Lipid chemistry, structure, and function. Biological membranes
Pinned to
9
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Kristina Redd
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Kristina Redd
over 7 years ago
|
|

Unsaturated fat is a _____ fat.
Saturated and trans fat and cholesterol are all _____ fat.
What are lipids: hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Are lipids polar or nonpolar?
What form of energy do lipids take in the diet?
What form of energy do lipids take in energy stores?
What are significant advantages of triglycerides?
What are specific amphipathic lipids?
What are examples of signaling molecules?
Name 4 fat-soluble vitamins.
What are the building blocks of most lipids?
CH3(CH2)16COOH

Identify the lipid and the shorthand.

What are all fatty acids ionized at?
Identify alpha, beta, and omega.
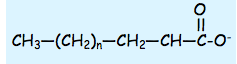
What does omega-# indicate?
What does "methylene-interrupted" mean?
If the shorthand for FA is 18:2w6, what dies it look like and what is the name?
Virtually all FA are esterified to 3-C glycerol as what?
What is the destination for "free" FAs (complexed w/ albumin)?
How are some FAs oxidized for energy?
How are FAs critical to life?
What is the correlation between melting point and chain length?
What are the two primary physiological functions of lipids?
A lipid must be long enough that the carbon chain outweighs its ____ end.
True/False: The melting points of fatty acis increase as saturation increases.
True/False: The MP for saturated fatty acids is typically below body temperature.
What two components of membrane lipids and adipose tissue triglycerides are regulated to maintain appropriate fluidity?
The last carbon of a double bond is always considered as the ____ in shorthand nomenclature.
What form do all C=C double bonds take: cis or trans?
What characteristics make trans-FA bad?
Why are "kinks" in fatty acids good for membranes?
T/F: Increasing saturation also increases oxidation.
Which is good cholesterol and which is bad cholesterol?
What does trans-FA do to LDL and HDL cholesterols?
What is the chemical reaction when an alcohol (glycerol) joins a COOH (fatty acid)?
Identify this fatty acid.
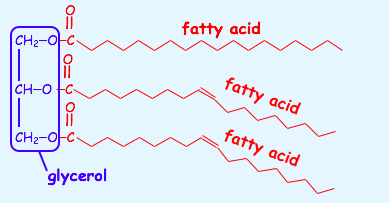
What makes plant oils better than animal fats when cooking?
_____ are esters of long-chain alcohols and long-chain FAs.
What are examples of waxes?
What is special about cetyl-palmitate?
What are other common waxes in nature?
What are 3 ways of assessing obesity?
How do you calculate calories when considering exercise?
What is the respiratory quotient (RQ)? What is the equation and how is it measured?
What is saponification?
What is the chemical process of saponification?
What makes phospholipids a vital component of membranes?
What is the THE defining component of biological membranes?
Name this phospholipid.
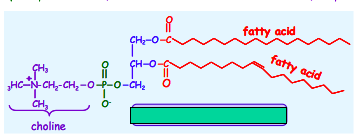
Name this phospholipid.
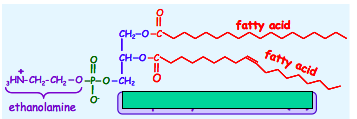
Name this sterol.*
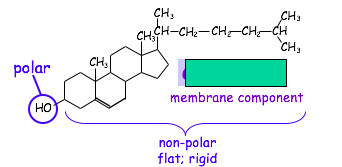
Name this sterol.*
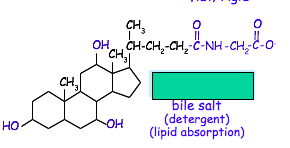
Name this sterol.
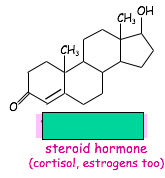
What is it about the amphipathic nature of PL and glycolipids that make it vital to life?
What is a liposome?
How do proteins diffuse?
What is coined as "lipid rafts" in a plasma membrane?
What two carbohydrate chains are specific only to the extracellular portion of a plasma membrane?
What are special proteins (such as PL, cholesterol, and glycolipids) called when embedded in lipid bilayer?
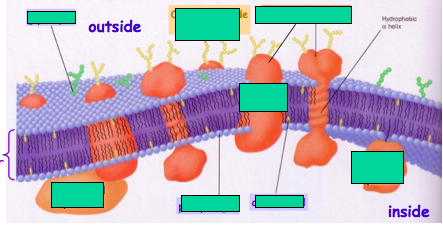
Identify the plasma membrane.
What is a potent "local" hormone derived from AAs in PL membranes via phospholipase A2?
Arachidonic acid can develop into these two eicosanoids (cell-specific synthetases) using cyclooxygenase as enzyme.
Arachidonic acid can develop into this eicosanoid using lipoxygenase as enzyme.
What are a few side effects of eicosanoids?
What enzyme is used for a phospholipid in a cell membrane to develop into an Arachidonic Acid?
How does aspirin/vioxx/celebrex decrease an eicosanoid from progressing into more detrimental forms?
How do hormones act?
Steroid hormones?
Hydrophilic hormones?
What specific omegas are required in the diet?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards