Close

objectives
protein-cell interactions
cell functions
cell types
cellular structure
Cell Plasma Membrane
Phospholipids
Lipid bilayer
Transmembrane Proteins
Selectively permeable
(depends on...)
"outside-in" signalling
"inside-out" signalling
Protein-based Receptors
Adhesion receptors
Common Receptor Molecules
Cell Adhesion Force
Types of cell contacts
Cell-cell interactions
(3)
Cell-ECM
Cadherins
Integrins
Cell surface interactions
Cell surface receptors
Extracellular Matrix
(ECM)
ECM types
Ex. 6.1
proteins often adsorb to biomaterial surfaces implanted in vivo or exposed to serum-containing media in vitro.
Many biomaterials do notsupport cell adhesion prior to adsorption of a protein layer. How might proteins facilitate adhesion of cells to a biomaterial?
Hint: consider to coat ECM proteins of biomaterial surface.
basic interactions
Cell spreading
in vivo
vs.
in vitro
Types of cell cultures
characterization methods
upright vs inverted microscope
bright field vs dark field microscope
Phase-Contrast microscope
Fluorescence microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy sample preparation
Confocal fluorescence microscopy
confocal fluorescence microscopy
common charactersistics
Cell Adhesion Assays
Cell Spreading Assays
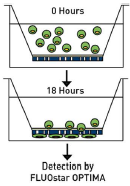
Centrifugation Assay (Normal Force)
Flow Chamber Assay (Shear Force)
Cell Migration Assay
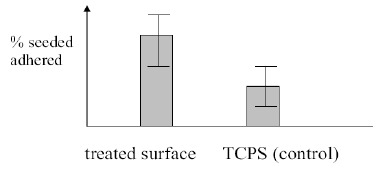
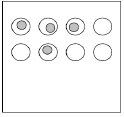
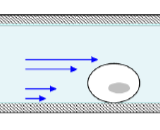
flow chamber vs centrifuge
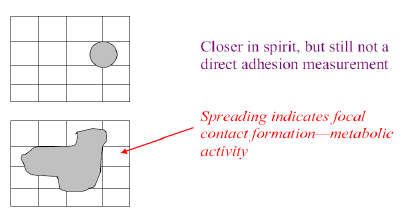

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards