Flashcards on EEG technology, created by Danielle Morley on 23/12/2013.
Pinned to
384
2
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Danielle Morley
almost 11 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Danielle Morley
almost 11 years ago
|
|

What is an electrode?
Ideally, what should an electrode do?
What are the properties of an electrode?
What are properties of polarized(non-reversible) electrodes vs non-polarized(reversible) electrodes?
Which is more desirable... a polarized(non-reversible) electrode, or a non-polarized(reversible electrode? Why?
What does it mean to say that an electrode has the property of a battery?
What does it mean to say that an electrode has the property of a capacitor?
What does it mean to say that an electrode has the property of a half cell potential?
What does it mean to say that an electrode has the property of a low frequency filter?
Do we want our electrodes to have a long or short time constant? What is an example of an electrode material that has this type of time constant?
How can electrode properties be minimized?
What is impedence?
How do we test impedance?
What is the desired level of electrode impedance for a routine recording?
Under what circumstances are impedance values of 0.1-10kΩ (100-10,000Ω) and equal acceptable
Are very low electrode impedances desirable? why or why not?
Are very high electrode impedances desirable? why or why not?
What is polarization?
How does an ohmmeter work? Why is/isn't this desirable for EEG?
What is a similarity between ohmmeters and impedance meters?
What are some differences between ohmmeters and impedance meters?
What is another name for the electrode electrolyte interface (EEI)?
What is an electrode potential?
What is a half cell potential?
What is more desirable... a small or large half cell potential, and why?
Where does each of the following types of electrodes record from? -surface, subdermal, sphenoidals (invasive and non-invasive), nasopharyngeal, tympanic, indwelling (grids/strips/depth electrodes)
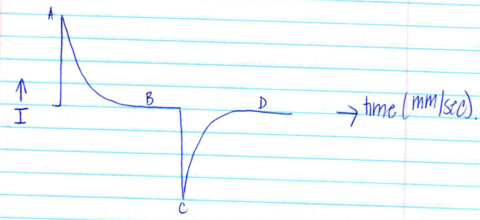
What is calibration?
What is damping? Name the 3 types of damping and describe what they mean and how to recognize them.
What are baselines and what should they be? What are the 2 kinds of baselines? differentiate between the 2 kinds.
What components make up the calibration circuit?
What does "pen alignment" refer to? What does incorrect pen alignment do to waveforms? What causes problems with pen alignment?
What is the standard paperspeed? What happens to brain activity when PPS is increased? decreased?
How would you calibrate/ verify the sensitivity on an analogue machine?
Define time constant.
What is the equation to find impedance?
High fidelity/ accuracy of signal reproduction depends on what?
What are each of the following electrode types made of? -surface, subdermal, sphenoidals (invasive and non-invasive), nasopharyngeal, tympanic, indwelling (grids/strips/depth electrodes)
What is a time marker? How do you check this?
What is amplitude linearity and how would you check it?
What will happen to the calibration pulse with changes to the HFF?
What is step gain control and why do we do it?
What is noise?
What causes noise?
How do you check noise levels? What should they be?
When does having acceptable noise levels become very important? Why is this?
What is a biological calibration (biocal) doing?
What will the output of a biological calibration look like when machine is functioning correctly?
On an analogue machine, full calibration was to be done ____ ____. and partial calibration was to be done _____ _____ ______.
What effects does current have on living tissue? What factors does this depend on?
Define macroshock and microshock.
How much current is needed to flow through the body to cause the following: pain, muscle tetany, respiratory arrest, ventricular fibrillation (often fatal)
How much current is needed to cause ventricular fibrillation when flowing through the heart? Which patients would be most at risk?
What are some types of electrical hazards?
Give examples of electrically susceptible patients.
What is leakage current and how does this create an electrical hazard?
What causes leakage current? What is the main source of leakage current?
What should be done to ensure that injury does not occur as a result of leakage current?
What are the acceptable levels of leakage current set by the CSA (Canadian Standards Association)?
What is a ground loop and how does this occur?
How can ground loops be prevented?
What danger is associated with a sagging plug?

What is the chassis ground?
What causes a short-circuit to occur?
What is the potential danger of a short circuit?
What is the potential danger of a broken chassis ground?
What safety measures are in place to prevent injury if a short circuit occurs?
How can we prevent the dangers associated with a broken chassis ground?
When is the use of extension cords acceptable? Give reasons to support this.
What is an electron? How does this differ from a proton or neutron?
What is a Coulomb?
What is a conductor? How does this differ from an insulator?
What is conductance? What is another way of stating this?
What is current? Also give symbol and units.
Give name and description of the 2 types of current.
What is voltage? Also give symbol and units.
What is resistance? Also give symbol and units.
What is ohm's law? What does it state? What is the equation for this?
What is a capacitor and what does it do? What basic components are needed to make a capacitor?
What is a resistor?
What is capacitive reactance? Also give symbol, units, and formula.
What is capacitance? Also give symbol and units.
What factors determine the capacitance of a capacitor?
What is an inductor? What is an additional property of an inductor?
What is inductive reactance? Also give symbol, units, and formula.
What is inductance? When is it produced? How can you increase inductance? Also give symbol and units.
What is a circuit? By definition, what must it contain?
What are the names of the 2 types of circuit layouts? What are the distinguishing characteristics?
Draw a circuit in series. Then give the equation that would determine Vt, Rt, and Ct in a circuit in series.
Draw a circuit in parallel. Then give the equation that would determine Vt, Rt, and Ct in a circuit in parallel.
What is a filter?
Filters act by...
How does a resistor's filtering effect differ from a capacitor's?
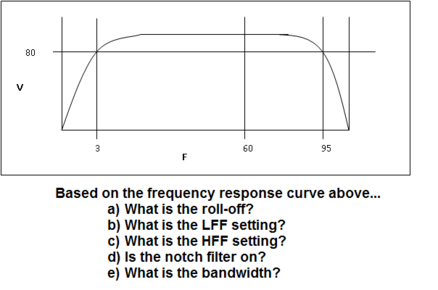
What is a frequency response curve?
What is bandwidth?
What is turnover frequency? At what frequencies does this occur?
What is roll-off? What electric component produces this effect? What are the units? How much does a given roll-off attenuate the signal?
What is a low frequency filter and what does it do? What is another name for a LFF?
What is the electrical construction of a LFF? Draw a simple diagram of this.
What is phase shift? Which electrical component does the property come from?
What type of phase shift will be prodcued by a LFF? Is this enough to be noticeable on the EEG?
What is the formula to determine phase shift?
What is a high frequency filter and what does it do? What is another name for a HFF?
What is the electrical construction of a HFF? Draw a simple diagram of this.
What type of phase shift will be produced by a HFF? Is this enough to be noticeable on the EEG?
What is a notch filter and what does it do? Which frequencies does this affect? What is another name for the notch filter?
When is/isn't use of the notch filter appropriate? Explain why.
Give the equation used to determine LFF value from a given time constant.
Give an equation that shows how LFF can be determined from resistance and capacitance values in the circuit. Then give an equation for time constant based on R and C values.
Give the equation used to determine HFF value from a given time constant.
Give an equation that shows how HFF can be determined from resistance and capacitance values in the circuit. Then give an equation for time constant based on R and C values.
How is digital filtering done? What are the names of the 3 main techniques used?
What is an amplifier and what are 2 types?
What is a power amplifier? What is the gain of a power amplifier?
What is the output voltage of a differential amplifier?
What is a differential amplifier?
Why is this desired for EEG?
What is CMRR?
What factors affect CMRR? How can we optimize the CMRR?
According to guidelines, what is the minimum CMRR for the EEG machine?
How can we measure CMRR?
What is a transistor? What type of devices use transistors?
What is a semi-conductor? Give an example of a semi-conductor and an example of where semi-conductors are commonly used.
What are properties of a good conductor vs a good insulator? What are some materials that make good conductors? insulators?
An in-phase signal of 4V is applied to both inputs. Using an out-of-phase signal, it takes 600µV to get an equal deflection. What is the CMRR? Show calculations. Is this adequate for EEG? Why or why not?
An in-phase signal of 500mV is applied to both inputs. Using an out-of-phase signal, it takes 45µV to get an equal deflection. What is the CMRR? Show calculations. Is this adequate for EEG? Why or why not?
What is the ground electrode? Where is it typically placed? What is the purpose of the ground electrode?
What is an analogue EEG machine and how does it work?
What is a digital EEG machine and how does it work?
What advantages does the digital have over analogue machines? Do analogue machines have any advantages over digital machines?
What is ADC? What does it involve?
Seeing as computers cannot digitize a continuous waveform, how is analogue to digital conversion done?
What are the 2 key factors to ADC? What does each factor represent?
What is horizontal resolution?
What is the main factor that determines the horizontal resolution?
Define sampling rate.
What is dwell time? What is another name for this?
What happens to information recorded during the dwell time?
Give formula that demonstrates relationship between sampling rate and dwell time. Include units.
What is aliasing? What causes this?
What aspects of a waveform can be affected by aliasing?
Which frequencies are most likely to be affected by aliasing? What kinds of changes can result?
What is the Nyquist frequnency?
Is the Nyquist frequency adequate for EEG? Why or why not?
What is vertical resolution?
What are the main factors that determine the quality of the vertical resolution?
What kind of process does the digital machine use to provide the vertical resolution? What does this mean?
What are BITs? What does the number of BITs represent?
Number of BITs is expressed as...
According to guidelines, what is the minimum number of BITs? How many BITS does a good system have?
What is dynamic range?
What determines the size of the dynamic range?
Vertical resolution is expressed as...
What is BIT precision? What does this represent?
Give the equation for BIT precision.
How do we determine the precision of machine?
Using a machine with 11 bits, what is the precision of the actual machine? Show all calculations.
What is saturation? What causes this to occur?
How do you know if saturation of the amplifiers has occurred?
What is screen resolution and why is this important?
According to guidelines, what is the minimum screen resolution?
What is sample skewing?
What causes sample skewing to occur?
What modifications can cause sample skewing to become more apparent?
The purpose of filters is to selectively reduce/eliminate certain frequencies by _________ ____ __________.
What is amplifier sensitivity/gain? What are the units?
Amplifier sensitivity/gain is the ratio of _______ _______ to _______ _______.
Give the equations/ratio for amplifier sensitivity/gain.
What is display sensitivity/gain?
What are the units?
Display sensitivity/gain is the ratio of _______ _______ to _______ _______.
Give the equations/ratio for display sensitivity/gain.
Since computer screens vary in size, using standard paper speed of 30mm/sec, a second will not always be equal to 30mm. Give the formulas to find: a) frequency b) duration. Include units.
What key component is needed for montage reformatting to be possible?
What is the purpose of the system reference electrode?
What is a good indicator that there is a problem with the system reference electrode?
How is montage reformatting done with digital systems? Explain and give equations if helpful.
What is your amplifier sensitivity if your input voltage is 0.05µV and your output voltage is 25µV? Show work.
If your display sensitivity is at 15µV/mm and a waveform is 450µV, how big (in mm) should the waveform appear on the screen?
What is the duration of (of each cycle) of a 15Hz rhythm (in msec)? Show calculations.
If your display sensitivity is 20µV/mm and you have a 1cm high waveform, what is the voltage of the waveform (in µV)? Show calculations.
What is the frequency of a rhythm where the duration of each cycle is 140msec? Show calculations.
You have an 8bit system and your voltage increments are every 3.9µV. What is your dynamic range? Show calculations.
According to the Nyquist Theorem, what is the fastest waveform that you can accurately display if your sampling rate is 100Hz?
If you want to digitize a 15Hz waveform, what is the... a)minimum sampling rate needed to reproduce the waveform b)guideline minimum sampling rate c)ideal sampling rate
Draw the frequency response curve for the following settings: LFF=5Hz, HFF=50Hz, notch filter off, assume roll-off of -3dB. What is the bandwidth? What will be the approx. %amplitude output of the following waveforms? a)100Hz b)60Hz c)20Hz d)5Hz e)1Hz f)0.1Hz
Draw the frequency response curve for the following settings: LFF=2Hz, HFF=70Hz, notch filter on, assume roll-off of -3dB. What is the bandwidth? Approximately what percentage of the amplitude of the following waveforms will be filtered out? a)100Hz b)60Hz c)20Hz d)5Hz e)1Hz f)0.1Hz
Draw the frequency response curve for the following settings: LFF=0.5Hz, HFF=70Hz, notch filter off, assume roll-off of -3dB. What is the bandwidth? What will be the approx. %amplitude output of the following waveforms? a)100Hz b)60Hz c)20Hz d)5Hz e)1Hz f)0.1Hz
Draw the frequency response curve for the following settings: LFF=0.5Hz, HFF=50Hz, notch filter on, assume roll-off of -2dB. What is the bandwidth? What will be the approx. %amplitude output of the following waveforms? a)100Hz b)60Hz c)20Hz d)5Hz e)1Hz f)0.1Hz
Resistors, capacitors and inductors all have a resistive function. Resistors oppose 1)_______ current in the form of 2)________ and the equation for this is 3)________. Capacitors oppose 4)_______ current in the form of 5)________ and the equation for this is 6)________. Inductors oppose 7)_______ current in the form of 8)________ and the equation for this is 9)________.
A 60 uV wave at a sensitivity of 6 uV/mm will produce a deflection of (have an amplitude of)?
A 10mm deflection at a sensitivity setting of 20uV/mm will have a voltage of?
A spike measuring 15 mm peak-to-peak, is recorded at a sensitivity of 10uV/mm. What is the voltage of the spike?
How much deflection will occur if a 100 uV spike is recorded at a sensitivity of 10 uV/mm?
What is rise time?
Rise time is the opposite of...?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards