Nursing Flashcards on Lights, Camera, Action! Lab 3- Vision, created by Elizabeth Babcock on 13/07/2017.
Pinned to
40
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Elizabeth Babcock
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Elizabeth Babcock
over 7 years ago
|
|

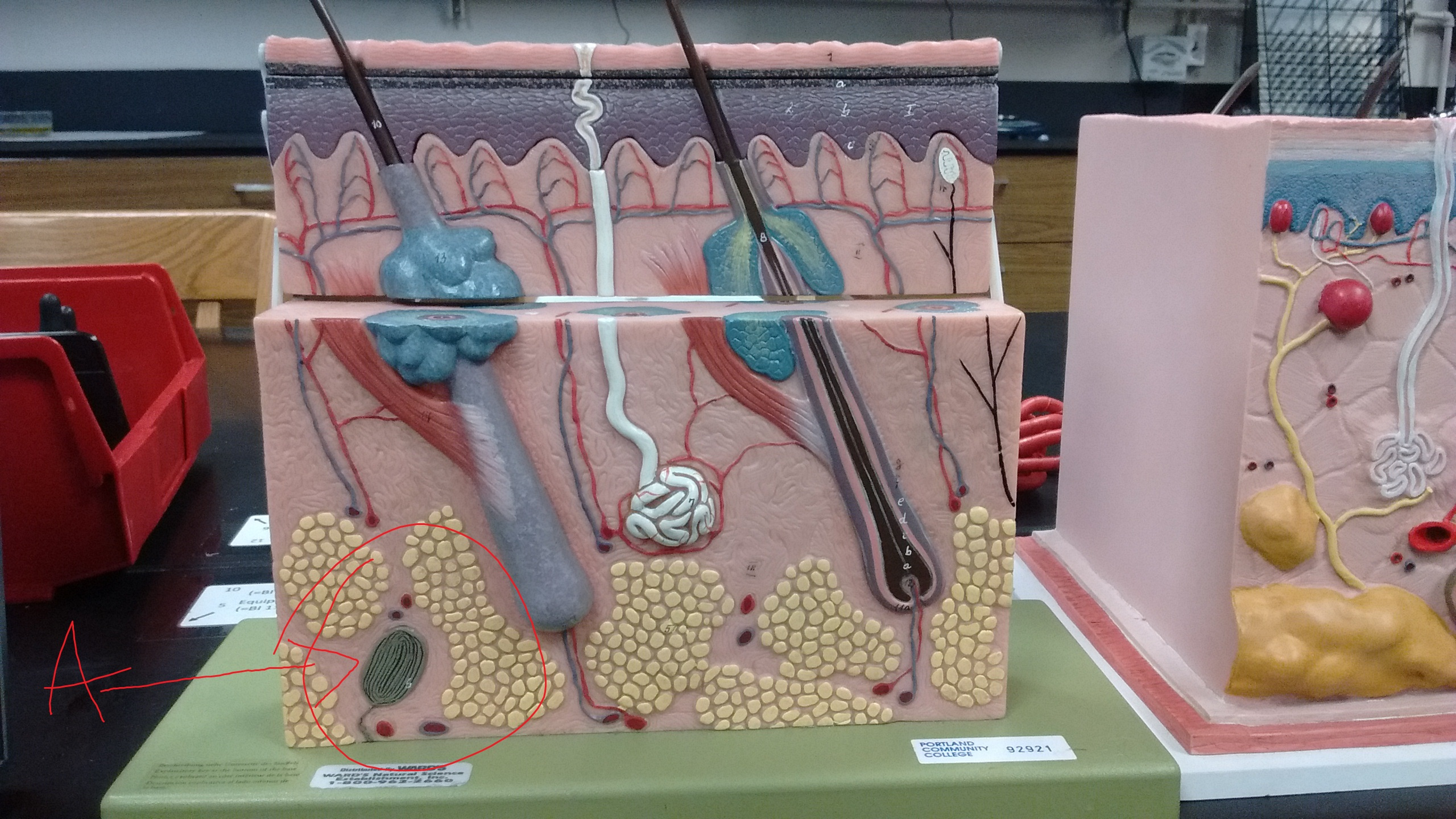
Name the structures

What sysyems? Explain

What is this receptor? Type, stimulus detection? Where is it found?
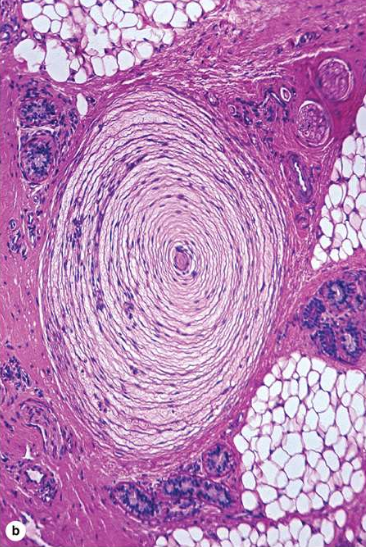
What is this receptor? Type, stimulus detection? Where is it found?
What is this receptor? Type, stimulus detection? Where is it found?
What is this receptor? Type, stimulus detection? Where is it found?
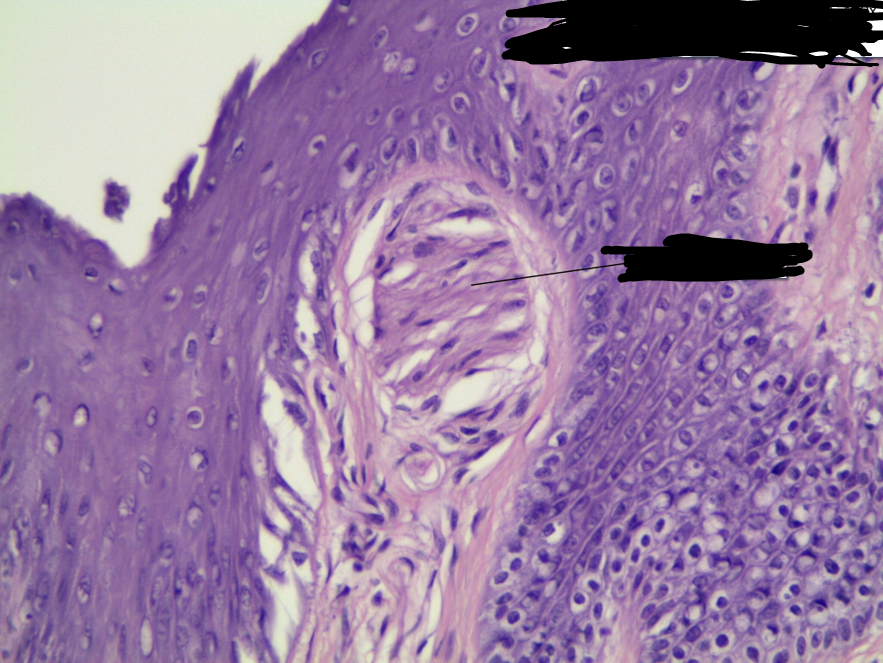
How does the density of heat receptors correspond to that of touch receptors? What about cold receptors?
What do calipers test for?
Which areas have the smallest distance from 2pt discrimination? Which has the greatest?
Put your hand in 45 degree C water. What sensation do you feel?
What external anatomy is a transparent mucous membrane. Lines eyelids and covers anterior side of eye except the cornea. Prevents eye ball from drying
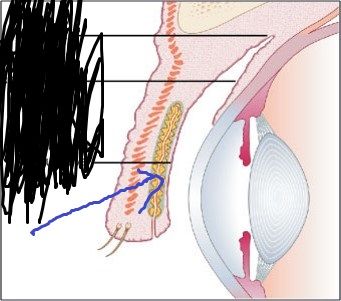
What is the site of tear production? Where are they drained?
Name 1 function of tears
What enzyme prevents the infection?
Fibrous Tunic (2)
Type of Tissue. Function. Innervation
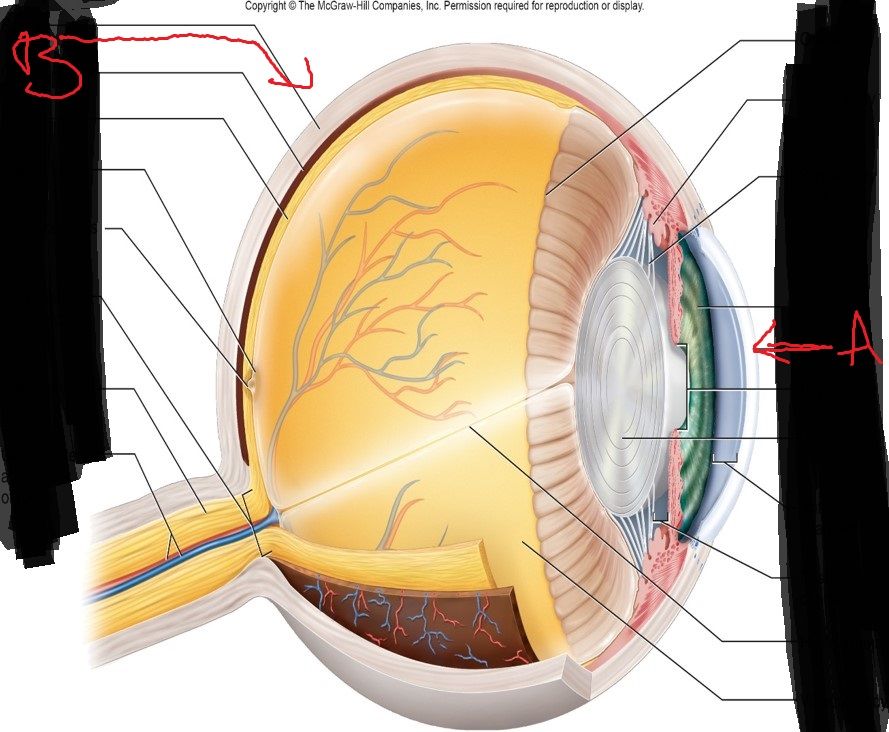
Vascular Tunic (5)
Which tunic? What does it contain?
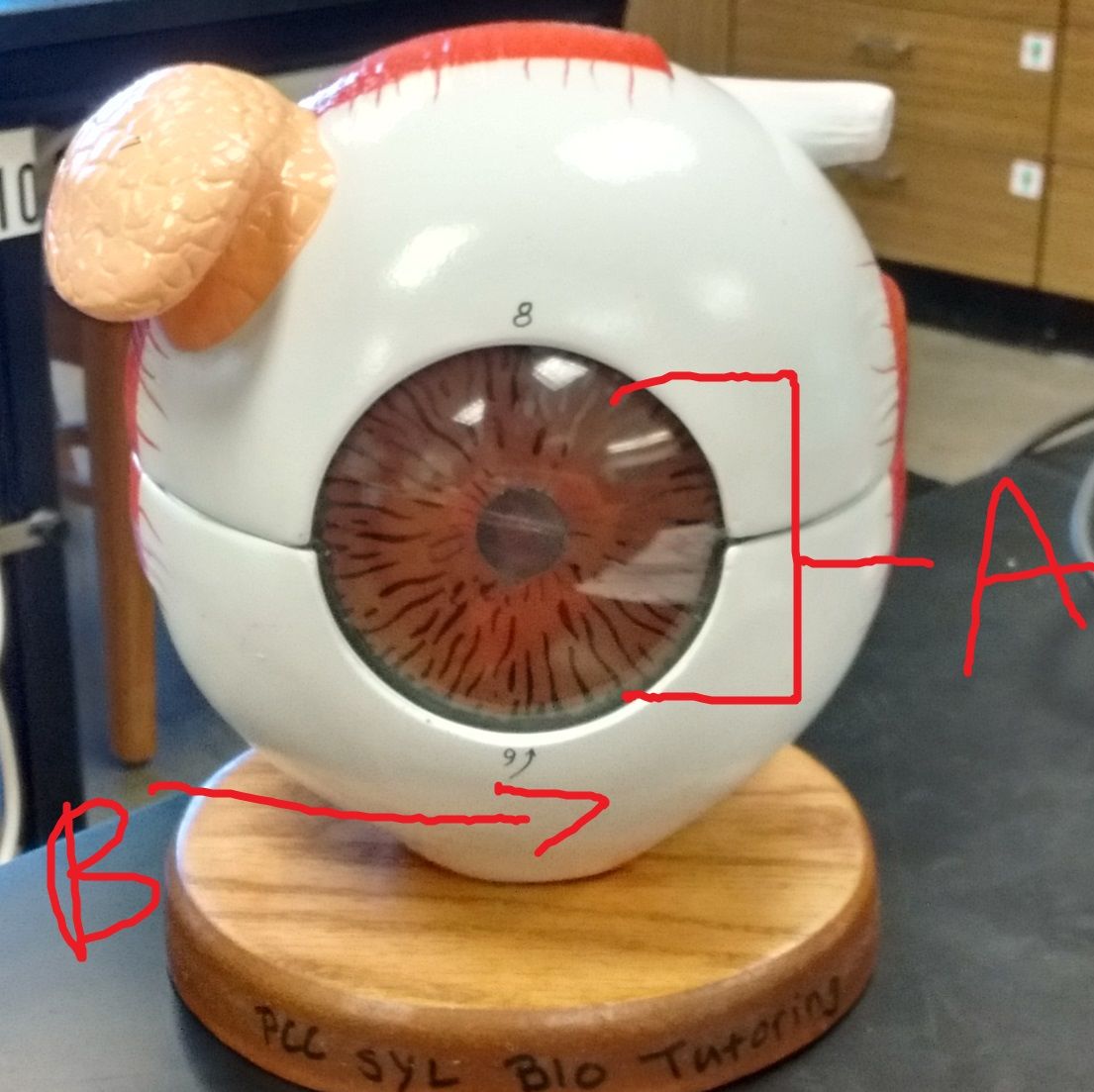
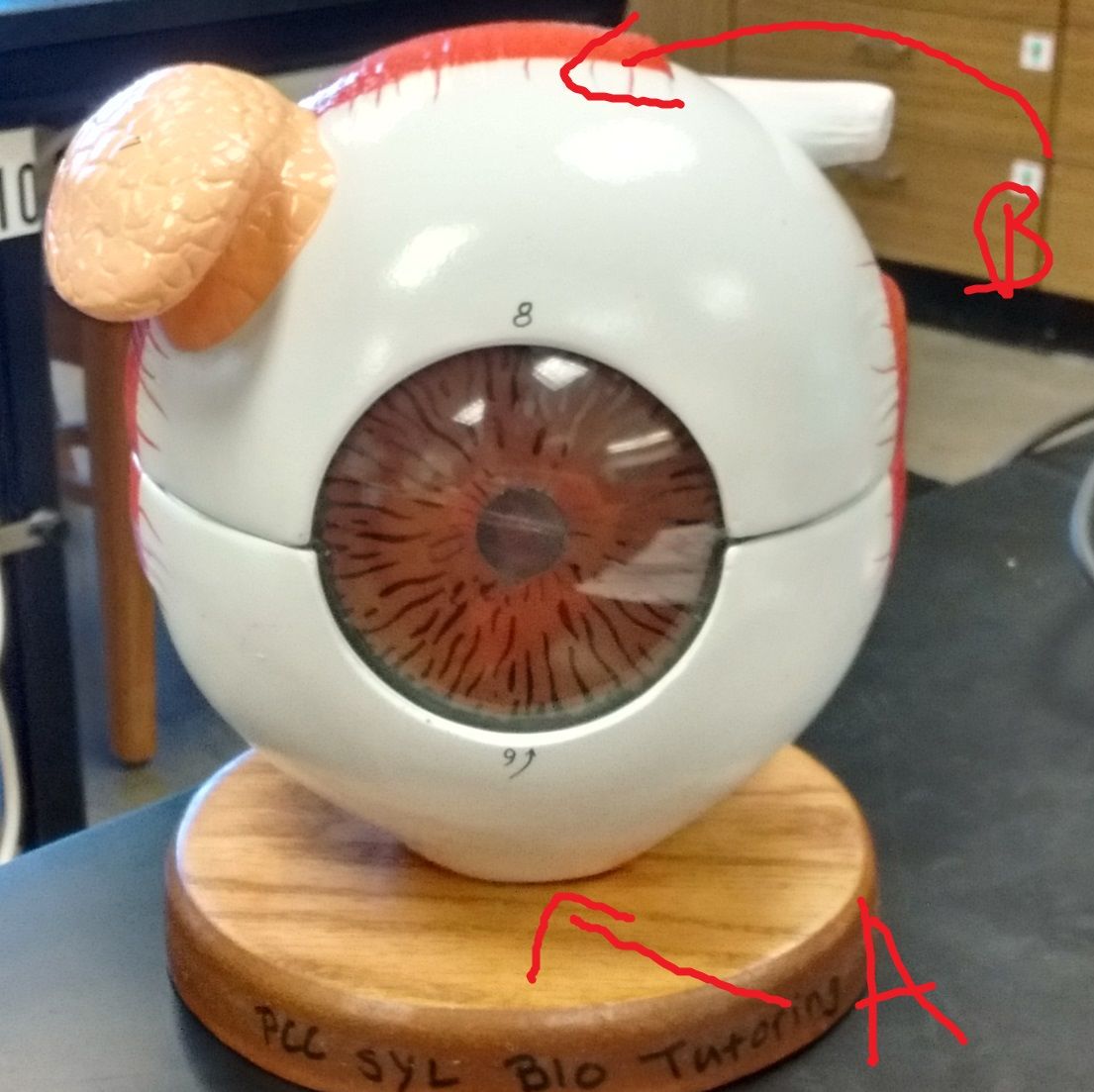
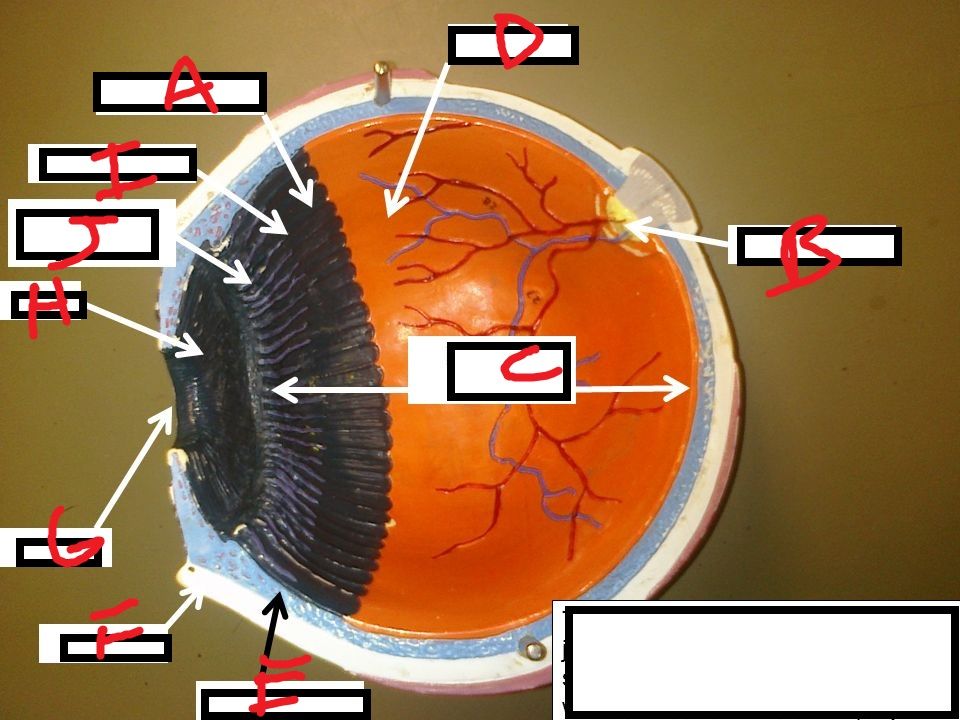
What is A? Function/Structure? Innervation? Attachment?

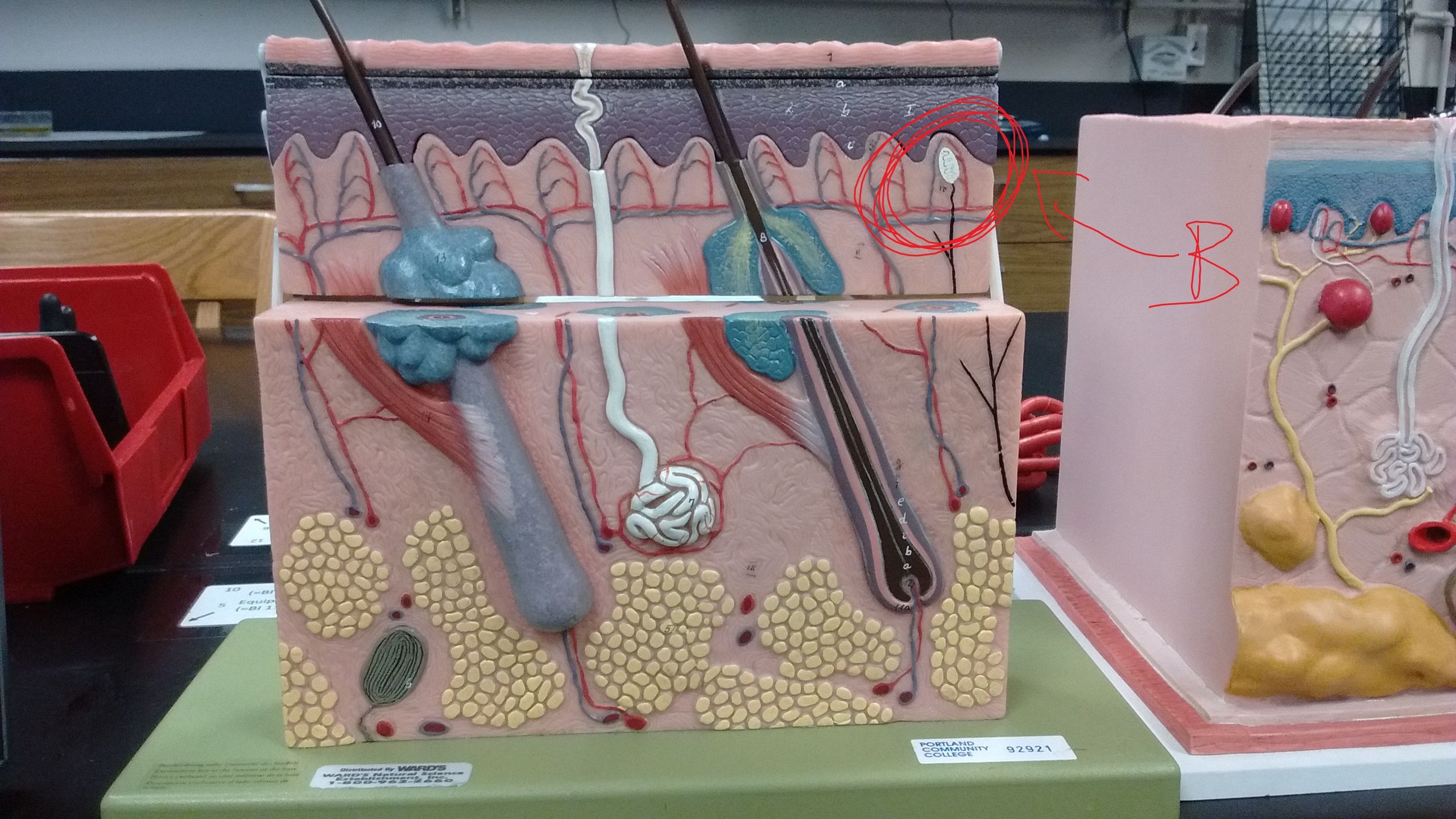
What is B? Function/Structure? Innervation?

What is C? Description. What is it held by? Function?

What layer is this? Name what each is
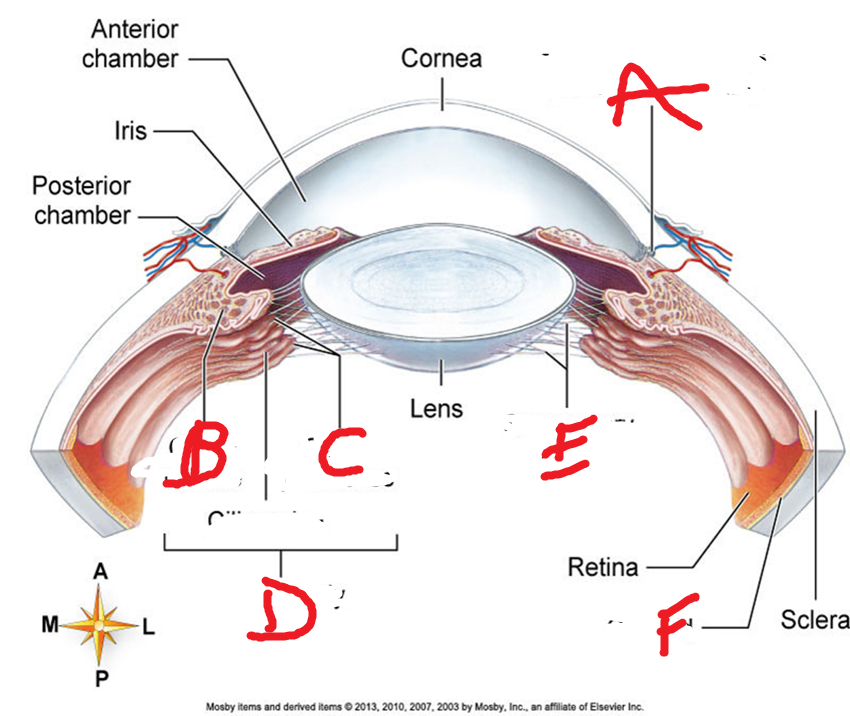
What are B,C,D, E? Functions?

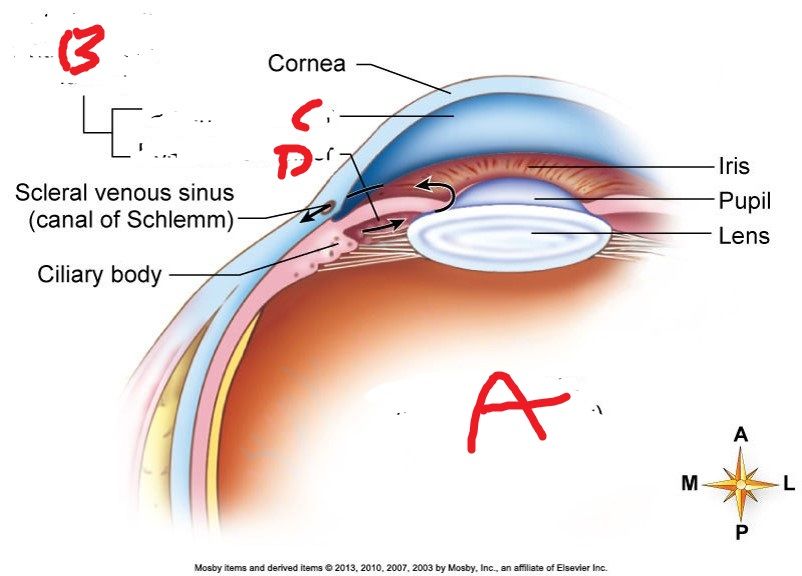
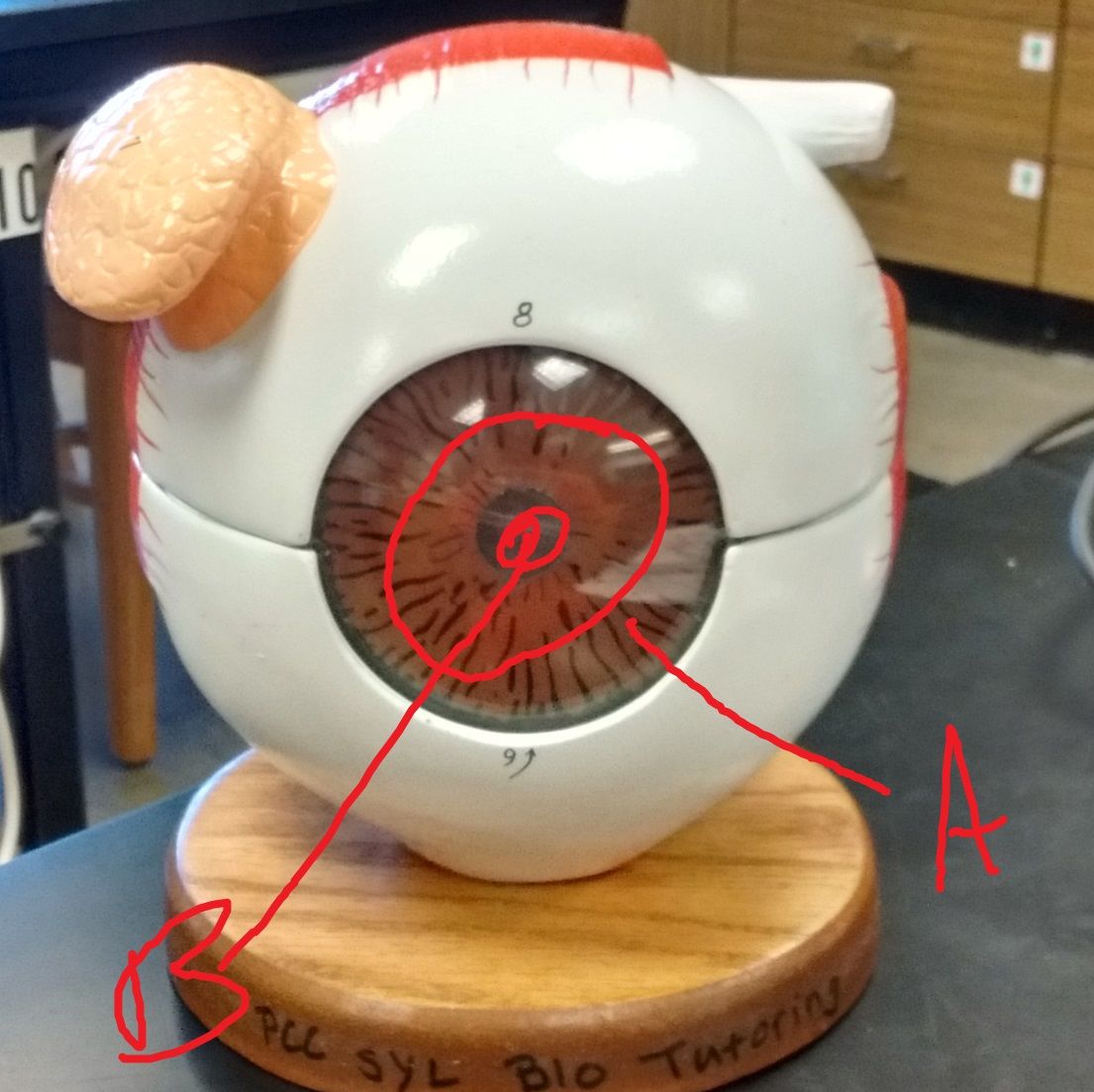
Which structure secretes aqueous humor? What tunic?
What are the autonomic reflexes of the pupil?
What is F? Structures? Function

Which structure provides nutrients to retina and contains melanocytes and blood vessels of the eye? Which layer?
What layer is the Retina? What its layers? Where does it attach? What happens if it detaches?
What are the 3 layers of the sensory retina?
What is the Fovea Centralis?
Optic Nerve (II), Function, and location
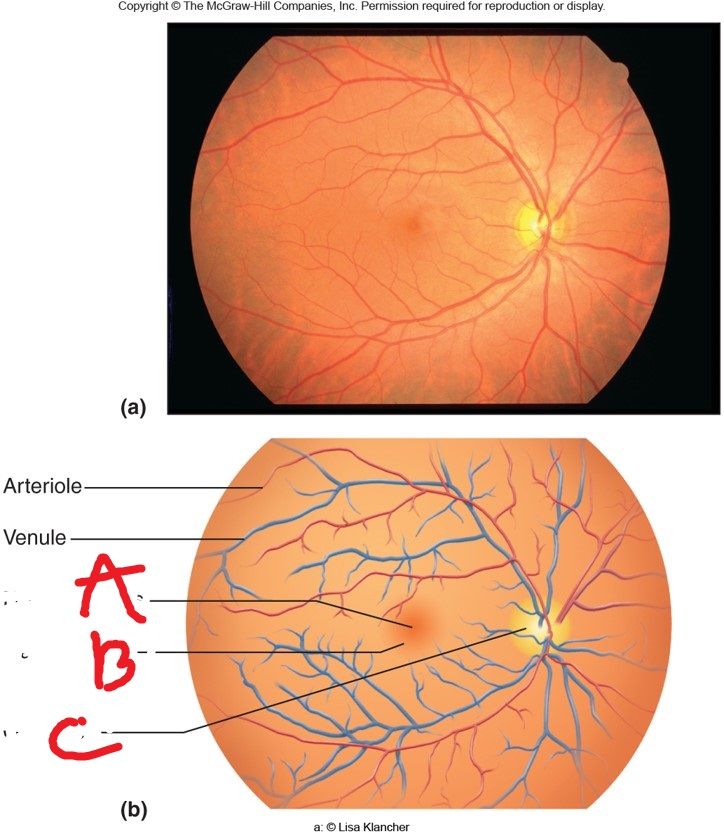
Optic Disc: Location and what it creates.
Central retinal artery and vein. Function
What is A,B,C. Fu
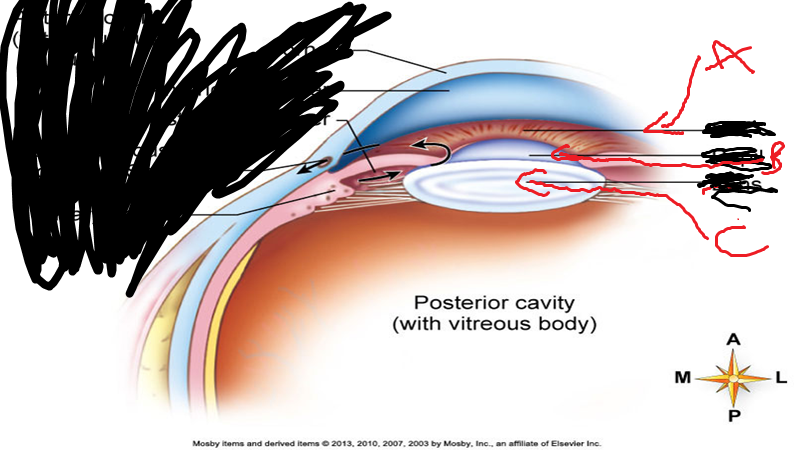
Which cavity is filled with a jellylike substance?
What is A,B,C,D? Location?
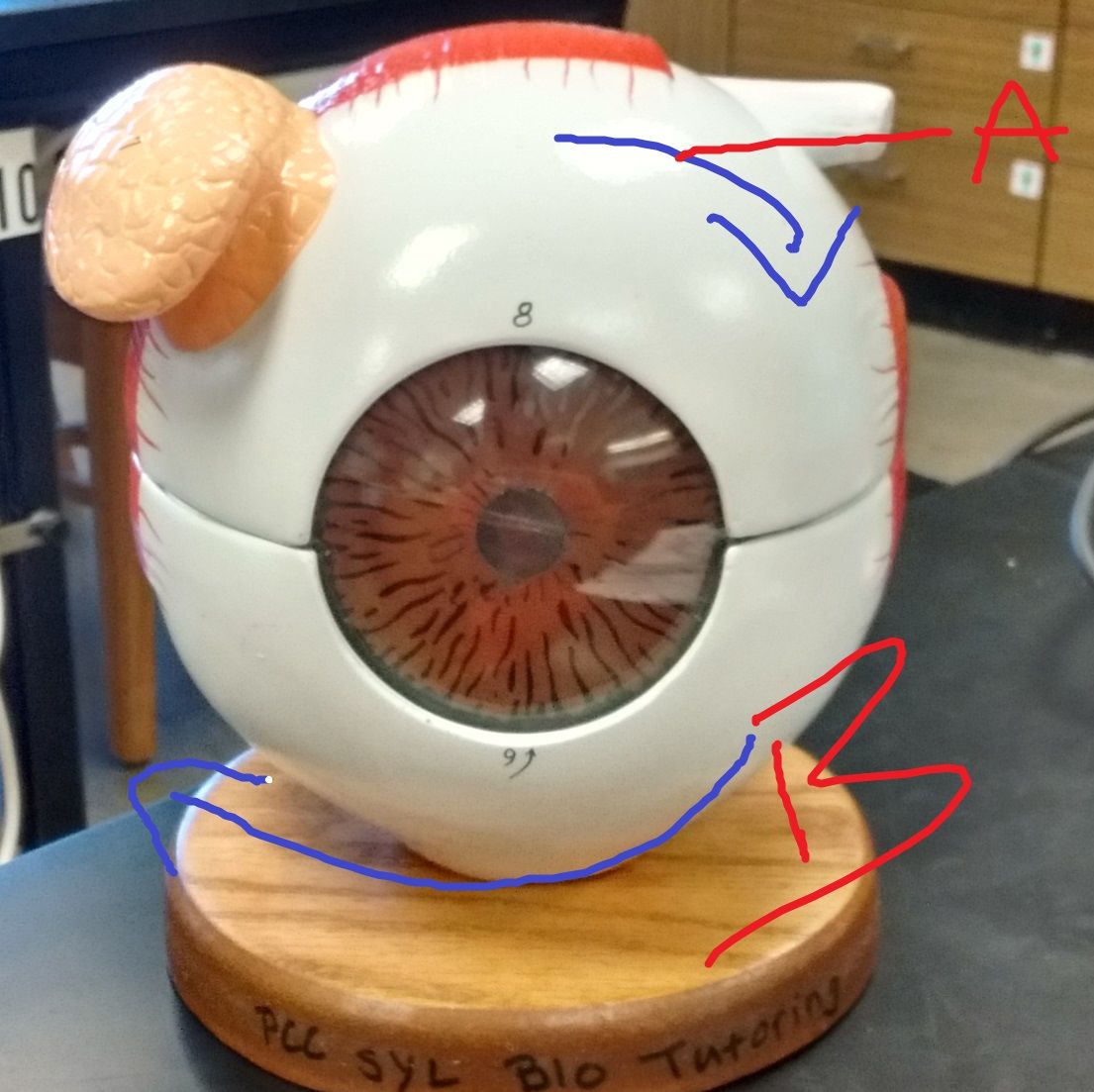
Name the extrinsic eye muscles
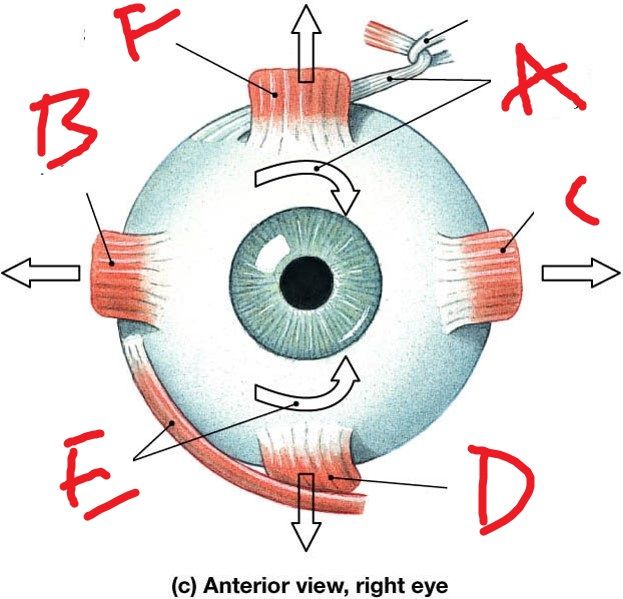
Name what A,B,Care Describe the eye movements. and CN that enervate each
What are the 2 intrinsic muscles of the eye? What are the functions? What tissue are they made of?
What are the muscles of the iris? What fibers innervate them? In what situations would they involved in?
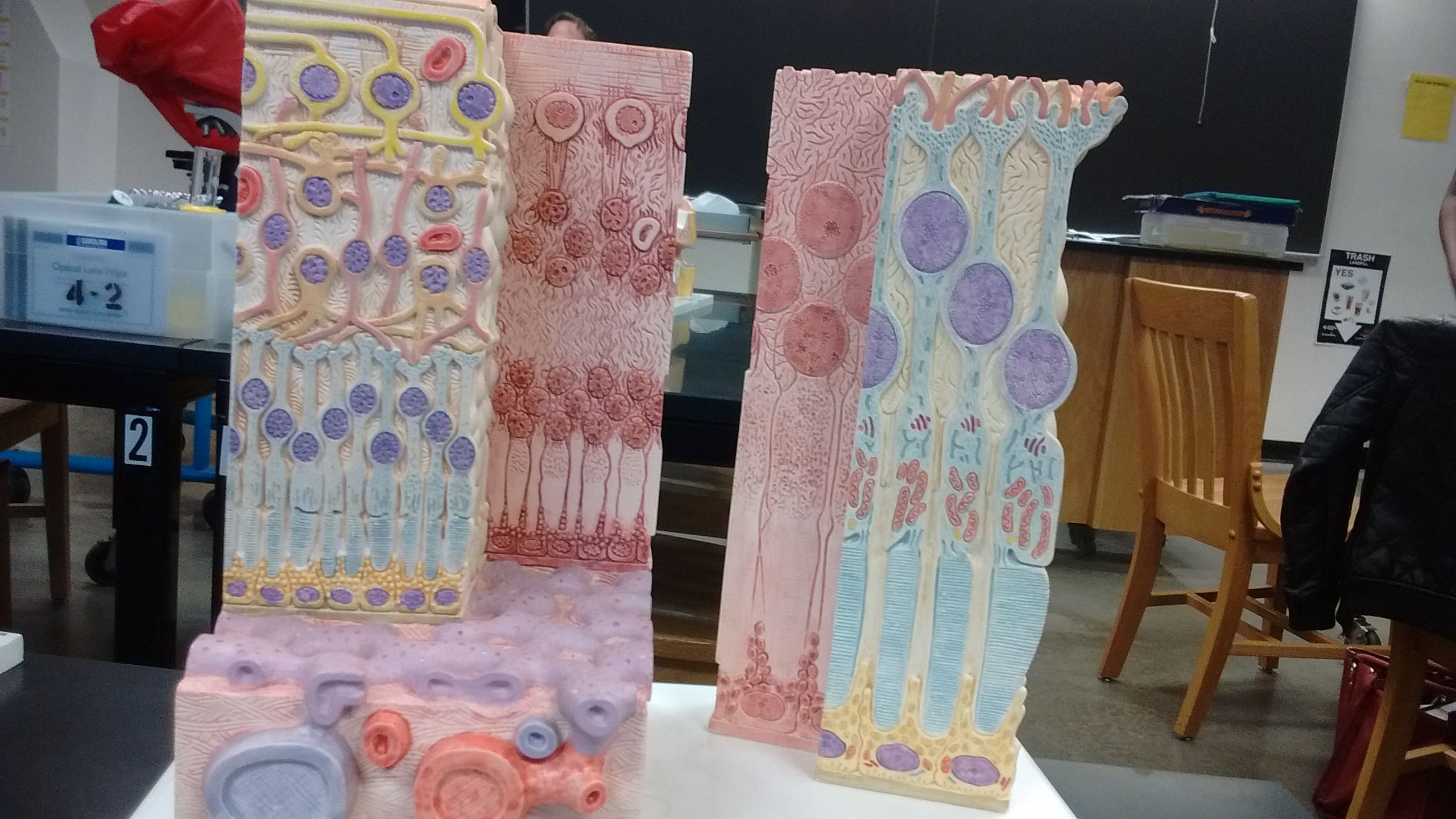
Histology of the Retina. Name the layers.
What is the blind spot? Why does the image disappear?
What are the 2 afterimage definitions?
What is the photosensitive pigment of rods? Why bleached?
What are the photoreceptors that detect color? What about responsible for vision in low light?
What is color blindness?
Night Blindness, difficulty seeing in low light
What is the bending of light rays?
What refracts more light anterior to the eyeball?
What does light pass thru? What is the end point of which it hits?
Specific point of intersection on the retina
Distance between the center of the lens and its focal point
Focal distance is determined by what 2 factors? What makes for shorter and greater focal distances?
Define Accommodation
Lens accommodation for near objects and distance objects. What happens to the ciliary muscle?
Normal vision
Eyeball is too deep or curvature is too great. Focal point is in front of retina. What visual dysfunction is this? How is it corrected?
Eyeball is too shallow or the curvature of lens is too flat. Focal point is behind retina. What visual dysfunction is this? How is it corrected?
Corneal surface is wavy, parts of image out of focus
What tests for visual acuity? What is normal? What is better? 20/15 or 20/30?
What is sensation?
What are the somatosensory vs special sense receptors?
Identify each number
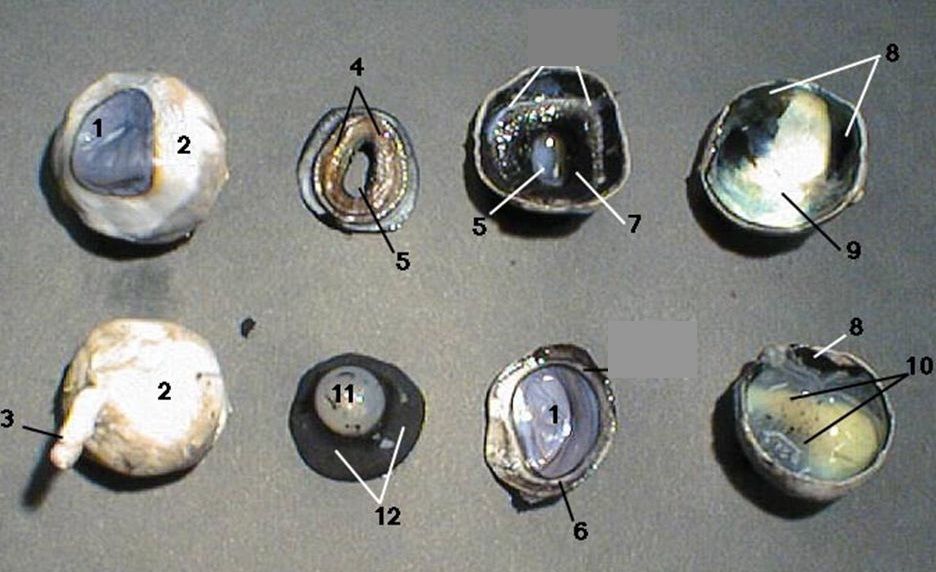
Identify
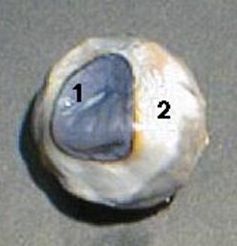
Identify

Identify

Identify

Identify

Identify
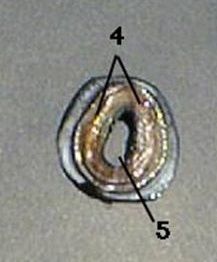
Identify
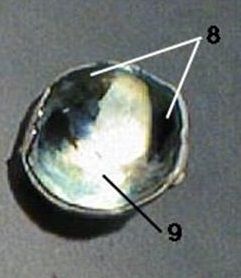
Disease: Blood Shot eyes. Inflammed
What fills the cavity of the posterior chamber posterior to the lens of the eye?
What fills the cavity anterior of the lens in the anterior chamber of the eye?
Chylamidia conjunctivitis
sympathetic ophthalmitis
Neonatorum
Strabismus ---> Amblyopia (Kids) and Diplopia (Adults)
Hyperopia
Disorders of the retina
Myopia
Nerves for Vision
What nerve carries visual impulses from rods and cones to the brain?
What does the Opthamamic branch of trigeminal nerve V do for the eye?
What nerve supplies lateral rectus, intrinsic eye muscle?
What does Trochlea IV supply?
What nerve supplies voluntary and involantary motor impulses?
Name these structures. Function/insertion

Name these structures. Function/insertion/ direction

Name these structures. Function/insertion

Name these structures. Function/insertion
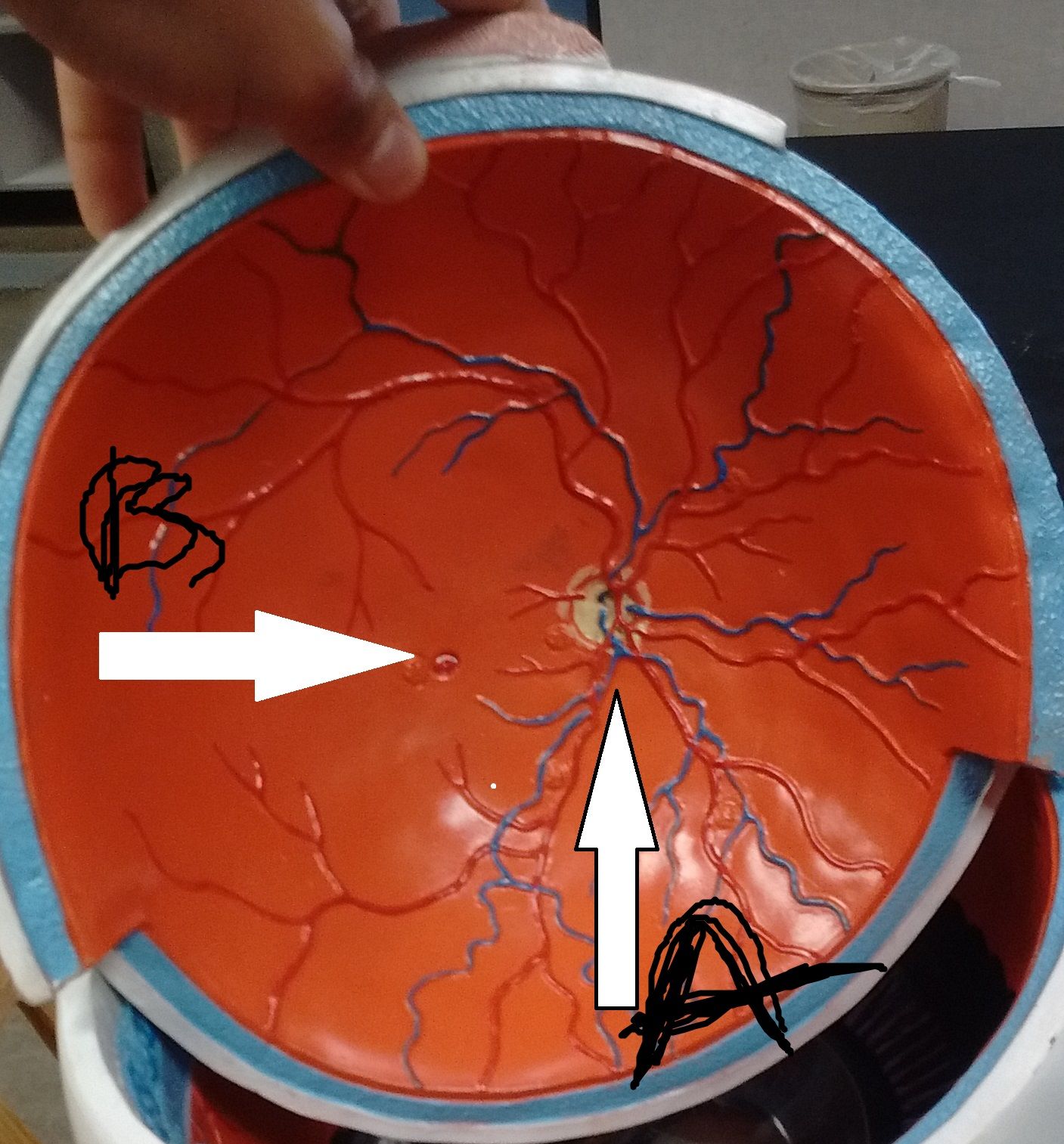
Name this structure Function/insertion
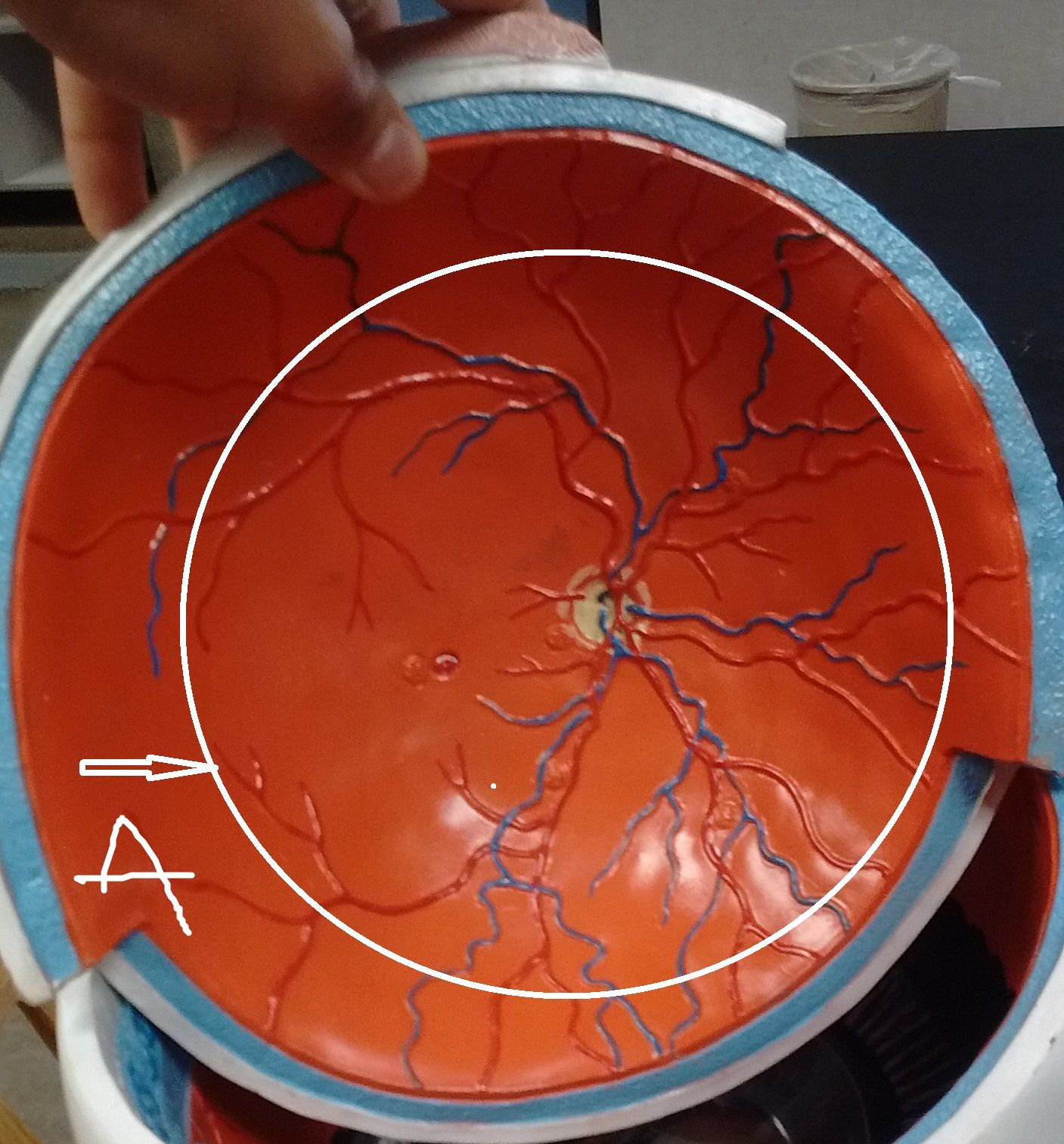
Name these structures
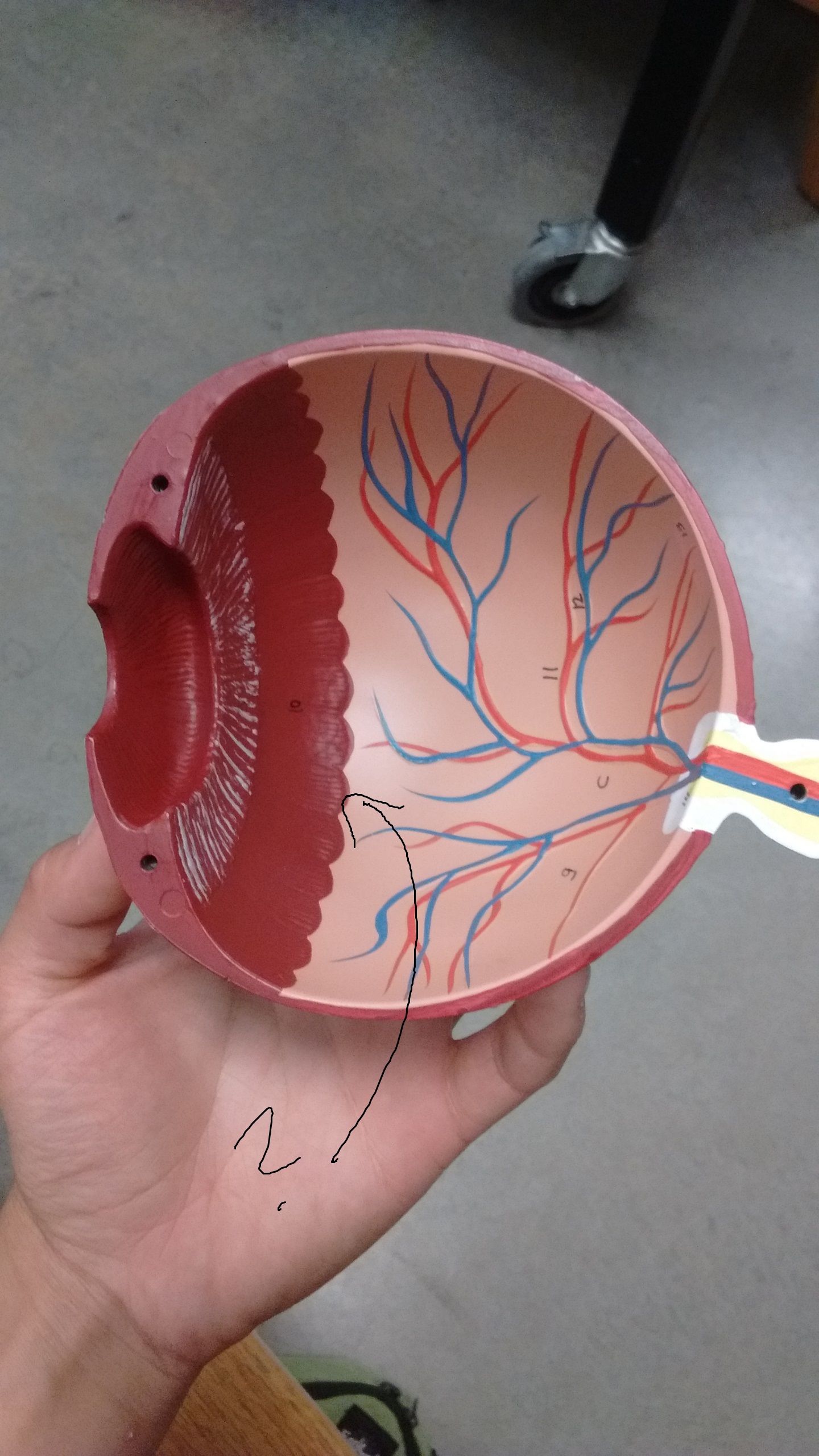
What can you see with an ophthalmoscope? (4) including retina
What is this a representative of? Explain it

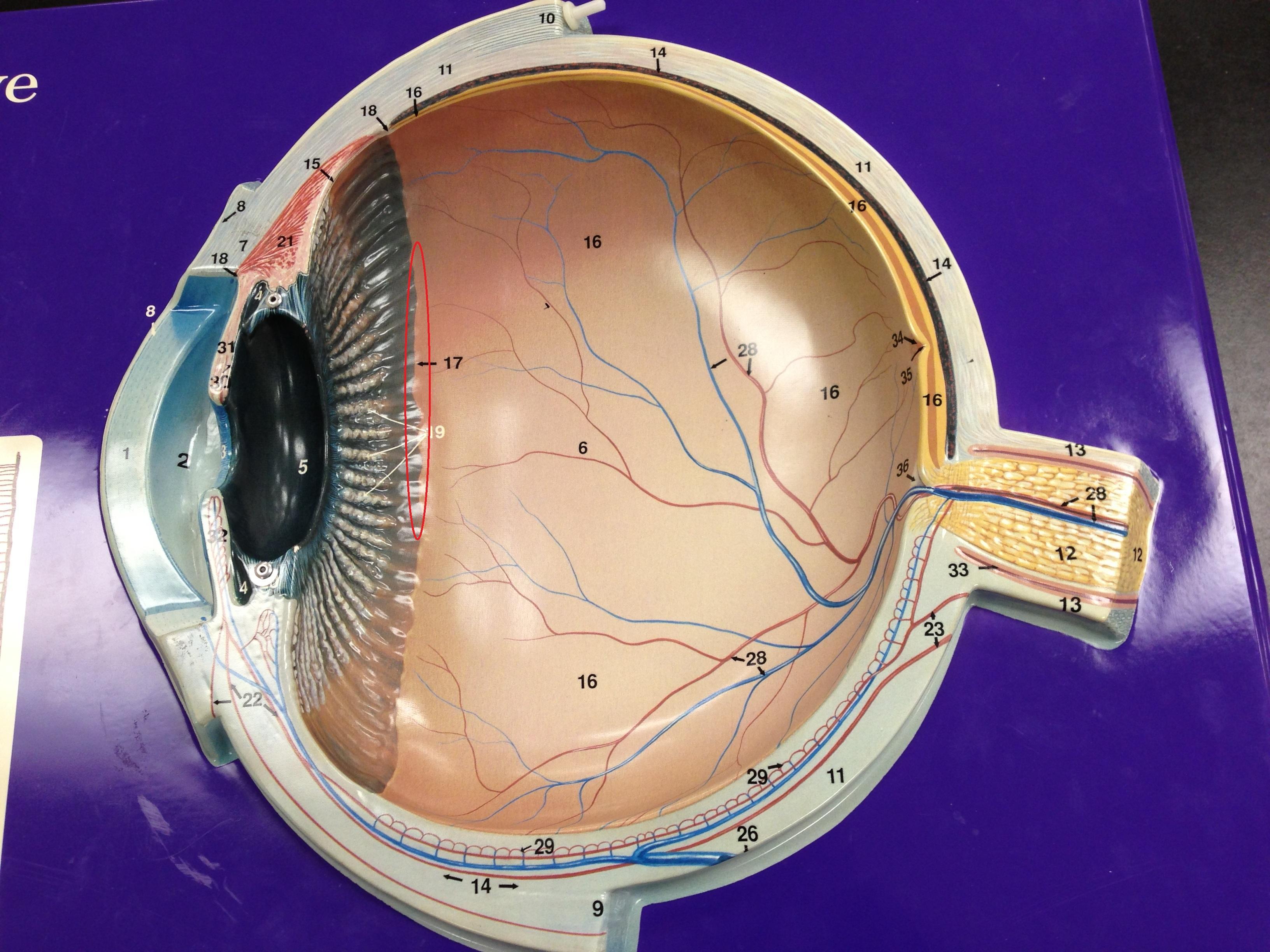
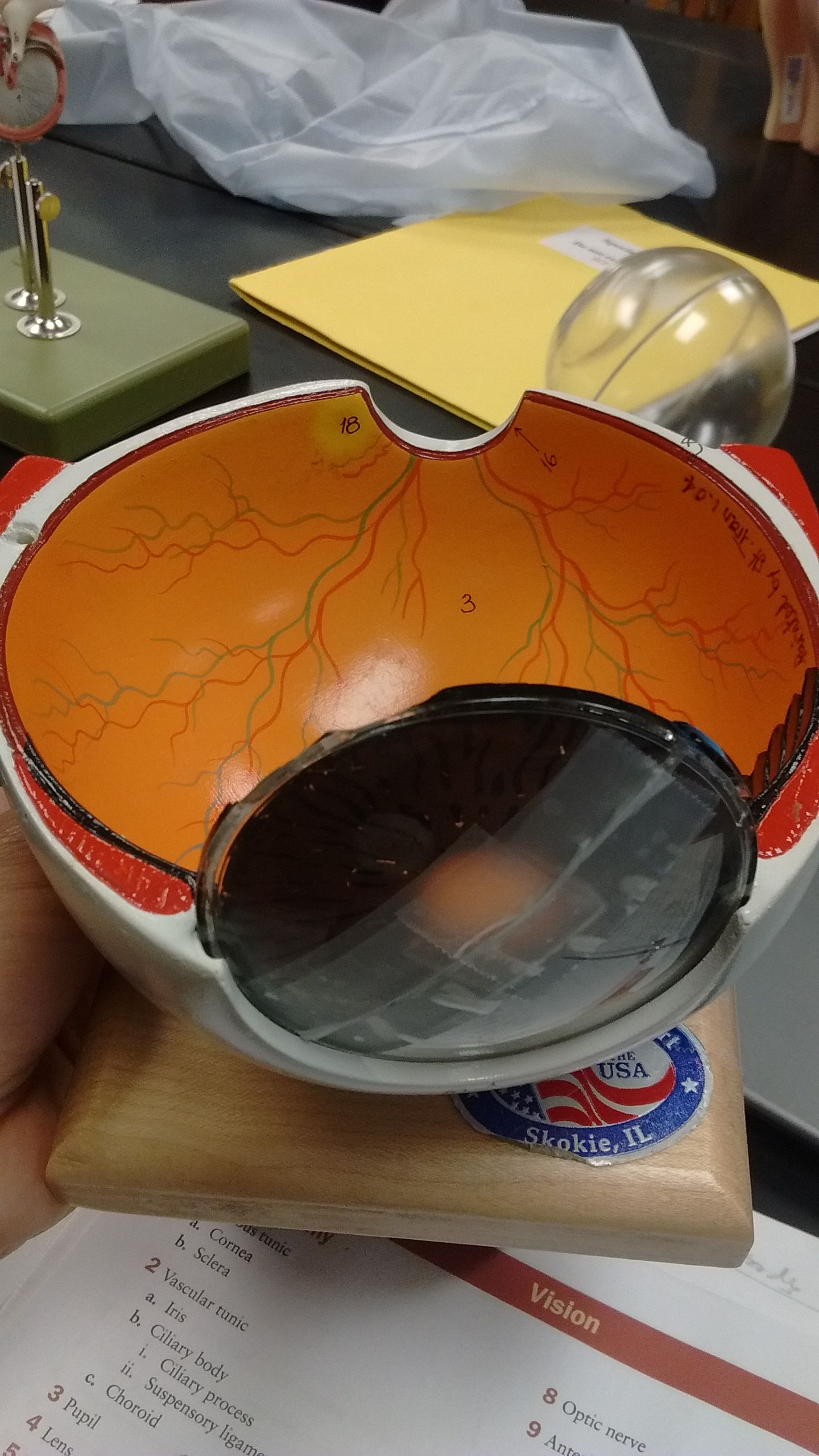
Identify the numbers

Circular muscle fibers contract in bright light to shrink pupil. Postganglionic parasympathetic fiber
Radial muscle fibers contract to dim light to enlarge pupil. Postganglionic sympathetic fibers
What collects aqueous humor from the anterior chamber and delivers it into the episcleral blood vessels via aqueous veins
D,E,F. Describe the eye movements. and CN that enervate each

Scotopic vision
Photopic vision
What are the parts of Rhodopsin? The moieties?
What are the parts of Cones?
How do you generate an optic nerve signal? Night and day scenerio
Identify
Identify and what does it contain?
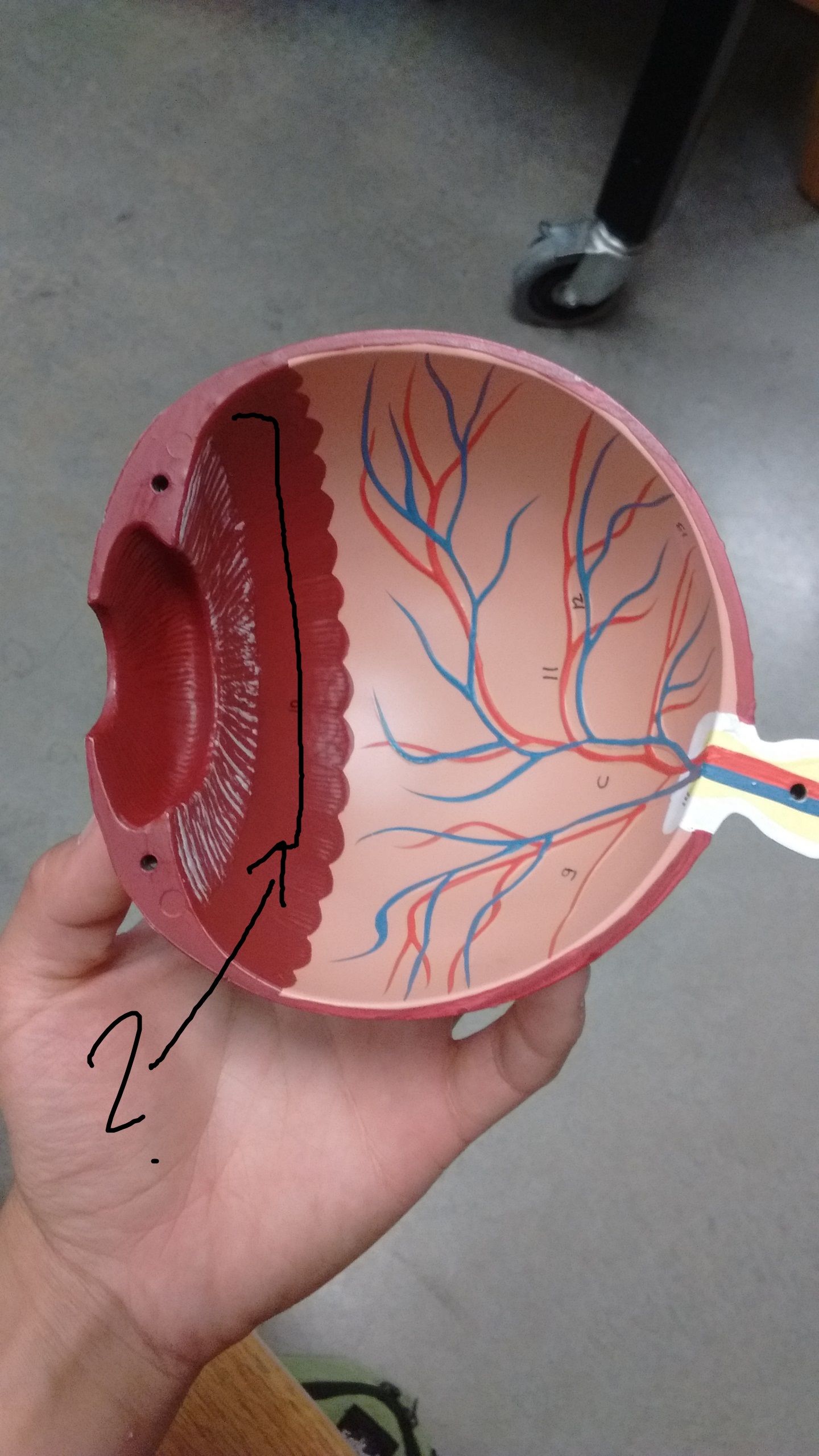
Identify and function
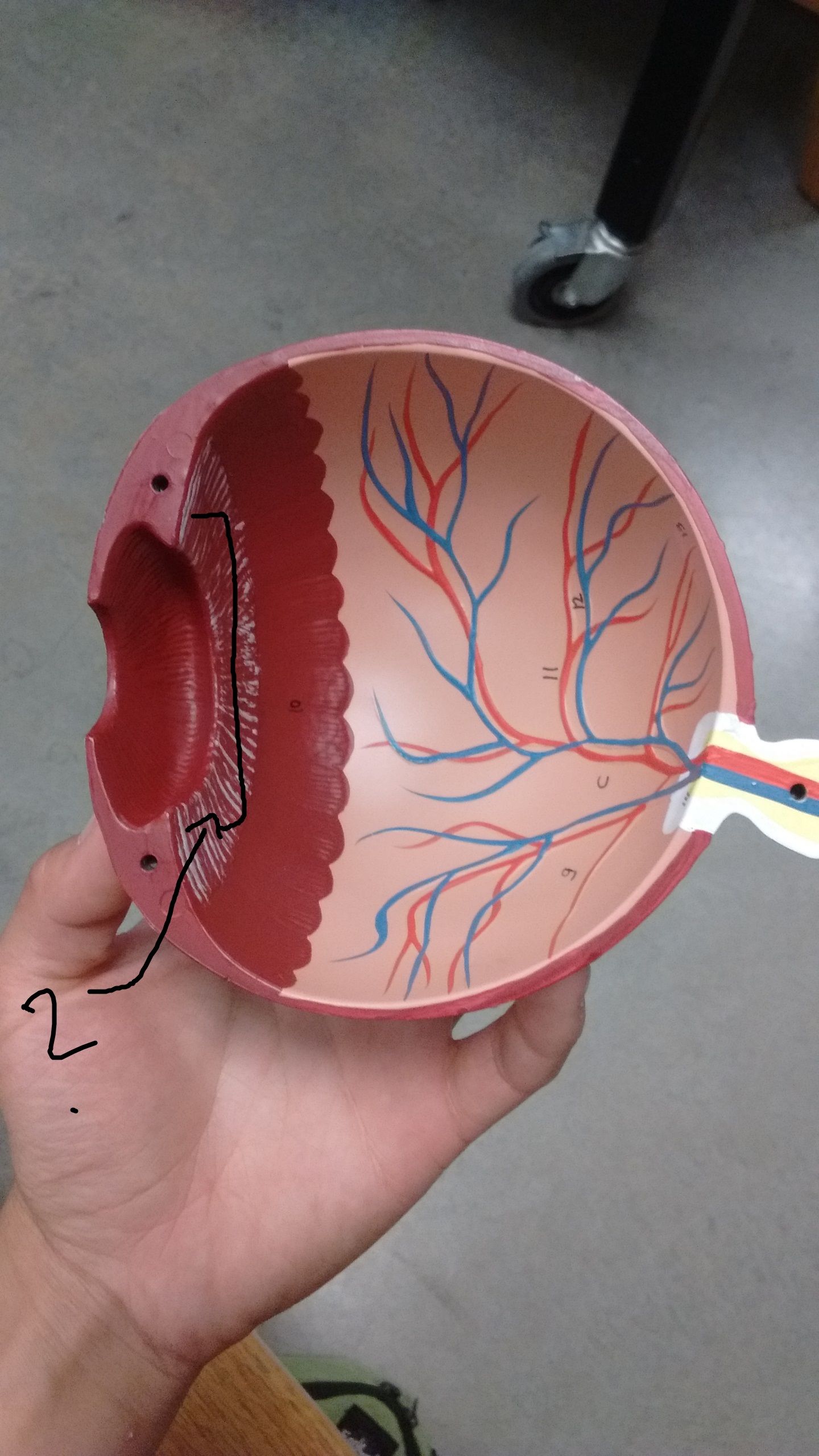
Identify and function
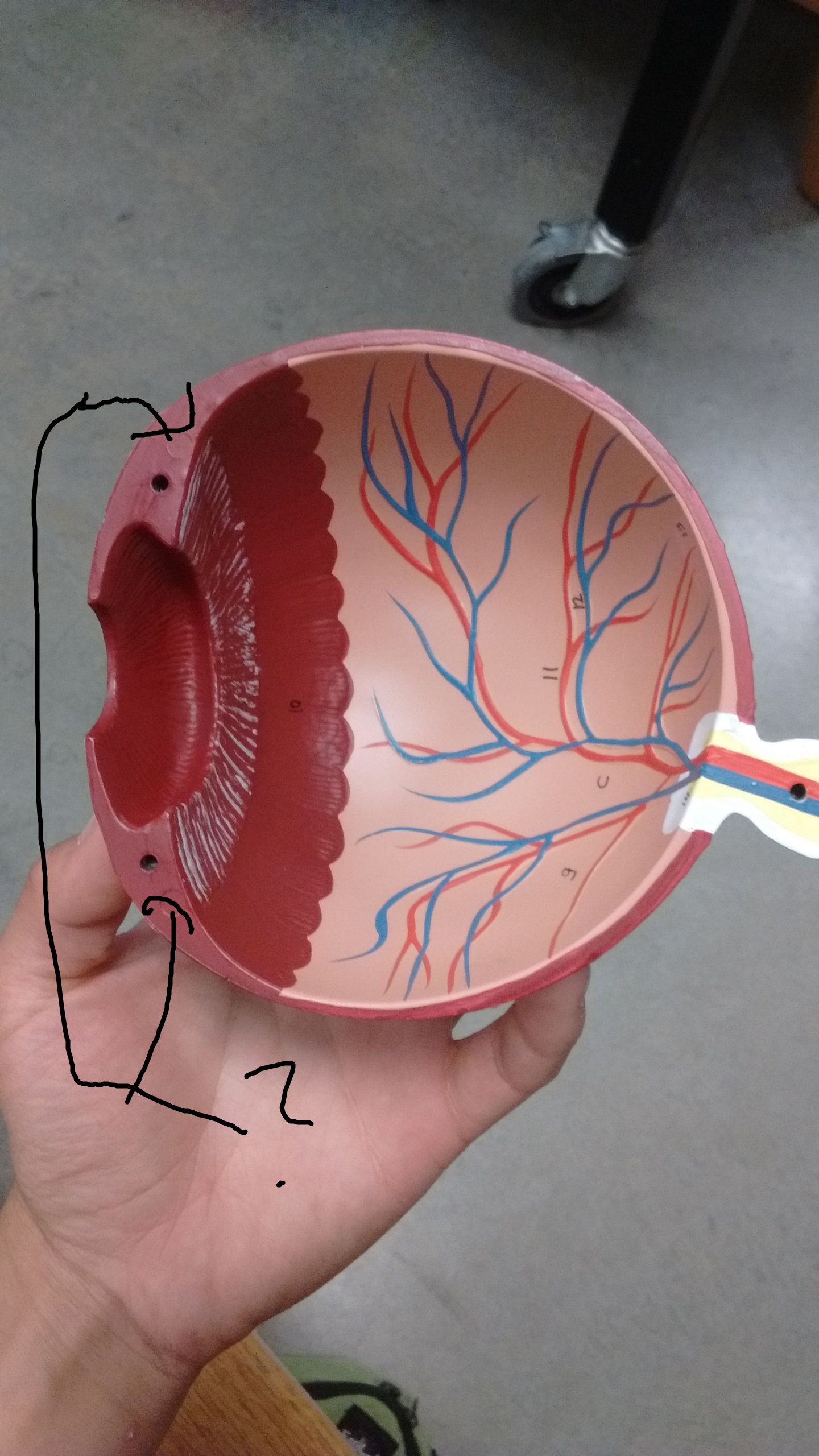
Identify and function
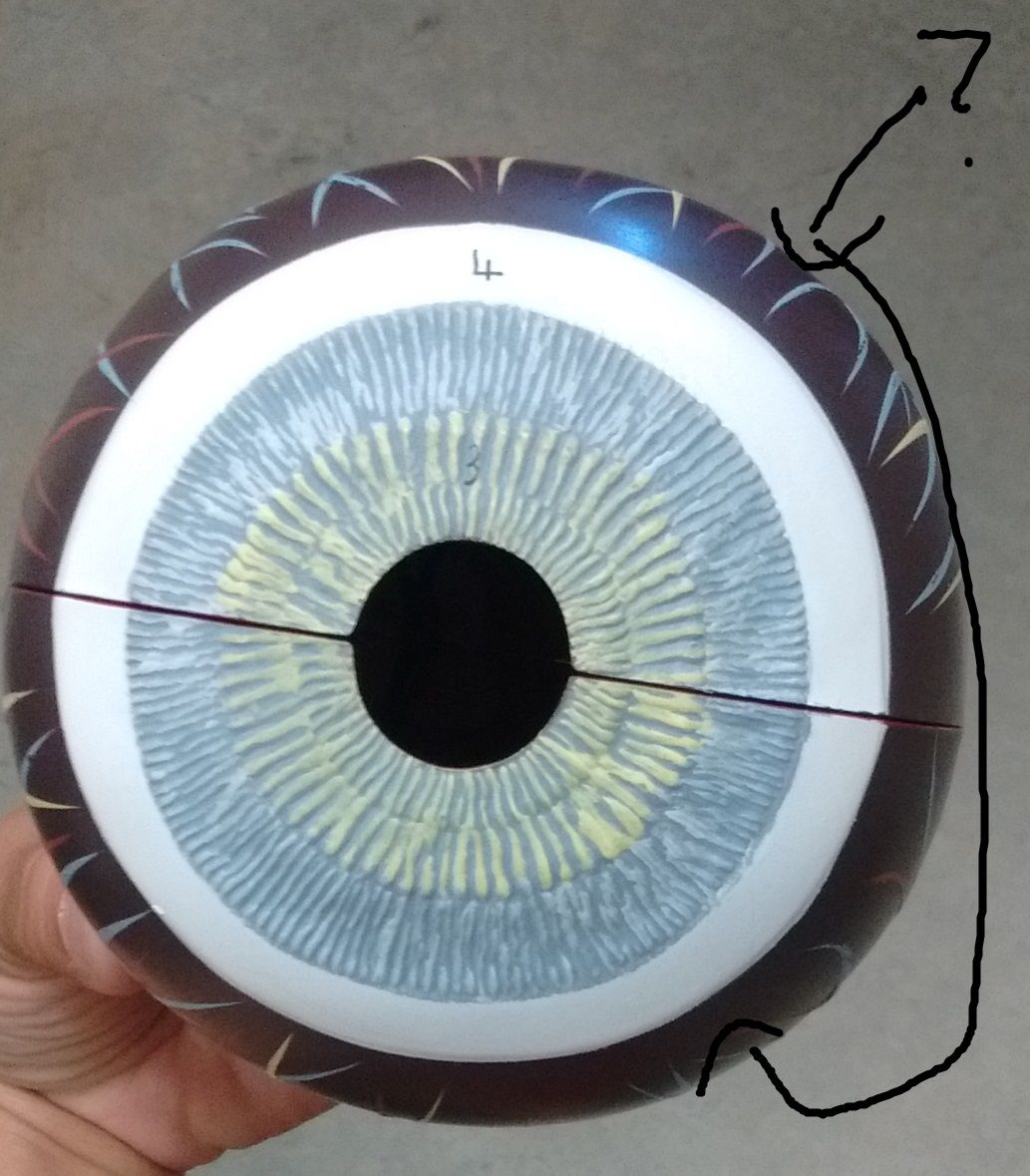

Identify and function
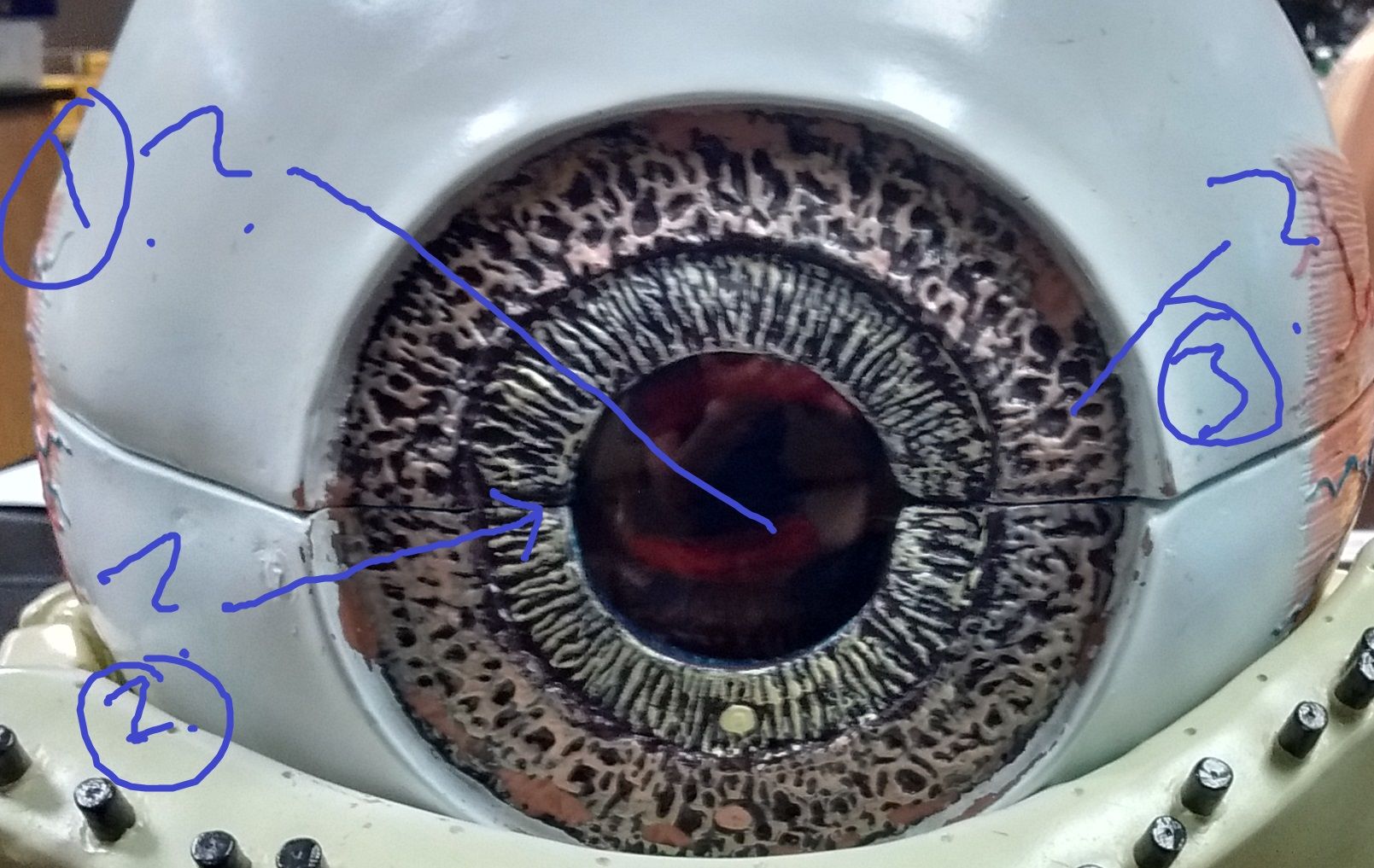
Identify and function
Eyelids - what it is separated by and where they meet
What gets swollen when you have a cold? What duct?
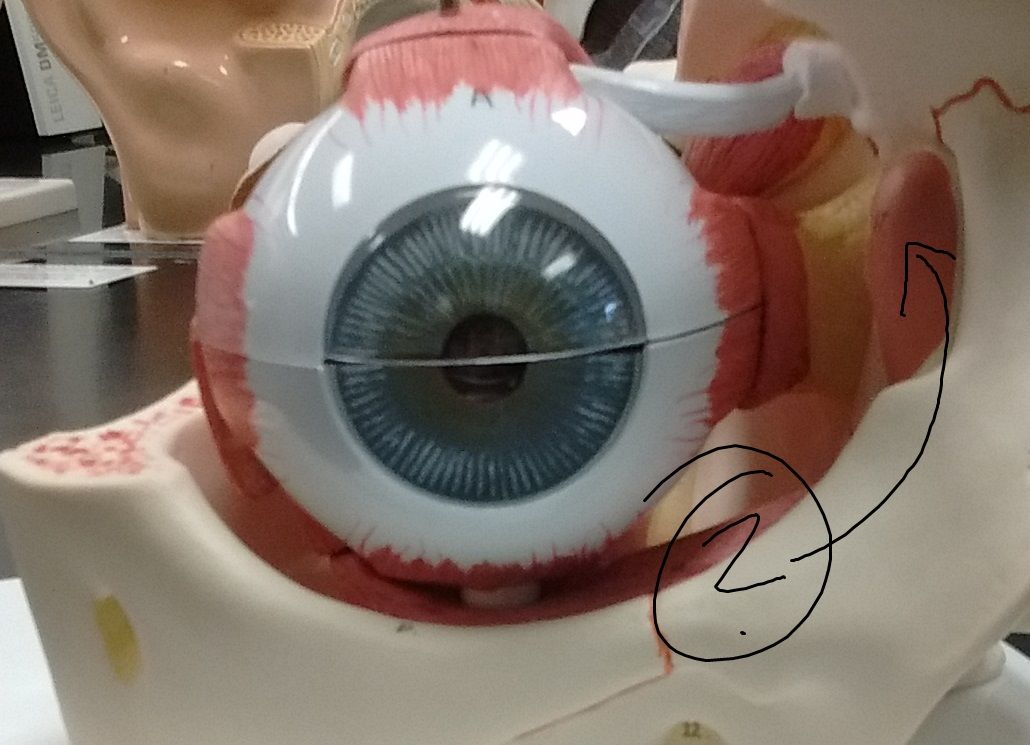
What tendon inserts on the superolateral area of the eye?
What gives the iris it's black, brown, hazel color? What about blue, green, gray?
What is the pupillary constriction in response to light? To admit less light in
Explain the 3 processes for near response?
Description of Rod vs Cone and it's moeities. Bleaching and regeneration
Retinal circuitry and veisual sensitivity
The visual projection pathway

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards