Year 1 Pathological Responses of Cells Flashcards on Consequences of Thrombosis, created by Anna mph on 16/04/2016.
Pinned to
25
1
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Anna mph
over 8 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Anna mph
over 8 years ago
|
|

What are the three main damaging consequences of thrombosis?
What are the two non-harmful consequences of a thrombus?
What is an embolus?
How do emboli cause damage?
What % of events are thromboembolic? Of these what % originate from the venous circulation?
How do superficial thrombi present?
What % of deep vein thrombosis are silent?
What is a thromboembolism? Where do the majority of them travel to?
What is PE? Who is at high risk for this?
Why is surgery a risk factor for embolism?
What is and what would DVT cause systemically and locally?
How many deaths per year are due to DVT?
Where do the majority of DVT travel to?
What are the effects of DVT embolism?
What increases the risk of DVT embolism having a thrombotic event?
What % occlusion of circulation to the lung results in death?
When would a patient particularly have to be observed after surgery? (2)
Without prophylaxis what % of people having hip surgery have DVT?PE? Knee?
How does deep vein thrombosis present? How common/rare are these presentations?
How does the size of the clot relate to symptoms?
Why is venous gangrene rare?
Describe the movement of a deep vein thrombus (in a pulmonary thromboembolism).
What do pulmonary thromboembolism look like?
Other than from deep veins what other parts of circulation might thromboembolism result from?
What else can cause a thromboembolism? Where causes this?
What is the main problem which result from arterial thrombi?
What is a laparoscopy?
What do air/gas embolisms result in?
What is Caisson disease?
What does Caisson disease cause?
What are the signs of decompression sickness?
What causes a fat embolus?
What is bone marrow made of? What properties does it have?
What usually happens to a fat embolism? What happens if it doesn't?
What/why/where do fat embolisms cause damage?
What percentage of patients following major fractures don't have fat embolisms? What percentage appear symptomatic? What percentage have severe manifestations, what causes this?
What is the most severe consequence of a fat embolus?
In the US where does amniotic fluid embolisms rank in terms of deaths in the late stages of pregnancy?
What is the normal order of birth? How is this disrupted to cause amniotic fluid embolisms?
What is amniotic fluid rich in? What effect does amniotic fluid have in the maternal circulation?
What is disseminated intravascular coagulation? What two things does this call?
Which coagulation pathway would the amniotic fluid activate?


What is the localised damaging consequence of thrombosis?
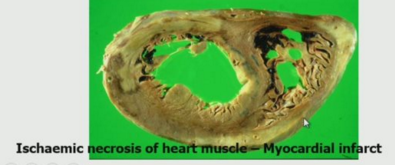
Describe the stages of myocardial infarction.
What are the general factors which mediate the response of a tissue to a reduction in blood flow?
Give examples of the general state of an organism which may cause an exacerbated response by the tissue to oxygen deprivation
Which organs have double circulation? Why? How does this affect the likelihood of a massive infarction?
Which organs have parallel circulation?
Which organ has rich anastomosis?
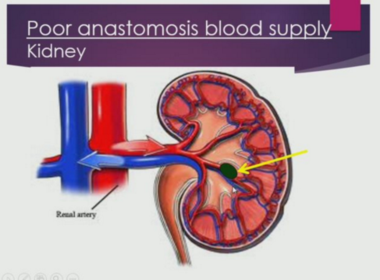
Which organ has poor anastomosis?
What is an anastomosis? How does this affect the risk of infarction?
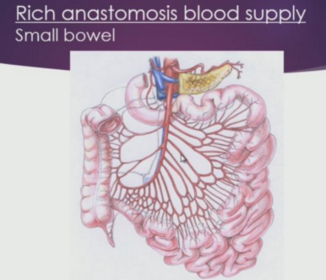
What is the benefit of parallel circulation?
How does the rate of occlusion development/ischaemia affect amount of infarction?
Give an example of a tissue which is resistant to ischaemia. Why is this the case?
TISSUE VULNERABILITY
How long can neurons/glia survive without oxygen?
How long can heart muscle/kidney tubules go without oxygen?
How long can connective tissue go without oxygen?
What is an important factor in ischaemia and infarction?
Define atherosclerosis
How long does the process of atherosclerosis take?
Describe the structure of an artery
What are the components of the tunica intima?
What are the components of the tunica media?
When does the damage of atherosclerosis occur?

What is found to accumulate in the tunica intima? Where?
What causes LDL to recruit inflammatory cells? What does this result in?
All in all how does atherosclerosis occur?
What happens if the plaque is stable? Unstable?
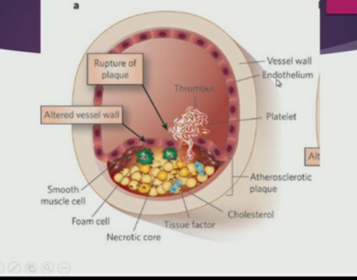
What are the consequences of a complicated fibrous plaques?
Why do intraplaque hemorrhages arise?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards