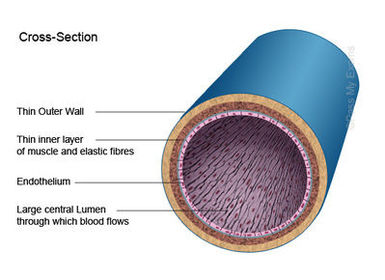
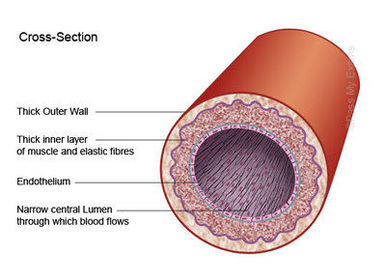
Basic revision for the heart and blood vessels structure and function
Pinned to
3
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by eimearkelly3
almost 9 years ago
|
|

|
Copied by Antonia Smith
almost 9 years ago
|
|
Close