Contents are from Uptodate, First aid and UW
Pinned to
38
0
0
|
|
Created by Mohamed Saad
over 7 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Mohamed Saad
over 7 years ago
|
|

Meningitis is defined as inflammation of the ----- matter of the brain?
Which of the following is the main mechanism of meningitis?
a. Hematogenous spread from a mucosal surface (nasopharynx)
b. Direct extension from a parameningeal focus (AOM, sinusitis, orbital cellulitis)
Majority of organisms
causing bacterial meningitis originate in ------
Most of agents causing viral meningitis are transmitted by:
1. Respiratory rout
2. Feco-oral route
The MCCs of bacterial meningitis in neonates are ------?
MCCs of bacterial meningitis in infants and children > 1 month?
Mention the most likely bacterial pathogens in the following scenarios:
1. Meningitis in asplenia patients
2. Meningitis in patients with complement deficiency
3. Meningitis in basilar skull fractures
4. Meningitis in patients on excess steroids
5. Meningitis in patients with absent opsonizing antibody
6. Meningitis in HIV patients
7. Meningitis in patients with bacteremia/endocarditis
The MCC of community-acquired bacterial meningitis in adults is ----?
The major causes of healthcare-associated bacterial meningitis are ---------? .
Which factors predispose to L. monocytogenes meningitis?
Give the potential causative agent in each of the following scenario:
a. Meningitis after exposure to rodents
b. Meningitis after exposure to ticks
c. Meningitis after exposure to mosquitoes
d. Meningitis after sexual activity
e. Meningitis after contact with other individuals with viral exanthems
f. Meningitis + VII palsy
Causes of aseptic meningitis?
Choose between encephalitis and meningitis?
1. HSV-1
2. HSV-2
3. Rabies
4. Enteroviruses (echoviruses, coxsackieviruses, poliovirus)
5. West Nile virus
6. CMV
7. VZV
8. EBV
9. HIV
10. Infleunza virus
11. Measles and mumps viruses
MCC of bacterial meningitis in infants and children > 1 month?
Mention the most likely bacterial pathogens in the following scenarios:
1. Meningitis in asplenia patients
2. Meningitis in patients with complement deficiency
3. Meningitis in basilar skull fractures
4. Meningitis in patients on excess steroids
5. Meningitis in patients with absent opsonizing antibody
6. Meningitis in HIV patients
7. Meningitis in patients with bacteremia/endocarditis
The classic triad of meningitis include ---?
What is Brudzinski's Sign?
What is Kernig's Sign?
Signs of Meningismus are --------?
Which of the following is more sensitive for meningitis?
A. Brudzinski's sign
B. Kernig's sign
C. Jolt accentuation of headache
Meningitis in neonates can cause hypothermia
a. True
b. False
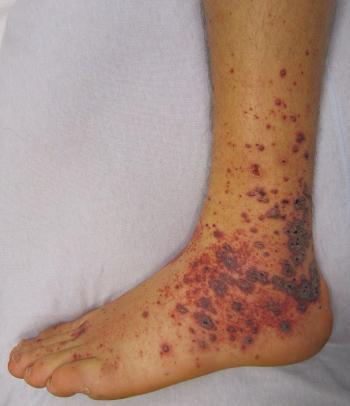
A patient with meningitis developed these skin lesions.
What is the most likely causative agent?
Hyponatremia in patients with meningitis can be caused by -----?
Basilar meningitis occurs in meninigitis caused by -------?
The definitive test to diagnose meningitis is ---?
Relative contraindications of LP include ------?
Indications for CT or MRI in meningitis?
Meningitis + low glucose/CSF?
Meningitis + high opening CSF pressure
Meningitis + high lymphocytes/CSF?
Can you describe the SEQUENCE of management of meningitis?
Indications of corticosteroids in meningitis?
Why is dexamethasone added in bacterial meningitis?
Antibiotics of choice for bacterial meningitis in a neonate baby (<4 weeks)?
Antibiotics of choice for bacterial meningitis in ages 1 month - 50 years?
When to add ampicillin in treatment for meningitis?
A patient with impaired cell immunity developed meningitis, how to treat ?
A patient with severe allergy to B. lactams develops meningitis, how to treat?
Which antibiotic should be added if L. monocytogenes is suspected?
What are the antibiotics of choice in these cases?
a. S. pneumoniae meningitis
b. N. meningitidis meningitis
c. H. influenzae meningitis
d. S. agalactiae meningitis
e. E.coli meningitis
f. Pseudomonas aeruginosa meningitis
g. Staph. epidermidis meningitis
Medications used for treatment of meningitis are given ----
How to treat meningitis after neurosurgery of peneterating head trauma?
Antibiotics of choice for bacterial meningitis in people >50 years?
Ampicillin can be used for treatment of meningitis caused by which pathogens ?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards