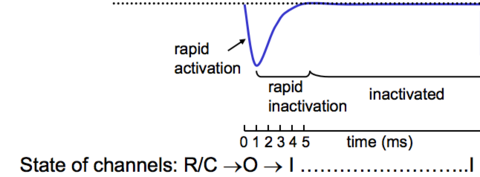
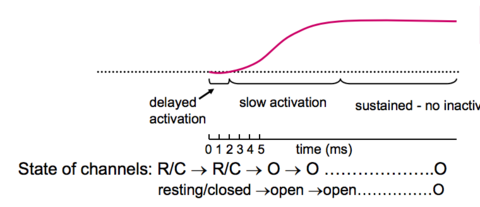
Degree Neuropharmacology Flashcards on Receptor Theory - L-type Calcium Channels, created by Anna mph on 14/10/2015.
Pinned to
48
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Anna mph
about 10 years ago
|
|
Close