
Type of ATOMIC BOND present in:

Covalent Bond
Ionic Bond
Aluminum, copper, silver, gold are examples of materials with this type CRYSTALLINE STRUCTURE.
Metals with BCC structure
Titanium is a metal with this type CRYSTALLINE STRUCTURE.
The material fails because of the presence of a flaw
Fatigue
In this type of failure the material fails because of the temperature and stress.
Nuclei
Is a tiny particle of solid that forms from the liquid as atoms cluster together. Is unstable can grow into a stable nucleus or redissolve.
The minimum size that must be formed by atoms clustering together in the liquid before the solid particle is stable and begins to grow.
Undercooling
To transformate the solid to liquid we need to increase the temperature above its boiling temperature.
Type of nucleation that occurs in high undercooling
Type of nucleation from a preexisting surfaces, like impurities in the molten metal or in the walls of the mold.
Inocutation
Specific Heat
Plannar Growth
The treelike structure of the solid that grows when an undercooled liquid solidifies
Type of growth mechanism present in not well inoculated liquids.
Solidification time
SDAS
To reduce SDAS:
Small SDAS:
Points:
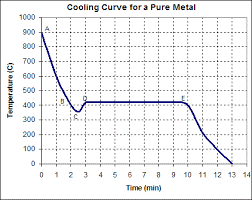
Cooling curve for a well inoculated liquid, or pure metal.
Casting product
Simple shape produced by a mold, than requires extensive plastic deformation before finished product is created.
Cast region of randomly oriented grains in the center of a casting
During solidification a material contracts, shrinks, as much as:
Pipe
Extra reservoir of metal, adjacent and conected to the casting to solve solidification defects
Gas Porosity
Gas produced during aluminum solidification
In this type of welding process the filler metal is brass.
Solid-Solution Strengthening
Dispersion Strengthening
Characteristics of a phase
Triple point
1 + C= F + P
Parts
Fredom degrees=2
Freedom degrees over a line in any phase diagram
Part in a phase diagram where the freedom degrees=0
Unlimited solubility
When only a maximum amount of a solute material can be dissolved in a solvent material.
Conditions for unlimited solid solubility.
Electrical conductivity and ductility is better in:
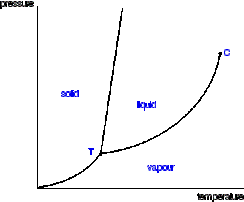
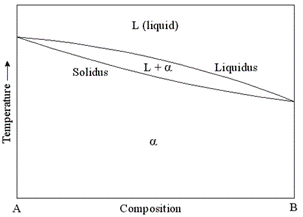
Ternary phase diagram
Solidus Temperature
The temperature above which the alloy is 100% liquid.
Segregation
Homogenization heat treatment
Eutectic reaction
Eutectoid Reaction
Intermetallic compound
Peritectic reaction

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards