Close

What is the main function of muscle tissue?
What does sarco- refer to?
What does myo- refer to?
Describe the activity of skeletal muscle.
Describe the activity of cardiac muscle.
Describe the activity of smooth muscle.
How do skeletal muscle fibers develop?
_______ cells are the source of muscle regeneration after injury.
_______ fuse to form a skeletal muscle fiber.
Myofibrils contain microfilaments that contain ____ and ____ .
What type of filament is actin: thin or thick?
What type of filament is myosin: thin or thick?
A Z line to Z line makes up a _____ .
____ band is made up of all myosin and a small amount of actin.
Why does the A band have a dark band and a density that causes a darkness to the stain?
This band is made up of all actin, which makes its stain light.
This line is a density of protein that actin binds to on the A band. It's a scaffolding of the entire muscle fiber.
True/False: The Z line changes during contraction.
Coined as the leverage point of the entire muscle.
During contraction, a repetition binding-movement-release cycles between the ____ heads and ____ filaments occurs.
What ion plays a significant role in activation?
Where are calcium sacs stored in the muscle?
What is a triad and what does it control?
What are invaginations of the sarcolemma (plasma membrane) or a membrane-enclosed tube that goes down into the cell hundreds of times within a muscle cell?
Where do T-tubules occur in mammalian skeletal muscle?
What do t-tubules form with two terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
How do triads at each A/I junction coordinate an impulse?
How does an impulse run down the neuromuscular junction?
Describe skeletal muscle:
fibers?
nuclei?
fiber innervation?
Describe cardiac muscle:
fibers?
nuclei?
fiber innervation?
Where do T-tubules run in cardiac muscles?
What is the difference in cardiac muscle t-tubules and muscle cells' t-tubules?
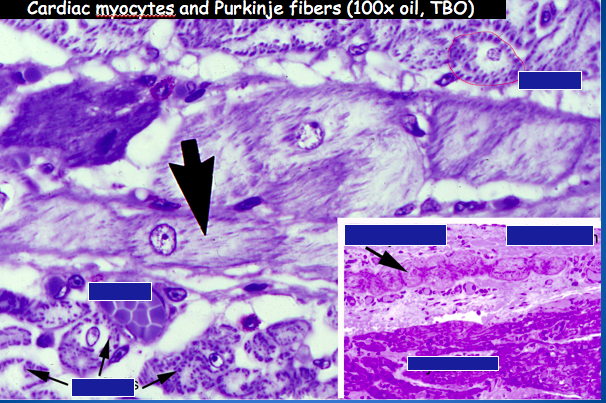
____ _____ are modified cardiac myocytes interconnected by gap junctions (electrical synapses).
Where can smooth muscle be found?
What type of muscle Controls peristaltic motions of tubular structures?
Which part of a muscle cell is responsible for contraction?
The portion of the muscle cell that surrounds each muscle fiber by a small amount of connective tissue created by fibroblasts.
What provides nutrition to a muscle cell?
This layer of the muscle cell surrounds the whole muscle.
This layer of the muscle cell surrounds fascicles and bundles of muscle fibers.
Where is the nucleus in a muscle cell?
This layer of the muscle cell separates muscle fibers.
What functions as the cell boundary in the muscle cell?
In what layer do collagen fibers exist in a muscle cell?
Identify the type of muscle tissue and indicate the stair-steps.
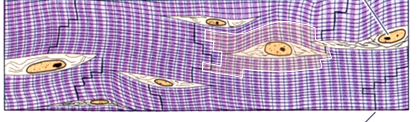
Identify this muscle type and types of sections.
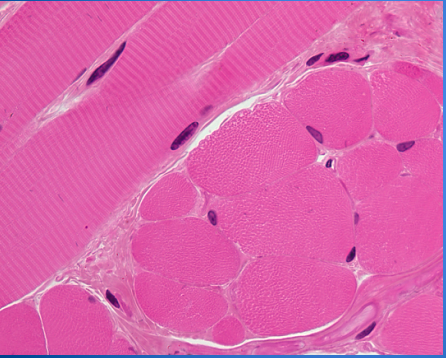
Identify the missing parts of this muscle cell.
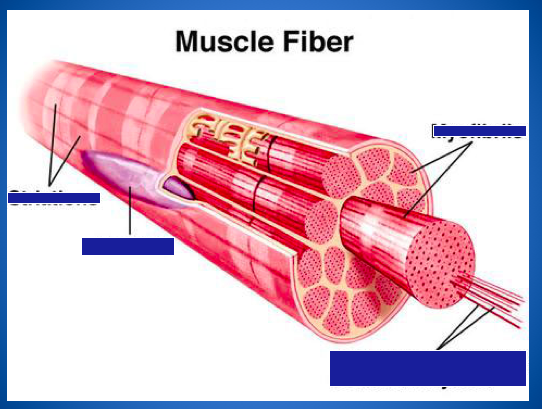
Identify the parts of the muscle fiber.
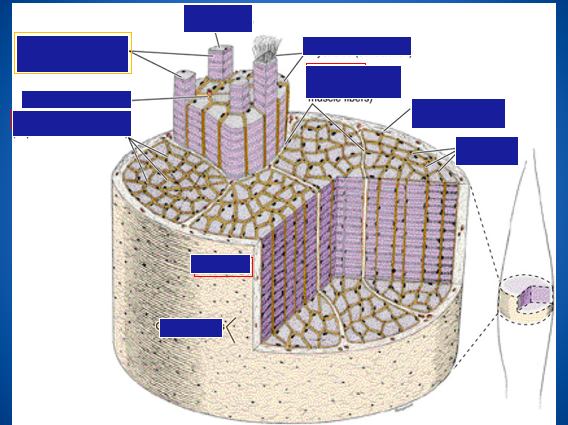
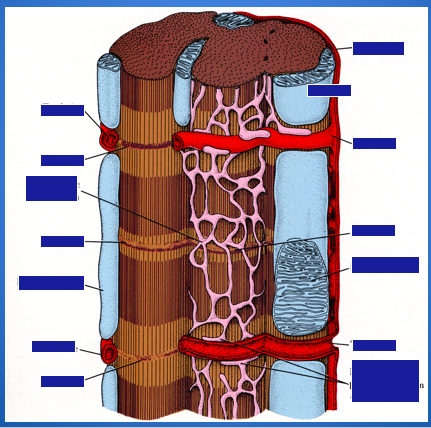
Identify the organization of a skeletal muscle: epimysium, perimysium, endomysium, blood vessels, and capillaries.
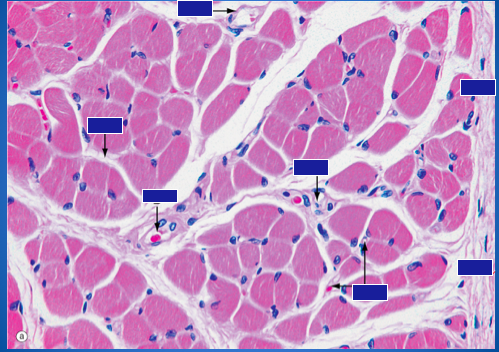
Identify the organization of a skeletal muscle.
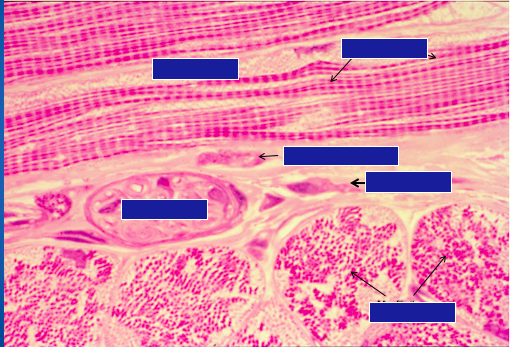
Identify myofibril, nucleus, sarcomere, connective tissue, and fibroblast.
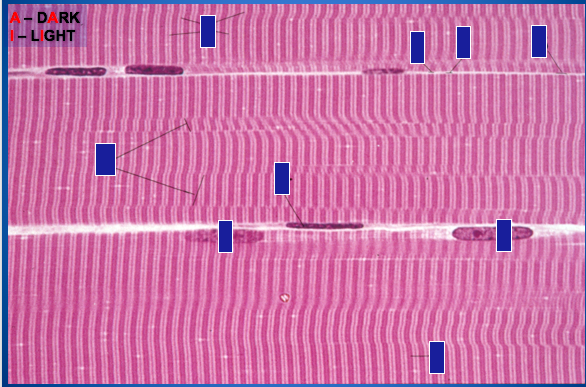
Identify.
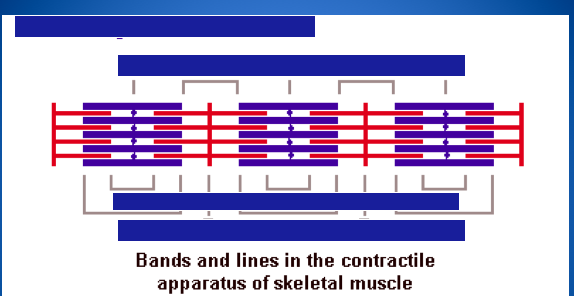
These indicate changes in band widths during contraction. Find contracted, rest length, and stretched.
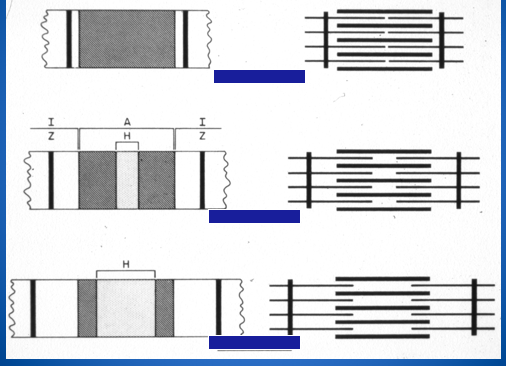
What does this picture indicate and in what type of muscle tissue?
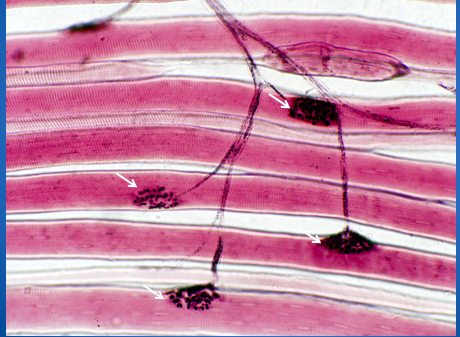
Identify these parts of a skeletal muscle.
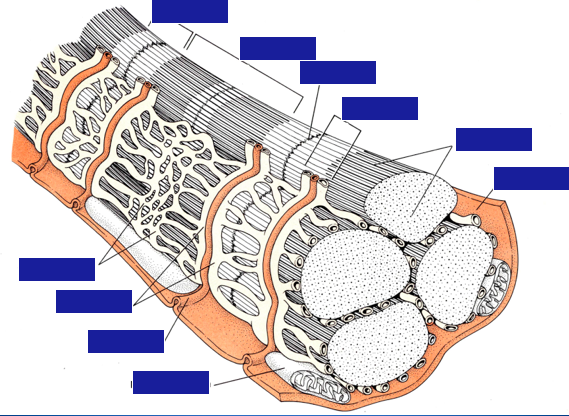
Identify parts of the neuromuscular junction.
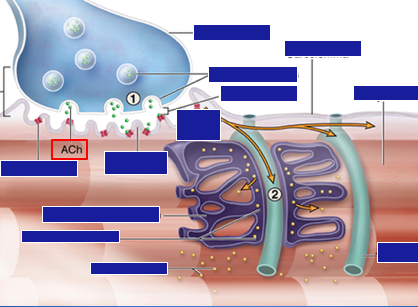
Identify the parts of a cardiac muscle t-tubule system.
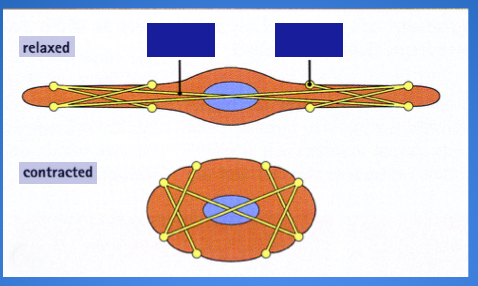
Name the parts of a smooth muscle contraction.
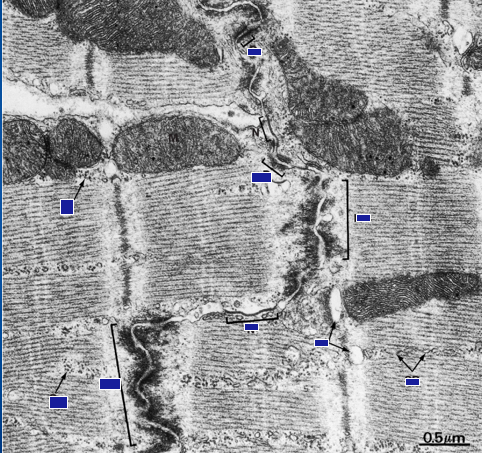
Name the parts of the cardiac muscle associated with intercalated disks.

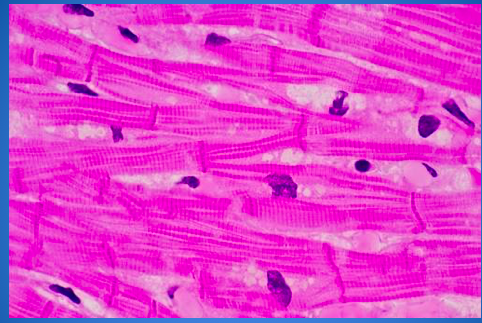
Identify this tissue.

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards