Close

Application of mechanics to the study of structure and function of living systems
The physiological processes and anatomy of the human body with respect to movement
Branch of mechanics dealing with systems in a constant state of motion
Branch of mechanics dealing with systems subject to acceleration
Study of the action of forces
Study of the description of motion, including consideration of space and time
Quantity of matter
Amount of gravitational force (ma) on the a body
AKA center of mass; point around which body's weight is equally balanced no matter how it is positioned
A push or a pull; is equal to mass (m) * acceleration (a); has magnitude, direction and point of application; measured in Newtons (kg * m/s^2
Resistance to change; resistance to acceleration; tendency to remain in current state
Rotary (angular) or turning force; force when something is rotating; T= Fd
A quantity expressing the motion of a body or system, equal to the product of the mass of a body and its velocity
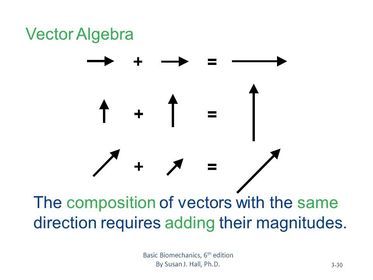
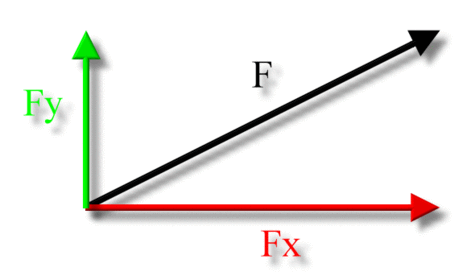
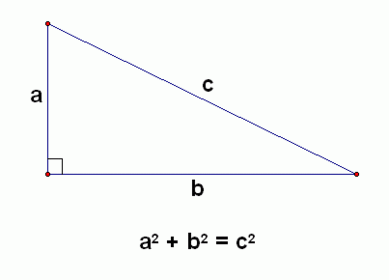
Name the 2 types of motion
Name the 4 steps of of Qualitative Analysis
What step of QA deals with obtaining pre-requisite knowledge,
establishing the problem or chief complaint goal
What step of the QA pertains to conducting the the analysis
This step of the QA is nothing the strengths and weaknesses of performance based on critical features
During this step of the QA is when instruction and corrective strategy is implemented
What are the effects of squat depth on the capsule and ligaments of the knee
What are the effects of the squat depth on the menisci and articular cartilage
What are the effects of squat depth on muscular development of the knee
Squat Depth
Squat Stance
Spine During Squat
A combination of stability, balance, postural control, coordination and perception
Name the 3 sources of dysfunction
Type of dysfunction that occurs when growth and the command the command movement are not linear
Type of dysfunction where injury or trauma is source
Type of dysfunction where unnatural activity repeated on a natural movement base and where natural activity repeated on an unnatural movement base
A developmental perspective and creates a systematic way to observe, rate, and rank movement patterns on on a numerical scale to focus on significant limitations or asymmetries
PRIMITIVE MOVEMENT PATTERNS 1:
Basic mobility and stability movement patterns
PRIMITIVE MOVEMENT PATTERNS 2:
Transitional movement patterns in which a higher degree of stability
HIGHER LEVEL MOVEMENT PATTERN:
FIRST YOU HAVE___________THAN YOU EARN ___________?
Name 4 Name Filters In FMS:
How to conduct an FMS; what we’re looking for in the 7 screens + 3 clearing tests
Name the BIG 3
Name the LITTLE 4
How to interpret the findings for shoulder mobility
How to interpret the findings for Active Straight Leg Raise
How to interpret the findings for Rotary Stability
How to interpret the findings for Trunk Stability Push-up
How to interpret the findings for Hurdle Step
How to interpret the findings for Inline Lunge
How to interpret the findings for Deep Squat
What a therapist/fitness specialist would address first
Common Mistakes in Prescribing Correctives
Common mistake in prescribing correctives is the one size fits all programming: weight loss, LBP
Common mistake in prescribing correctives is isolated target muscles approach
Common mistake in prescribing correctives is to mimic function in poor way
Common mistake in prescribing correctives is arbitrary strengthening to prevent injury
Corrective examples for Shoulder Mobility
Corrective examples for Active Straight Leg Raises
Corrective examples for Rotary Stability
Corrective examples for Trunk Stability Push- up
Corrective examples for Hurdle Steps
Corrective examples for Inline Lunge
Corrective examples for Deep Sqaut
Corrective examples for Deep Squat
Corrective examples for Deep Squat

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards