Close

Microtia and congenital meatal atresia, right Unilateral disease is best treated by:
A: Hearing aid
B: Reconstructive surgery at age 12 months
C: Reconstructive surgery before school age
D: No treatment required
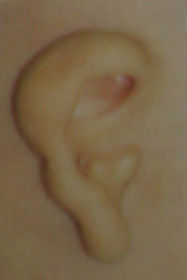
Diagnosis: Heamtoma auris, left this condition may be complicated by:
A: Abscess formation
B: Perichondritis
C: Cauliflower ear
D: All of the above
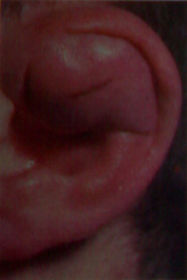
Diagnosis: Perichondritis, right ear. This condition does not follow whitch of the following:
A: Acute otitis media
B: Hematoma auris
C: Furuncle of external canal
D: Postoperative
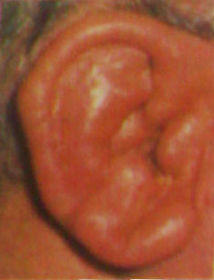
Diagnosis: cauliflower ear this ear condition is a common sequelae of:
A: Carcinoma of external canal
B: Basal cell carcinoma of auricle
C: Perichondritis of auricle
D: Herpes zoster
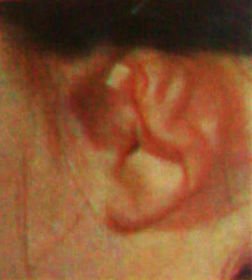
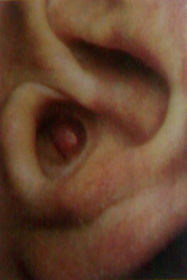
External canal aural polyp, left ear. Symptoms of this condition may include:
A: Conductive hearing loss
B: sensorineural hearing loss
C: Facial paralysis
D: All of the above
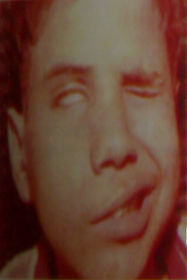
Facial paralysis, complete, right side. Electroneuronography in case of facial paralysis is:
A: A good diagnostic test
B: A good indicator for nerve degeneration, and thus surgical decompression
C: A good test for muscle wasting
D: Has no value

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards