Fichas sobre Temperature effects, creado por Alvaro Vargas Calero el 01/05/2018.
Pineado a
19
0
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Alvaro Vargas Calero
hace más de 6 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Alvaro Vargas Calero
hace más de 6 años
|
|

Temperature effects
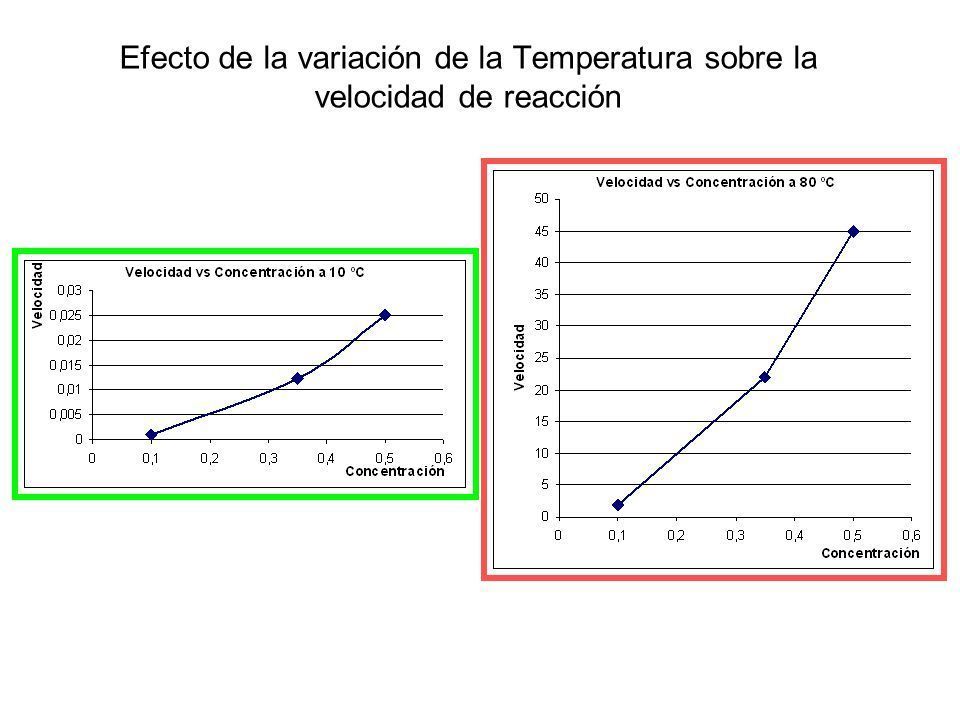
Conversely, the reaction rate of virtually all reactions decreases with decreasing temperature. For example, refrigeration retards the rate of growth of bacteria in foods by decreasing the reaction rates of biochemical reactions that enable bacteria to reproduce.
In systems where more than one reaction is possible, the same reactants can produce different products under different reaction conditions. For example, in the presence of dilute sulfuric acid and at temperatures around 100°C, ethanol is converted to diethyl ether:
At 180°C, however, a completely different reaction occurs, which produces ethylene as the major product:

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes