CIPS Procurement Flashcards on D2, created by Josie Robinson on 23/05/2017.
Pinned to
28
1
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Josie Robinson
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Josie Robinson
over 7 years ago
|
|

CHAPTER 1
What is a business case?
'Inputs' examples
Strategic / commercial objectives
Four stages in the way procurement has developed
the procurement cycle
1. identify the need
2. define the need
3. develop contract terms
4. source the market
5. appraise the market
Three types of purchase
straight re-buy
the buyer may already have a preferred supplier
straight re-buy
(or inventory replenishment)
involves...
modified re-buy
requirements -
some of the requirements have changed
modified re-buy
involves..
New purchase
a good or service which has not been specified or purchased before
purchasing research
value engineering
eliminates waste
early buyer involvement (EBI)
influences whole-of-life impact
early supplier involvement (ESI)
Capital procurement
production materials
maintenance repair and operating (MRO)
commodities
goods for re-sale
informal business case structure
comprehensive, formal business case structure
(for high-risk, high-value procurements)
value
competitive advantage
costs
risks
(e.g. outsourcing, single sourcing, international sourcing)
cost/benefit analysis
advantages of outright purchase vs advantages of leasing
strategic alignment
environmental procurement
triple bottom line
CHAPTER 2
price vs cost
price and cost research
external factors to supplier pricing decisions
internal factors to supplier pricing decisions
cost-based pricing
market-driven pricing
price analysis
cost analysis
understanding costs - components of the cost base
overheads
***profit is not a cost - although along with cost, it is a component of price***
what is cost behaviour?
fixed cost vs variable cost
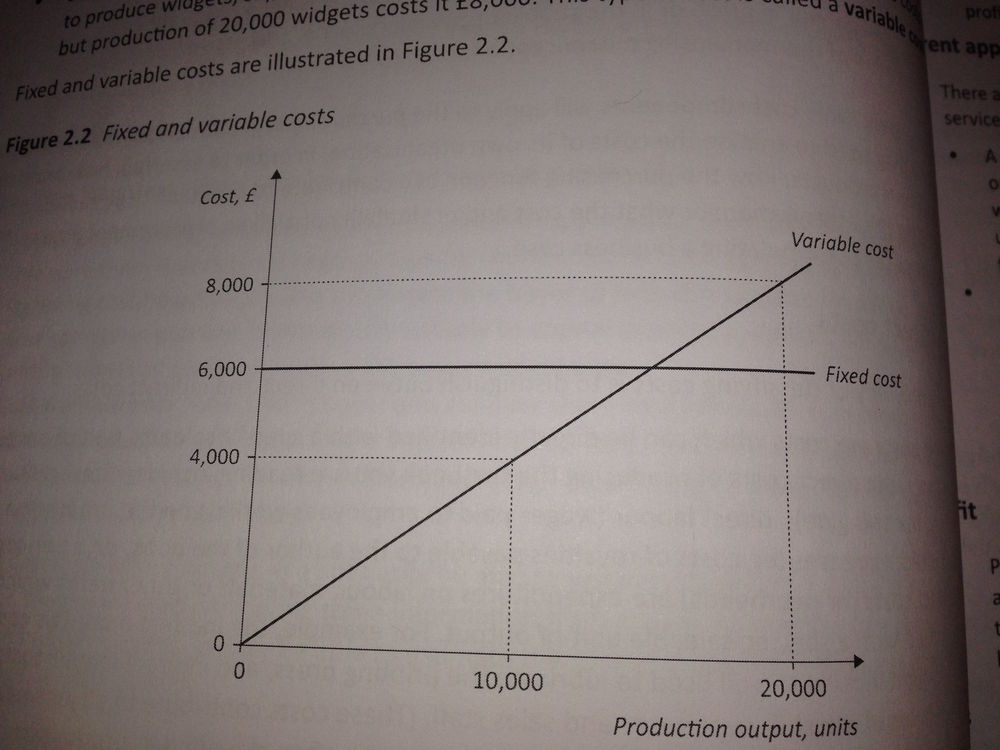
calculating costs
1. marginal costing
2. absorption costing
profit?
contribution analysis
total cost of ownership
Ways to calculate whole life costs
benefits of calculating whole of life costs
limitations to whole of life costing (WLC)
qualitative methods used to estimate cost
budget
procurement budget info (page 38)
primary data sources
secondary data sources
a cash budget should include...
(objective: to anticipate cash shortages or surpluses and allow time to make plans for dealing with them)
CHAPTER 3
Benefits of budgeting
limitations of budgeting
two types of budget
incremental budget
zero-based budget
two budgeting techniques...
1. forecast - at intervals during the year the budget is revisited and updated inline with new information
fixed budget
flexible budgets
variance analysis
examples of explanations for variances
CHAPTER 4
what is a specification?
a specifications must:
tolerance
a supplier can not always meet the exact requirement of a specification every time
use the 'five rights of procurement' when defining a specification
zero defects implications
why don't all specifications have zero tolerance?
specifications give purpose for what a purchased item is to be used for
advantages of specifications
disadvantages of specifications
types of specification
evaluating conformance specifications
(generally becoming less common)
circumstances where conformance specifications are appropriate...
evaluating the use of performance specifications
circumstances where performance specifications are appropriate...
specification by chemical or physical properties
(conformance specification)
Four other types of conformance specification:
1. specification by brand
2. specification by sample
output based specification (performance specification)
specifying services
services are....
outcome based specification
(performance specification)
sustainable specifications - triple bottom line
CHAPTER 5
an effective specification is...
procurement professionals provide:
Four possible approaches to organising the specification process
the buyers role in specification
early buyer involvement (EBI)
information required for specification development
(page 80)
Definition of 'standard'
two methods of minimising stock proliferation
proactive approach
reactive or remedial approach
benefits of standardisation
CSR specific specifications
best to incorporate sustainability criteria is at the need definition, specification and pre-qual stages, then again through negotiations and post-contract
waste hierarchy
Information assurance
- corporate governance
- contingency
- strategic development and management
information assurance involves these steps:
CHAPTER 6
what is supplier performance measurement
the purpose of performance measures
supplier performance appraisal can be used to...
what is a KPI
quantitative KPIs
focus on efficiency
suitable for purchase of products
qualitative KPIs
focus on effectiveness
suitable for purchase of services
advantages of using KPIs
disadvantages of KPIs
process of developing KPIs
definition of benchmarking
four types of benchmarking
the benchmarking process
(cons = can be costly and reqires effective communication internally)
focus of contractual performance in this textbook
the eight dimensions of product quality
service level agreement
the purpose of an SLA
benefits of SLAs
(communication, relationship management, conflict management, performance monitoring, review and evaluation)
limitations of SLAs
contents of SLAs should include...
(print page 107)
what is the process of developing and implementing SLAs
CHAPTER 7
What is a contract?
The information found in a contract includes...
Express terms
e.g. specify price, delivery dates, sharing of insurance costs
Implied terms
contract conditions
warrenties
general contract structure
Model form contracts - who are they published by?
advantages of using standard and model form contracts
disadvantages of using standard and model form contracts
Contract clause : time and performance
Contract clause : passing of title / property
Contract clause : liquidated damages
Contrat clause : penalty clause
Model clause examples
Contract clause : Force majeure
Contract clause : guarantees
Contract clause : exclusion
Contract clause : Indemnities
Contract clause : insurances
Contract clause : subcontracting
Ethics / CSR
CHAPTER 8
Two types of pricing arrangements
Pricing schedule
firm price agreements
firm price arrangements are appropriate when...
firm price arrangements are advantageous to the buyer because:
Pricing schedule
lump sum contracts
reasons for cost/price variations
the use of indexation and price adjustment formulae
fixed price incentive (or gainshare) contracts provides adjustment of the final price to include various supplier incentives
cost-based pricing arrangements
cost-plus pricing
(cost-based pricing arrangement)
types of cost-plus pricing
disadvantages of cost-plus pricing arrangements for the buyer
target costing
each member of the supply chain must work closely with others to identify opportunities for cost reductions, driving costs downwards
target cost with maximum price
target cost with maximum price are suitable when...
target cost without maximum price
target cost without maximum price are suitable when...
payment methods
credit terms
credit limit
stage or progress payments
commercial and legal considerations in regard to payment terms
express payment terms are used to specify
Romalpa clause
CHAPTER 9
make/do vs buy decisions
factors which influence make/do vs buy decisions
advantages of making / doing
advantages of buying in / outsourcing
supply chain management
outsourcing
subcontracting
globalisation
drivers for outsourcing
benefits of outsourcing **
can only be secured by excellent supplier relationship management because of risks of selecting the wrong supplier, service standards, ethical issues etc
risks / disadvantages of outsourcing **
costs involved in outsourcing
offshoring
advantages of 'in-sourcing'
competencies
--> non-core competencies should be outsourced
when should you out-source?
CHAPTER 10
main criteria for making a procurement proposal business case

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards