
What is the definition of electric charge?
How does rubbing a plastic rod with a cloth make it charged?
What is the definition of an electric field?
What is electric current, in four words?
Charges don't move very quickly - so how come a bulb switches on immediately when a circuit is connected?
How does a battery work?
In which direction does conventional current go and in which direction do electrons flow? Why does this matter?
What happens to a bulb when a current increases?
What is used to measure current?
In a series current, what would roughly happen to a current of 10A after it's past through a bulb?
What two advantages are there of circuits in parallel?
What happens to a bulb when a current increases and why?
How does a bulb use resistance to work?
When resistance increases, what happens to current?
What rule means 'the current through a resistor is proportional to the voltage'?
Name two variable resistors and explain how they work.
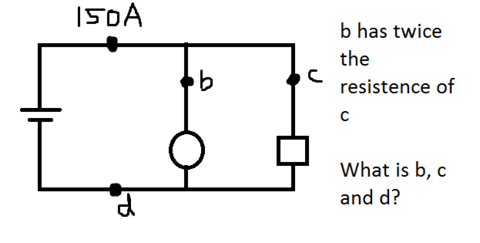
What happens to the total resistance when a resistor is added to a simple circuit in parallel or in series?
What is the definition of voltage?
What is potential difference?
What is the potential difference for resistors in a parallel and in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, which would have the bigger potential difference, a small or a large resistor?
How does potential difference have a use in circuits? Describe.
What is 'power' in electric circuits and how is it worked out, with units?
What is one watt equal to in energy terms?
There's a link between electricity and magnetism. Describe this link, without an explanation.
A square wire is placed between a north and a south magnet. When a current is passed through it, what happens and why?
What makes the wire turn more than 90 degrees?
What is the name of the process in which a potential difference is generated in a wire when it's in a changing electromagnetic field?
What does it mean that potential difference is generated in a wire during electromagnetic induction and how?
In what four ways can the induced voltage produced be increased?
Describe alternating current and direct current.
What is a transformer, how does it work and what's it used for?
Why is the voltage stepped up and later stepped down in the National Grid?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards