Cerrar

Concepts to understand
LIPIDS
Lipid molecules contain relatively large ___ fragments
____: do not dissolve in water but do dissolve in non-polar solvents
•Do ___ form polymers but held together by hydrophobic forces
Lipids Major FUNCTIONS
Cell membrane:
-____ components
-Regulation of membrane _____
- Membrane ____ (cholesterol, saturation of fatty acids)
-Membrane flexibility
Energy storage:
Fuel RESERVES of a typical 70-kg man
Triacylglycerols (adipose tissue): 100'000 kcal (30-40 days)
Glycogen (liver): 600 kcal (1 day)
Glucose (blood): 40 kcal
Protein (muscle): 25,000 kcal
Lipids Major FUNCTIONS
Protection:
-Protection of internal organs
-____ insulation
-Electric insulation (____ in myelin cells)
-Skin oil
Cell signaling:
There is a wide spectrum of signal molecules (e.g., steroid hormones)
Storage and transport:
-Fat-soluble ___
-____ transport fats in blood plasma
And it tastes good too ...
Overview of all types of Lipids
These types are formed from a few rearranged functional units, like in a LEGO game.
Simplest building block: FATTY ACIDS (FA)
FA: R-COO(-)
Acyl group: RCO-
Hydrocarbon tail: R
>100 FAs that vary in:
-Length
-# of double bonds
-position of double bonds
-branching
-Mostly hydrophobic
-Polar carboxyl group --> acid
SATURATED FAT
-__ double bonds in the hydrocarbon tail
-FAs that are saturated have the ____ number of H atoms.
UNSaturated Fat
Fatty acids that have ___ ___ in their hydrocarbon tails (R) are UNsaturated.
-One double bond = ____ FA
-Many double bonds = _____ FA
Melting point = temperature at which solid fat becomes ___
Cis = 13 degrees Celsius
Trans: 45 degrees Celsius
Linear molecules pack ___
*This concept is important for membrane fluidity (need Cis b/c fats stay liquid under physiological conditions.)
Rotation is ___ around the double bond with cis and trans configurations
__ conformation is prevalent in FA
(even though ___ is often more stable)
*Trans fat may occur at ___ concentrations
The problem of dietary trans fats:
-UNsaturated fat (vegetable oil) can be ____ to become partially saturated, and therefore solid --> longer shelf life, spreadable "butter."
A certain fraction of trans molecules is inevitably produced.
Trans fats are known to be ____ : increase "bad" cholesterol
Melting Point in FA's
-___ with carbon chain length
-Decreases with addition if a __ ___
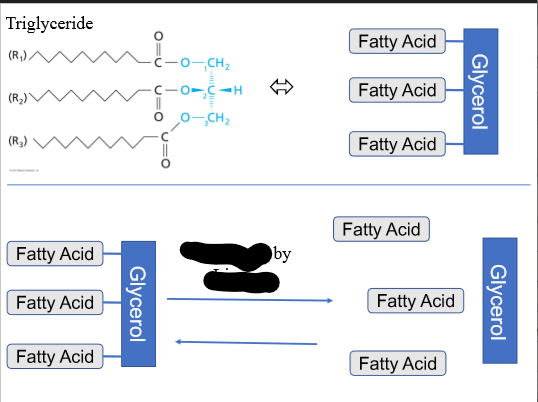
GLYCEROL
-is the backbone of many fat molecules
-The three hydroxyl groups can form up to ___ linkages
Glycerol + ester linkages with FAs give _______
Come from vegetable oils, milk products, meat
Body-produced from ___ calories we consume.
ROLE: energy depot
-However, high levels may cause ___
When glucose levels are poorly controlled in diabetes, ___ levels may increase indicating the problem.
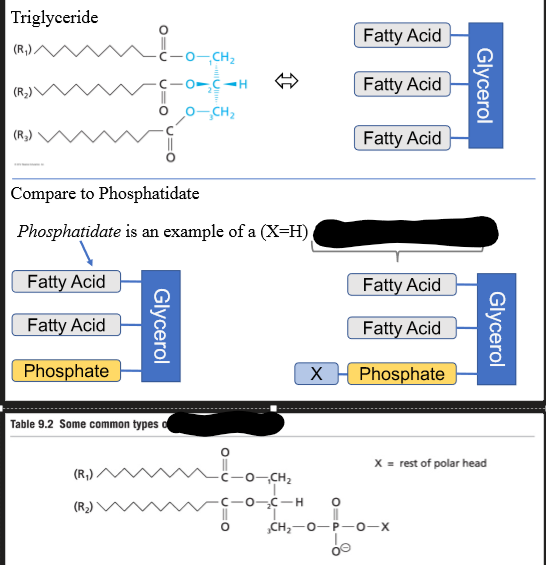
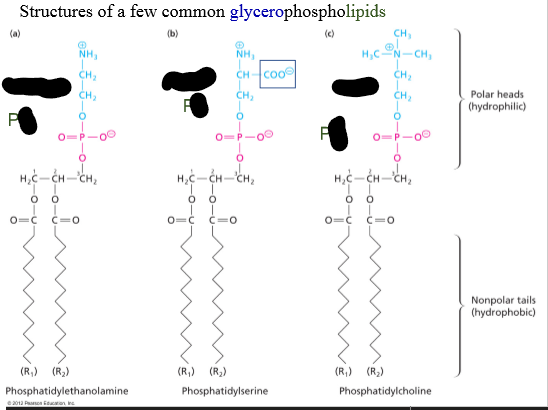
Glycerophopholipids are ___ molecules
They have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups.
The lipid composition of different membranes __ throughout the cell.
Sphingosine (another backbone)
-is similar in structure to glycerol but has a derivative (___ group)
-However, it is a backbone for a new lipid class:
______
Sphingomyelin is abundant in the ___ ___ system.
______ : glycosphingolipid in which one monosaccharide residue is attached toa ceramide
Compare:
Phospholipid versus Glycosphingolipid
___ = oligosaccharide chain is attached to a to a cerebroside
(a cerebroside + more sugars)
Cholesterol
-precursor to ___
Membrane fluidity:
-At WARM temperatures cholesterol ___ movement of phospholipids
-At COOL temperatures it maintains ___ by preventing tight packing
-Can be both made & consumed
Steroids are derivatives of ___ including:
-Steroid ___, such as androgens (m) & estrogens (f), cortisol
-Bile ___ (facilitate absorption of lipids in the intestine)
Isoprenoid Class
-Consists of steroids, lipid vitamins, & tr terpenes
-Squalene = precursor of most steroids
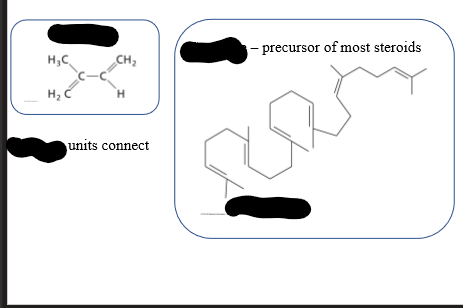
Reconnecting to Lecture 10
A, D, E, and K are the lipid vitamins; contain long ___ chains. They belong to the ___ class.
These fat-soluble vitamins are stored in fat tissues and the ___.
Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of preventable childhood ___ in developing countries.
Vitamin A is the precursor for a light-sensitive pigment in rhodopsin.
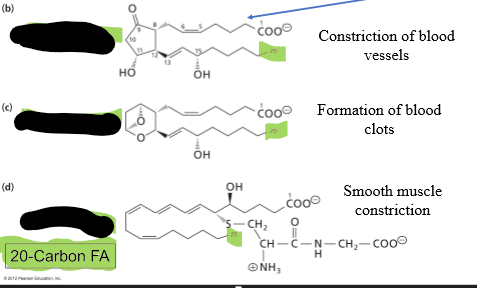
Eicosanoids are ____ molecules that play roles in inflammation, fever induction, blood pressure regulation, and clotting, & the immune response.
Aspirin ___ synthesis of prostaglandin E2
___ are esters of long-chain fatty acids and long-chain alcohols
Lipids summary:
• Largely hydrophobic
-May have a polar group => amphiphilic
-3 Fatty Acids + glycerol => ____
{2 Fatty Acids + phosphate-X}+ glycerol => ______
Glycerophospholipids are major components of cell membranes
Sphingolipids have a different (____, not glycerol) backbone
Sphingolipids are also part of the cell membrane
Steroids.
Cholesterol modulates membrane ___
Terpenes
Waxes
Eicosanoids: signal molecules that are locally formed near membranes
Vitamins

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes