Cardiovascular Flashcards on 279 - Heart Murmurs, created by Victoria Wright on 30/05/2017.
Pinned to
3
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Victoria Wright
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Victoria Wright
over 7 years ago
|
|

Describe Aortic Stenosis Heart Murmurs
In Aortic Stenosis, the murmur is loudest where? And where does it radiate to?
In Aortic Stenosis, the pulses are weak with a delayed what?
Aortic Stenosis can lead to what? What is the mnemonic device to remember?
Aortic Stenosis is most commonly do to what?
Describe Mitral Regurgitation Murmurs
Describe Tricuspid Regurgitation Murmurs
What can cause either Mitral regurgitation or Tricuspid regurgitation?
Where is the murmur loudest in Mitral regurgitation? Where does it radiate to?
Mitral regurgitation is often due to what?
Where is the murmur loudest in Tricuspid regurgitation?
What commonly causes Tricuspid regurgitation?
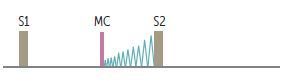
Describe Mitral Valve Prolapse Murmurs
What is the most frequent valvular lesion?
Where are mitral valve prolapse murmurs best heard?
When are mitral valve prolapse murmurs loudest?
What can mitral valve prolapse predispose someone to?
What can mitral valve prolapse be caused by?
Describe Ventricular Septal Defect
Where is a ventricular septal defect loudest?
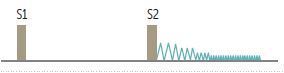
Describe Aortic Regurgitation Murmurs
What is aortic regurgitation often due to?
What does aortic regurgitation progress to?
Describe Mitral Stenosis
Mitral stenosis is often a late sequela of what?
Chronic mitral stenosis can result in what?
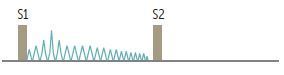
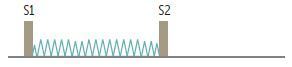
Describe Patent Ductus Arteriosus Murmurs
When are Patent ductus arteriosus murmurs loudest?
Patent Ductus Arteriosus is often due to what?
Patent Ductus Arteriosus is best heard where?
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur (ejection click may be present).
What type of heart murmur is described below?
LV >> aortic pressure during systole.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Loudest at heart base; radiates to carotids.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
“Pulsus parvus et tardus”—pulses are weak with a delayed peak.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Can lead to Syncope, Angina, and Dyspnea on exertion (SAD).
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Most commonly due to agerelated
calcification in older patients (> 60 years old) or in younger patients with
early-onset calcification of bicuspid aortic valve.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Holosystolic, high-pitched “blowing murmur.”
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Loudest at apex and radiates toward axilla.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Is often due to ischemic heart
disease (post-MI), MVP, LV dilatation.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Loudest at tricuspid area.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Commonly caused by RV dilatation.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Late systolic crescendo murmur with midsystolic click (MC; due to sudden tensing
of chordae tendineae).
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Best heard over apex. Loudest
just before S2. Usually benign.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Can predispose to infective endocarditis.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Can be caused by myxomatous degeneration (1° or 2° to connective tissue disease such as Marfan or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome), rheumatic fever, chordae rupture.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Holosystolic, harsh-sounding murmur.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
High-pitched “blowing” early diastolic decrescendo murmur.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Long diastolic murmur, hyperdynamic pulse, and head bobbing when severe and chronic.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Wide pulse pressure
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Often due to aortic root dilation, bicuspid aortic valve, endocarditis, rheumatic fever.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Progresses to left HF.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Follows opening snap (OS; due to abrupt halt in leaflet motion in diastole, after
rapid opening due to fusion at leaflet tips).
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Delayed rumbling mid-to-late diastolic
murmur (decreased interval between S2 and OS correlates with increased severity).
What type of heart murmur is described below?
LA >> LV pressure during diastole.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Often a late (and highly specific) sequela of rheumatic fever.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Chronically, can result in LA dilatation.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
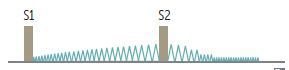
Continuous machine-like murmur.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Loudest at S2
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Often due to congenital rubella or prematurity.
What type of heart murmur is described below?
Best heard at left infraclavicular area.
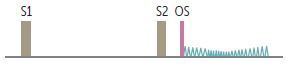

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards