Hematology, Anemia, Bone Marrow Aspiration
Pinned to
32
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Michelle Evans
about 8 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Michelle Evans
about 8 years ago
|
|

What tube do you use for a serum chemistry panel?
Does a red top tube contain anticoagulant?
What is the purpose of a tiger-top (red/grey) tube?
Which tube contains the anticoagulant EDTA with potassium salt? What is the purpose of EDTA?
Which tube is used for coagulation testing?
What additives does the blue top tube contain? What is their purpose?
What is a common mistake when filling a blue top tube?
Which tube is used for glucose collection, if the sample is going to ship and can't be spun?
What additives are in the grey top tube? What are their purpose?
What is the purpose a green top tube?
What additives are in the green top tube? What are their purposes?
Why shouldn't you refrigerate a blood film or freeze a blood sample?
You see a sample with very swollen red blood cells and degraded leukocytes. What error was made to leave to these changes?
If you under fill a lavender top tube, what changes in CBC results?
You have a sample that is taking an extremely long time to clot. Assuming the animal does not have a clotting disorder, what could explain these results?
What is packed cell volume (PCV)?
What is the purpose of plasma protein refractometry?
What factors can alter the results of protein concentration estimate?
What does an increase in blood albumin indicate?
Increased PCV and increased TP indicate:
Decreased PCV and decreased TP indicate:
PCV is WNL, TP is decreased:
PCV is WNL, TP is increased:
PCV decreased, TP is WNL:
PCV increased, TP is WNL
Which is more useful: the percentage of nucleated cells that belong to each cell type, or the absolute concentration of each cell type?
What is the best technique for blood film preparation?
Which area of the blood film do you examine to find large items, such as microfilariae and aggregated platelets?
What determines if an anemia is regenerative?
Which species never release reticulocytes in response to anemia?
In cats, which form of reticulocytes are important for determining if regeneration is ongoing?
What is the buffy coat?
What does yellow pigmented serum indicate?
What does white opaque plasma indicate?
What does red plasma indicate?
What are the components of a CBC?
What parameters are included in the erythrogram?
Which parameters are directly measured?
Which parameters are determined via microscope examination?
What parameters in a CBC are calculated?
A decrease in which parameters indicates anemia?
What does an increased in mean cell volume (MCV) indicate?
In a cat with macrocytosis (increased MCV) and a non-regenerative anemia, what disease do you consider as a top differential diagnosis?
What does a decreased MCV indicate?
What is the MCHC?
What does an increased MCHC indicate?
What does a decreased MCHC indicate?
What is the RDW? What does an increase in this parameter indicate?
What information does the reticulocyte count give you?
What does an increase in the reticulocyte count indicate?
What does a decreased reticulocyte count, or a reticulocyte count that is not increased in an anemic animal, indicate?
What is a hypochromic RBC?
What CBC parameter confirms whether an anemia is hypochromic or normocrhomic?
What is anisocytosis?
What CBC parameter determines the degree of anisocytosis?
What is poikilocytosis?
What are these cells?
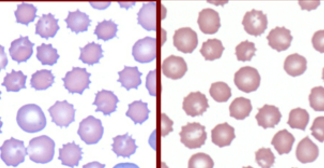
What are echinocytes?
Rattlesnake envenomation is associated with what shape change in RBC?
What is this RBC shape called?

What disease process is associated with the presence of acanthocytes?
Keratocytes are indicative of which kinds of processes?
What is the term for these kinds of cells?
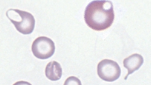
What are schistocytes? What are they caused by?
What are spherocytes pathognomonic for?
What are these cells?

What are these cells?
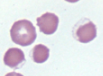
What process causes eccentrocytes?
What processes can lead to increased nucleated red blood cells (nRBC) in the peripheral blood?
You see nRBC with no significant polychromasia -- what disease processes are you concerned about?
What is a Howell-Jolly body?
What is cellular feature is often seen in ruminant regenerative responses?
If you see basophilic stippling with few other signs of regeneration, or without anemia, what should you worry about?
How do you distinguish intracellular bacteria, like Anaplasma, from Howell-Jolly bodies?
Mycoplasma is important in which domestic species?
A large, tear-shaped inclusion in a canine RBC is indicative of which intracellular parasite?
What are Heinz bodies?
What stain can be used to determine if Heinz bodies are present?
What causes agglutination?
What is anemia?
What parameters are used to assess anemia?
What are the three causes of anemia?
If regeneration is present, what are the possible causes of the anemia?
If no regeneration is present, what do you know about the anemia?
If plasma protein is decreased in the presence of anemia, what is the most likely cause of anemia?
What does macrocytosis indicate in anemia?
What does hypochromasia indicate?
What signs found during a physical exam can be indicative of anemia due to blood loss?
What sign found during a physical exam can be indicative of anemia due to hemolysis?
If the bone marrow is responding to an anemia and regenerating RBCs, what should the reticulocyte be?
A macrocytic, non-regenerative anemia is indicative of which disease processes?
What is pancytopenia?
What can cause pancytopenia?
In pancytopenia, which cell lines will decrease first?
What is pure red blood cell aplasia?
What is RBC hypoplasia?
Does chronic inflammatory disease cause regenerative or non-regenerative anemia?
What is the mechanism of anemia due to inflammatory disease?
Why is anemia common in animals with renal failure?
How do endocrine diseases cause non-regenerative anemia?
Non-regenerative anemia with neutrophilia, left shift, and monocytosis is most likely caused by:
What are some causes of pancytopenia?
If you have a non-regenerative anemia with azotemia (increased BUN, creatinine), the most likely cause of anemia is:
What is the benefit of looking at the bone marrow (via aspirate or core biopsy) during non-regenrative anemia?
If a bone marrow aspiration shows dysplatic maturation of RBC, the most likely cause of anemia is:
If a bone marrow aspiration shows precursors present in high numbers, but there are no signs of regeneration in the peripheral blood, the anemia is most likely due to:
In what species can you not use iron stores in the bone marrow to determine if anemia is due to chronic inflammation?
What is regenerative anemia?
What are causes of regenerative anemia?
If you see regenerative anemia with low protein concentration, the top differential for the anemia is:
In acute blood loss, what signs are seen?
Chronic blood loss should lead to:
What are the causes of chronic blood loss anemia?
What is the most common site associated with chronic blood loss?
What are the signs of iron deficiency?
What are is main causes of blood cell destruction?
Destruction of RBC leads to what kind of anemia?
What is the mechanism for intravascular hemolysis?
What is the mechanism for extravascular hemolysis?
What are signs are pathognomonic for IMHA?
What is the mechanism of IMHA?
What is a Coomb's test?
What is neonatal isoerythrolysis?
How do baby's obtain maternal antibodies in neonatal isoerythrolysis?
Why is neonatal isoerythrolysis common in mule foals?
How do you diagnose infectious causes of anemia?
Are Mycoplasma intracellular or extracellular bacteria?
What is an infectious cause of acute hemolytic anemia in cats?
Why are splenectomized dogs more likely to get disease from Mycoplasma haemocanis?
What is an infectious cause of severe hemolytic anemia in cattle?
Is Anaplasma intracellular or extracellular?
What is the mostly likely cause of a tear-shaped intraerythrocytic organism visualized on a canine blood smear?
What does Babesia cause in horses?
What is a protozoal cause of hemolytic anemia in ruminants?
What is a protozoal cause of hemolytic anemia in cats?
A cat presents with hemolytic, nonregenerative anemia, keuopenia, thrombocytopenia, and organisms visible within the RBC and macrophages. What is the most likely cause?
What is a consequence of macrophages phagocytizing Cytauxzoon felis?
What species is most likely to get Heinz body anemia? Why?
What is the cause of Heinz body anemia?
Why do animals with Heinz body occasionally have elevated MCHC?
How doe water intoxication lead to hemolytic anemia?
What is polycythemia?
What are relative causes of polycythemia?
What is absolute polycythemia?
What is relative polycythemia?
What is primary absolute polycythemia?
What myeloproliferative disorder describes a chronic leukemia of erythroctes?
What is secondary primary polycythemia?
What is appropriate secondary polycythemia?
What is inappropriate polycythemia?
What is MPV? Why can this value be clinically significant?
What is thrombocytopenia?
When you see thrombocytopenia without clinical signs, is the most likely cause something pathologic in the animal?
Causes of Thrombocytopenia
An animal presents with severe hemorrhage and bleeding. Do you worry about thrombocytopenia with this patient?
What are the indications for bone marrow aspiration?
What type of anemia is an indication for a bone marrow aspirate?
What is the advantage of a bone marrow aspirate?
What are the advantages of core biopsy?
Why should you stop aspirating as soon as the bone marrow sample starts entering the syringe?
True or false: Bone marrow aspiration is a useful diagnosis tool without any other tests.
What is the M:E ratio?
What is an increased M:E ratio?
What is a decreased M:E ratio?
If an anemia is due to a lack of production, what would you expect to see in the bone marrow?
If a cytopenia is caused by consumption, what do you expect to see in the bone marrow?
If a cytopenia is due to destruction, what do you expect to see in the bone marrow?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards