Flashcards on BISC 100: Lecture 31, 32, 33, 34 :Ecology, created by Chelsi Souch on 10/08/2016.
Pinned to
30
0
0
No tags specified

|
Created by Chelsi Souch
over 8 years ago
|
|
Close

|
Created by Chelsi Souch
over 8 years ago
|
|

ECOLOGY
3 WAYS TO LOOK AT ECOLOGY
ECOLOGICAL LEVELS
BIOSPHERE
Abiotic factors of the biosphere
Biomes
Freshwater biomes
Marine biomes
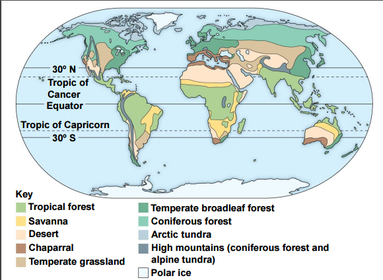
How climate affects terrestrial biome distribution
Uneven heating of Earth
How climate affects terrestrial biome distribution
How uneven heating of Earth produces various climates
ECOSYSTEM
ECOSYSTEM COMPONENTS
COMMUNITY
DESCRIPTIVE PARAMETERS FOR
COMMUNITIES
BIODIVERSITY:
THREE TYPES
ECOLOGICAL COMMUNITY
STABILITY
TROPHIC STRUCTURE
What is a population?
Population Structure and Dynamics
Density and Dispersion
Density
Dispersion patterns
How to quantify a population?
Mark and Recapture (formula)
Dispersion patterns: CLUMPED
Clumped patterns usually result from
Dispersion patterns: UNIFORM
Dispersion patterns: RANDOM
GROWTH OF A POPULATION
Exponential increase:
The Exponential Growth Model
The Logistic Growth Model
POPULATION GROWTH
CURVES
POPULATION GROWTH IS LIMITED BY
ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE
Density Dependent Factors
POPULATION GROWTH IS LIMITED BY
Density Independent Factors
SURVIVORSHIP CURVES
GROWTH AND REPRODUCTIVE STRATEGIES
Principles of population ecology have practical applications
– Principles of population ecology are useful in managing
natural resources
Three such principles in practice are
3 DETERMINANTS OF
COMMUNITY STRUCTURE
ECOLOGICAL NICHE
RESOURCE UTILIZATION AND TOLERANCE
Opportunistic Populations
Equilibrial populations
APPLICATION OF POPULATION OF ECOLOGY
Human Population Dynamics
Most Populous Cities of the World
2015
What is demographic transition?
What is the age structure of a population?
What is “Ecological Footprint” (EFP)?
The ecological capacity of the world
may already be smaller than
COMMUNITY INTERACTIONS
1. Competition
COMMUNITY INTERACTIONS
2. PREDATION
Keystone Species
Effects of predation on communities
DEFENSE MECHANISMS AGAINST PREDATORS
PREY’S ADAPTATIONS TO AVOID PREDATION
Adaptation to avoid predation
Camouflage
Adaptation to avoid predation
CHEMICAL DEFENSES: Poison arrow frog
Mimicry
Adaptation to avoid predation
Deceptive mimicry: Mullarian mimicry
Coevolution of Predator and Prey
1. COMMENSALISM
2. MUTUALISM
3. PARASITISM
3B. INTERNAL PARASITISM: ENDOPARASITE
7
Extremely Specialized:
3C: Brood Parasitism
SUMMARY OF COMMUNITY
INTERACTIONS
In short: Ecological succession
Disturbance is a prominent feature
of most communities
– Disturbances are events thaT
Primary succession
Secondary succession
– Energy flow and chemical cycling
Trophic relationships
Trophic levels
Energy flow
–Chemical cycling
Trophic structure is a key factor in
community dynamics
Herbivores, which eat plants, algae, or autotrophic
bacteria, are the
Secondary consumers
Tertiary consumers
Quaternary consumers
Detritivores, or decomposers
Food chains
interconnect,
forming food webs
Productivity and the Energy Budgets of Ecosystems
An energy pyramid
Ecosystem alteration can upset chemical
cycling
Environmental changes caused
by humans, such as

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards