Theory test for physiology lab covering special senses, rat surgery, and ultrasound
Pinned to
6
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Maddie Allen
9 months ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Maddie Allen
9 months ago
|
|

Five senses
Adaptation definition
Proprioreceptiors
Mechanoreceptor that senses gentle pressure
Receptive field
Order from most localization to least: forearm, fingertip, wrist, palm
What determines tactile sensitivity for a given area
Penny experiment: why is pressure sensation soon lost?
What temperatures are thermoreceptors sensitive to?
Homeostatic thermoreceptors
Do warm temp. receptors transmit absolute or relative information about temperatures
Define reflexes
Steps of knee jerk reaction
Are muscle stretches mono- or polysynaptic
Grey matter
Grey matter: Posterior horn
Grey matter: lateral horn
Grey matter: Anterior (ventral) horn
Roots: posterior (dorsal) root
Roots: dorsal root ganglion
Roots: Anterior (ventral)
When the volunteer performed Jendrassik maneuver, how did the knee-jerk reflex change?
What does the effect of the Jendrassik maneuver indicate about neural pathways involved in simple reflexes?
Why do you multiple the distance between patellar tendon and sacrum by two
Would you expect the conduction velocity to be the same or different with Jendrassik maneuver?
Consider the two volunteers: Liam is 1.8m (5.9ft) tall and Jacqui is 1.4m (4.6ft) tall. Which volunteer will have a faster response time
Why is it important that neurons in this reflex are myelinated?
Guillain-Barre syndrome is a demyelinating disease caused by infection. People with this will have loss of knee-jerk reaction. Why is this true?
Myopia
Hyperopia
Presbyopia
Astigmatism
Conduction deafness
Sensorineural deafness
Weber test
Rinne test
Weber/Rinne example:
Participant 1 lateralizes left for the Weber test. After the Rinne test, they report they can hear the tuning fork on the left side. This person has ______deafness in the ________ear
What do the semicircular canals detect
What are the three doses of drugs that will be given
What drugs can be given to reverse the effects of xylazine and bupivacaine
Preparation of the rat
disinfection order
Three layers of the abdominal wall
Which side receives oxygenated blood
Where does blood go after left ventricle
Which side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood
Where does the blood go after it is received in the right side of the heart
Papillary muscles
Chordae muscles
Blood flow through the heart
What is ultrasound
Hyperechoic
Anechoic
Isoechoic
Hypoechoic
List the following structures from closest to farthest from the probe: liver, gallbladder, abdominal muscles
True or false: Organs have homogenous ethnogenicities
What axis are we viewing the heart from
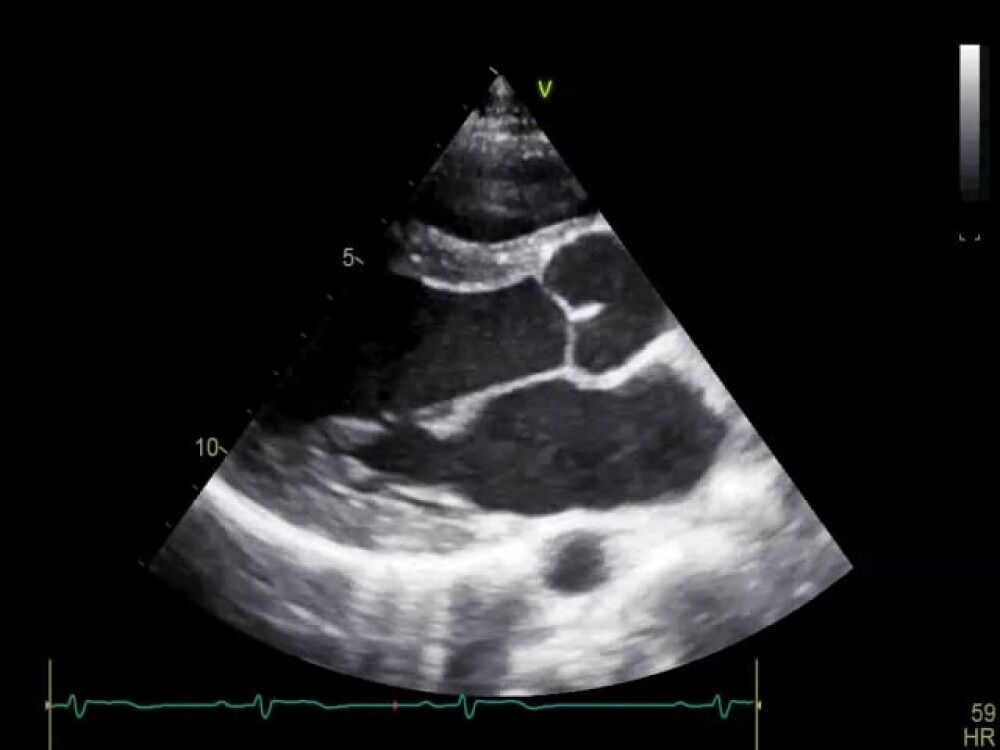
Which probes do you use for: heart, abdomen, and neck
What would happen to the blood pressure in the brain if the internal jugular vein did not change during the Valsalva maneuver
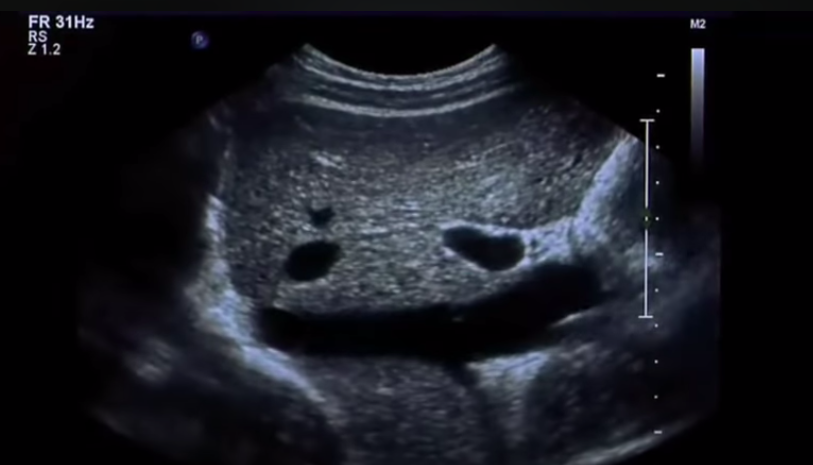
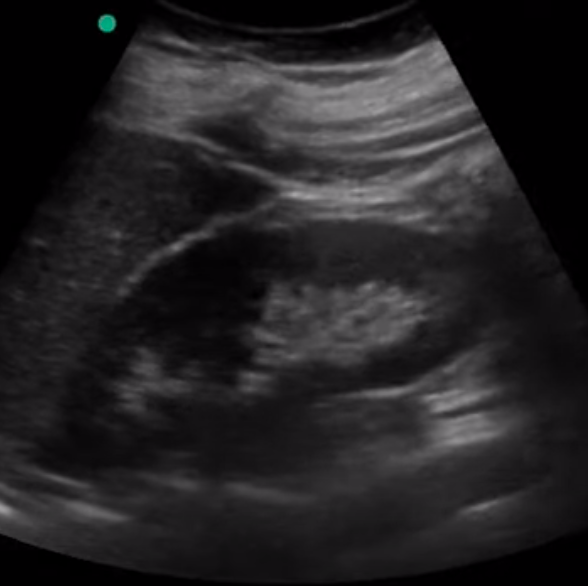
What are the ethnogenicities of the kidney
When the left ventricle is contracting, which valve is open
When the left ventricle is relaxed, which valve is open?
Do the ends of the leaflets of the valves ever touch

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards