Flashcards on vertebrate biology - history of fish to land!, created by ameliabmargrave on 12/11/2015.
Pinned to
35
1
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by ameliabmargrave
about 9 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by ameliabmargrave
about 9 years ago
|
|

what are darwins 4 postulates?
what evidence is there for evolution?
radiation of mammals occurred when?
biogeographical evidence for evolution is?
what is comparative anatomy and how does it link evolution?
what is convergence?
comparative embryology
molecular evidence
what is heritability and its range?
what is macro evolution?
what is micro evolution
what is gene flow
what is genetic drift?
in what age were the origins of multicellular animals?
what time did prokaryotes appear?
what time did eukaryotes appear?
how old are the burgess shale?
what is the first chordate ancestor?
Urochordata
cephalochordata
myxiniformes
petromyzontiformes
gnathostomes
ray finned fish
lobe finned fishes
cartilaginous fish
name 3 functions jaws benefit
placoderms (such as?) have what adaptations?
how do shark teeth develop, compared to ours?
jaws developed during which orders?
what order are chimeras and ratfish?
what class are they?
what order are sharks, skates and rays under?
in what class/super order?
what do shark jaws do to benefit catch success?
latin for Ray finned fish?
Teleosts started what?
what are the two main groups in teleosts?
what teleost developed ram feeding and how does it work?
what other teleost developed suction feeding?
moray eel has what adaptation?
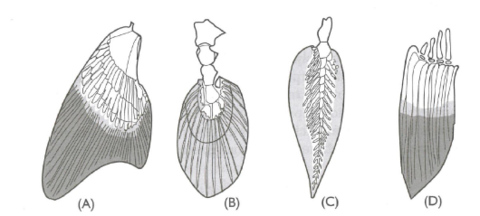
What problems are created by an aquatic existence?
what direction do these factors move the fish?
-bouyancy
-weight
-thrust
-drag
oscillation =?
what is a myotome? What are these separated by?
functions?
what shape muscle creates what kind of movement?
what function do myotomes have?
fast twitch muscle provides....?
slow twitch muscle provides....?
Water causes what effect on thermoregulation?
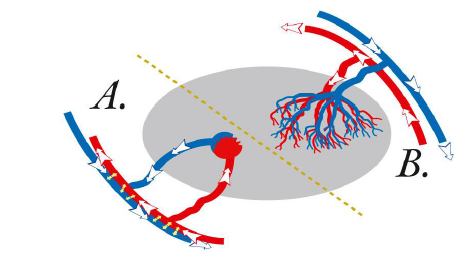
what type of movement do these fish use?
Eels?
Tuna?
Box fish?
Rays?
Bowfin?
Cod?
Triggerfish?
Wrasse?
where is drag most potent?
what reduces drag?
Lift prevents the fish from sinking, what are the two main types + how do they work?
What is the gas bladder structure and and how does it work?
what are the 2 swim bladder types?
how does a physostomatous fish fill and empty its air bladder?
how does physoclistus?
this image shows....?
which is what iknd of lift?
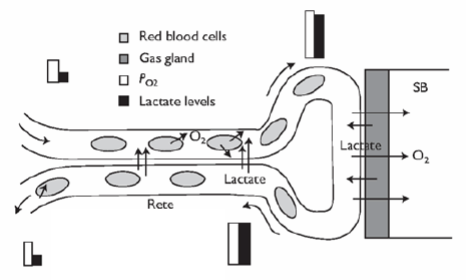
what other function does the swim bladder have?
what is squalene?
what are the 4 key forces fish must content with?
name mechanisms to generate lift?
what function does the gill arch have?
what is a special feature of lungfish? and what type of swim bladder does it use?
There is a lower concentration of oxygen in water compared to air. What happens to oxygen as the temperature of water:
increases?
decreases?
what is the latin for an Antarctic icefish?
In waters of -2 to 4 degree's C, how does it survive?
how does buccal pumping work?
what is another method of ventilation (sometimes obligate)?
what system is altered in order to cope with ram ventilation and how?
How does the circulatory and respiratory system of fish larvae function?
gill arches -
average number?
which arch supports the mandibles formed by the "?" arch?
how did this change the development in humans?
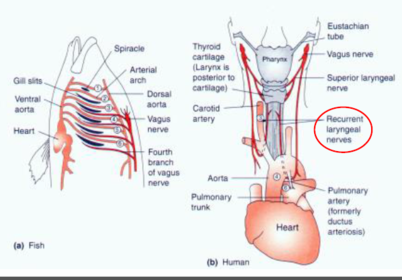
why does the laryngeal nerve have to travel to the heart and back to the face?
how do the gill rakers work? Explain in 3 steps
what are the two different methods?
how do marine fish cope with osmoregulation?
how do they cope with the high salt levels?
where else does osmoregulation occur?
how do freshwater fish osmoregulate?
so if for example a flounder (paralichthys lethostigma) loses:
8% of body weight from osmosis of fluids
-0.4% of body weight through urine
2.7% through feces
how does it regain lost osmotic components?
in what order does evolution workfor physiological processes?
why is the operculum important? list 3 reasons.
what roles do gills have?
what does gas exchange depend on?
what lineage do vertebrates come from?
what new technologies allowed further investigation and new discoveries in fossils?
what species did fish tetrapod transition start with?
the second transition species was...?
the third?
fourth?
and finally the 5th?
why would fish benefit from evolving limbs for use underwater?
what other factor occurred at the same time as limb development?
what advantages did the early lolobe-finned fish Eusthenopteron have that helped the evolution to limbs?
around what time was Acanthostega present, with what adaptations?
what did ichthyostega have to benefit the transition onto land.
when were the first tetrapod tracks on land found to be dating to?
what could have happened to the ichthyosteglians?
what is the name of the gap showing a gap of tetrapods being present for ...how many years?
what happened in the end?
how many species went extinct in the late devonian extinction?
what did mass extinctions allow?
what did the late devonian extinct allow?
when did pentadactyly evolve?
what happened after the devonian extinction that benefited being on land?
define an amniote
(developed in the carboniferous period)
which species was it that evolved pentadactyl foot?
there was also a return to what kind of lifestyle? (in start of carboniferous)
what time did all the amniote (and most tetrapod)lineages become extinct?
what was this extinction called?
how many marine (?) and how many terrestrial vertebrates went extinct?
what was the supposed cause
what were the Aistopoda, and what did they help evolve?
what did temnospondyli look like?
which tetrapod is not an amniote?
when did first amniotes appear?
what did this allow?
amniote evolution led to...?
what were the permian-only aquatic amniotes?
the earliest amniotes weren't viviparous, what did they have?
what is an innovation of being an amniote?
this new head and jaw adaptation allowed what to evolve?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards