Psychology Frontiers and Applications by Passer
Pineado a
206
2
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Susannah Mackenz
hace alrededor de 10 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Susannah Mackenz
hace alrededor de 10 años
|
|

Transduction
Psychophysics
There are ___major branches of psychophysics.
2 branches of psychophysics?
2 Branches of psychophysics?
Absolute threshold
Lower the threshold, ___the sensitivity
STUDY
standard of how certain they must be that a stimulus is present before they will say they detect it
Signal detection theory
Affected by characteristics of the participants and nature of the situation
Difference threshold
Compare difference and absolute threshold.
WEBER'S LAW ****
Subliminal stimulus
diminishing sensitivity to an unchanging stimulus with the passage of time as sensory neurons habituate to the stimulation
Sensation refers to the activities by which our sense organs receive and transmit information, whereas perception involves the brain's processing and interpretation of the information.
Normal stimulus for vision?
The portion of the visual stimuli that we perceive is?
How does red compare to blue?
Cornea
Behind cornea?
Iris
Ciliary muscles STUDY
Image entering eye is ____ by the lens and then ____on the retina, which contains ______cells.
Thinner to focus on distant objects; thicker to focus on nearby objects;
behind pupil; reverses image and focuses it on the retina
near-sightedness; light focused before retina; eyeball longer than normal
Hyperopia
Label?
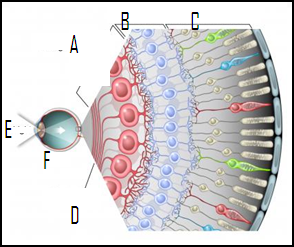
STUDY: PARTS OF THE EYE
STUDY: PATHWAY THROUGH RETINA
STUDY
RODS
cones
Cones ___ in concentration?
Rods?
Bipolar cells
Ganglion cells
Visual acuity
Rods and cones translate light waves into nerve impulses through the action of protein molecules called
is the progressive improvement in brightness sensitivity that occurs over time under conditions of low illumination
Trichromatic theory
the theory proposed by Hering that the retina contains three sets of colour receptors that respond differentially to red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white; the opponent processes that result can produce a perception of any hue
Dual-process theory
Colour blindness?
the area of the occipital lobe which receives impulses generated from the retina via the thalamus and analyzes visual input by using its feature detectors
sensory neurons that respond to particular features of a stimulus, such as its shape, angle, or colour
Parallel processing
cortical areas in the occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes that analyze visual stimuli sent to the primary visual cortex in relation to stored knowledge and that establish the “meaning” of the stimuli
is the technical measure of cycles per second
the number of sound waves, or cycles, per second
refers to the vertical size of the sound waves—that is, to the amount of compression and expansion of the molecules in the conducting medium.
The sound wave's ______ is the primary determinant of the sound's perceived loudness
Differences in amplitude are expressed as_____ , a measure of the physical pressures that occur at the eardrum
a small coil-shaped structure of the inner ear that contains the receptors for sound
a membrane that runs the length of the cochlea and contains the organ of Corti and its sound receptor hair cells
study
study
structure embedded in the basilar membrane that contains the hair cell receptors for sound
the theory of pitch perception that holds that the number of nerve impulses sent to the brain by the hair cells of the cochlea corresponds to the frequency of the sound wave; this theory is accurate at low frequencies
the theory of pitch perception that holds that sound frequencies are coded in terms of the portion of the basilar membrane where the fluid wave in the cochlea peaks; this theory accounts for perception of frequencies above 4000 Hz
Conduction deafness
hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlear receptor cells or the auditory nerve
Gustation
Olfaction
are chemical senses because their receptors are sensitive to chemical molecules rather than to some form of energy
the receptors for taste in the tongue and in the roof and back of the mouth that are sensitive to the qualities of sweet, sour, salty, and bitter
Olfactory bulb
chemical signals found in natural body scents
The tendency for some women who live together over time to become more similar to one another in the timing of their menstrual cycles
theory that proposes that the experience of pain results from the opening and closing of “gating mechanisms” in the nervous system
Endorphin
the body sense that provides feedback on the position and movements of our body parts
the sense of body orientation or equilibrium
devices that provide sensory input that can, to some extent, substitute for what blind and deaf people are not supplied by their sensory receptors
Bottom-up processing.
Top-down processing
Perception is selective . People are given
Shadowing
Unattentional blindness.
Unattentionsl blindness
Figure ground relations
Gestalt laws
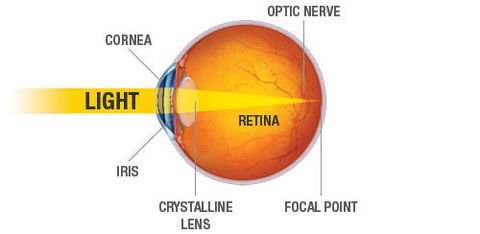
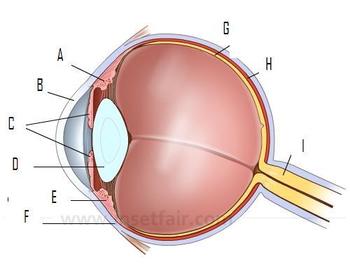
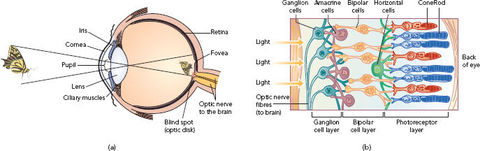
STUDY:

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes