Cerrar

What is stress? (as defined by Dr.Hoey)
What is a stressor?
Are all stressors bad?
Which 2 endocrine systems constitute the major components of the stress response?
What is a stress response?
Name the 3 phases in the general adaptation syndrome.
When is a stress response adaptive; long term or in short term stress?
Recall the HPA axis diagram.
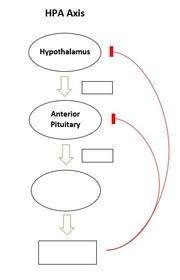
The HPA axis is activated so that ________, __________, and __________ are released in response to stressors.
List the 3 reasons why glucocorticoids are good candidates for mediating behavioral effects of stress.
At which stage of the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) is the stressor detected?
The resistance stage is where one c_____ with the stressor.
The exhaustion stage is characterized by the t__________ of the stress response and the o_________ of stress pathology.
The immune system is s____________d by a stress response in _______ term stress.
Fast epinephrine and norepinephrine release ---> e______ & a______
Slower but longer lasting Cortisol release ----> e________ mobilization
B. endorphins & Cannabinoid release --> p_______ & r_________ suppressin
Urocorticon release --> e________ CRH response
Vasopressin release --> i________ blood pressure --> e_______ gets to muscle f________.
Prolactin release --> s________ g________ functions
Glucagon release --> E__________
The MOST consistent effect of stress response hormones (as discussed in class).
In long-term stress, the immune system is i____________.
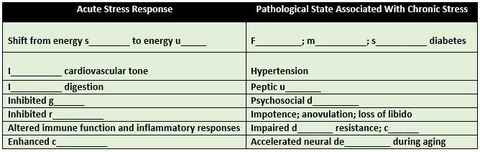
Wound healing time in caretakers of people with Alzheimer's increased by _______%?
Increased dendrites in the amygdala results in f_____, a_______, and e______ response.
stress response -> i_________ in blood pressure -> causes p_______ + risk of i_________?
High ranking ______ (M/F) in _______ (stable/unstable) group had increased clogged arteries because they have to keep establishing _______?
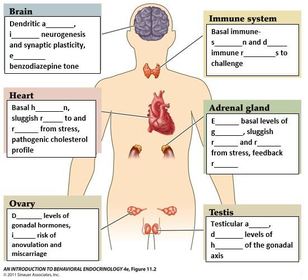
Long term exposure to glucocorticoids results in reduced n_______ (involved in better learning and memory) in h___________(which brain area)?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes