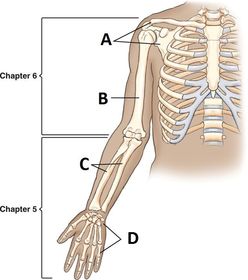
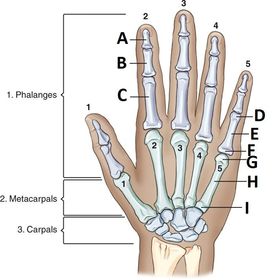
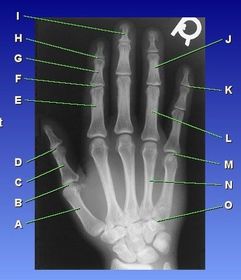
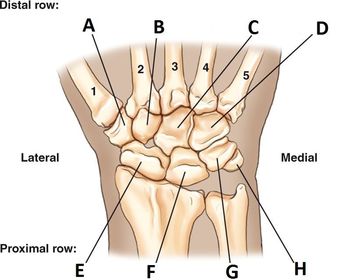
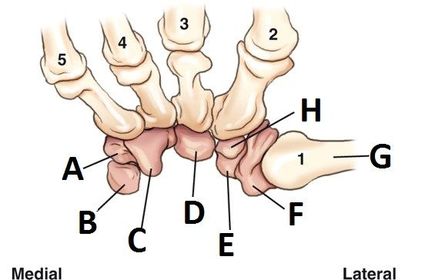
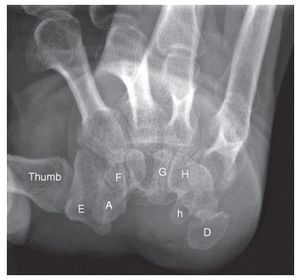
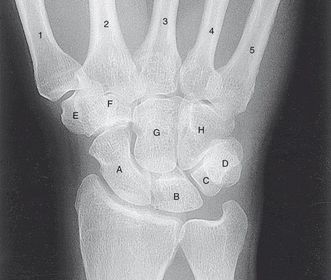
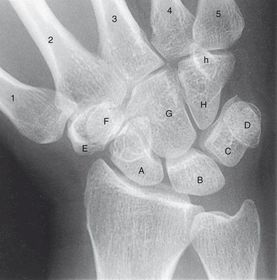
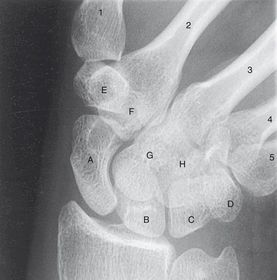
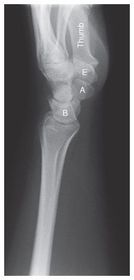
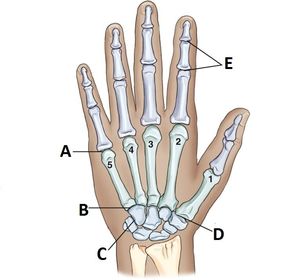
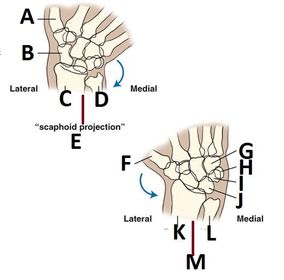
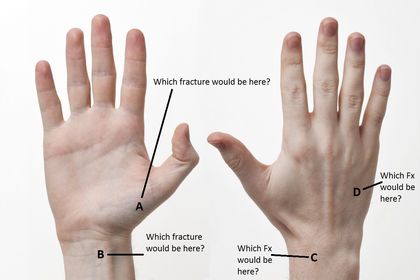
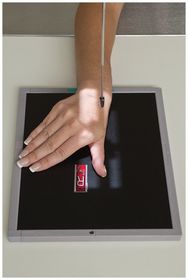
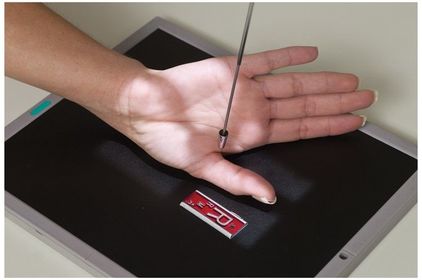
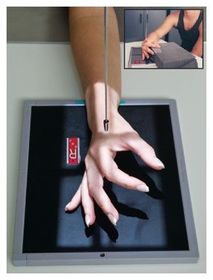
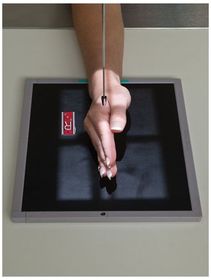
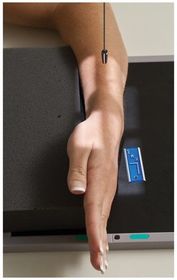
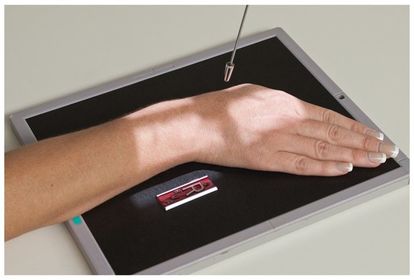
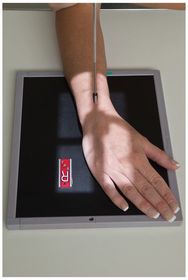
ARRT Radiologic Procedures I Flashcards on Hand and Wrist Procedure, created by RadTech Fairy on 04/10/2016.
Pinned to
752
4
0
No tags specified
|
Created by RadTech Fairy
about 8 years ago
|
|
Close