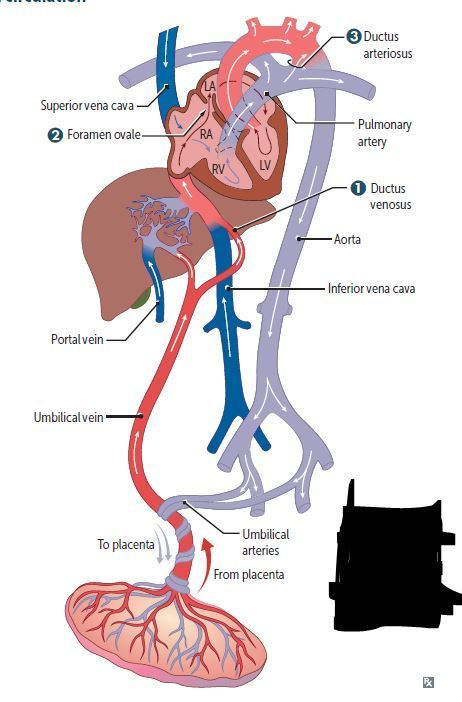
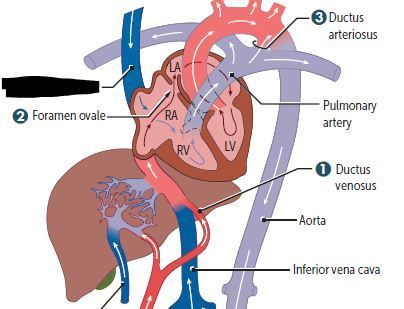
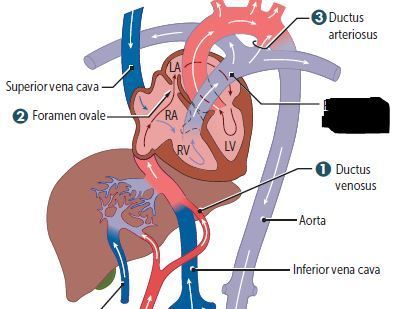
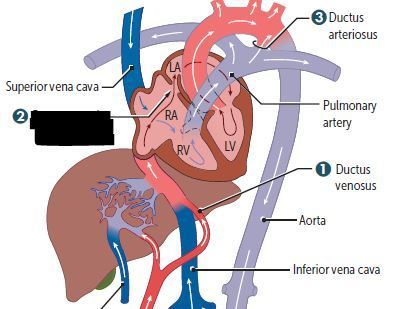
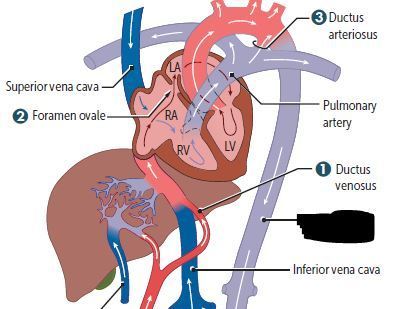
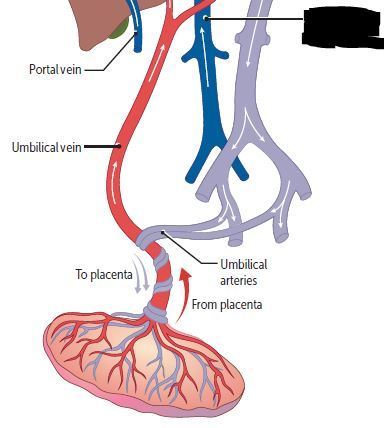
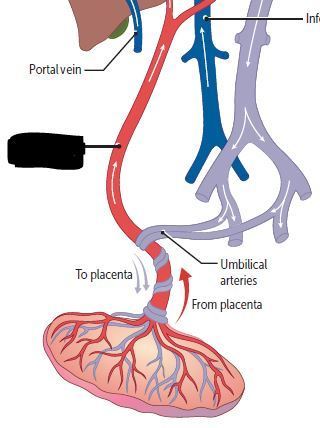
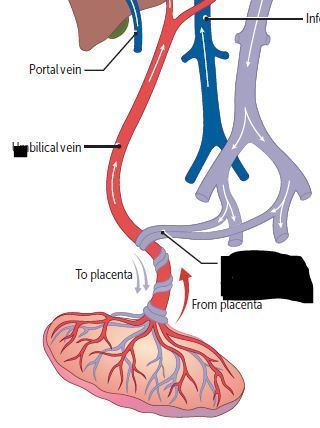
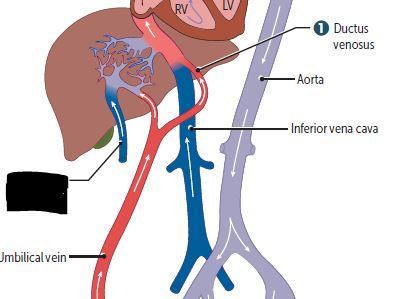
Cardiovascular Flashcards on 270- Fetal Circulation & Fetal-Postnatal Derivatives, created by Victoria Wright on 15/05/2017.
Pinned to
225
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Victoria Wright
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close