Cerrar

Physics Unit 2:
WAVES
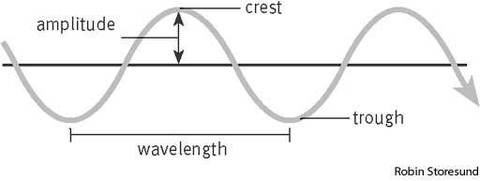
Key wave definitions:
Frequency: number of oscillations per second/number of wave fronts passing a point per second
Time period: the time taken for one complete oscillation to occur
Speed
Transverse waves: waves oscillate at 90˚ to the direction of travel
e.g. light, radio (electromagnetic spectrum)
Longitudinal waves: waves oscillate along the direction of travel
e.g. sound
When 2 waves interfere, superposition occurs. The resultant displacement of the point on the 'new' wave is the sum of the displacement at that point of the other two waves, which interfere.
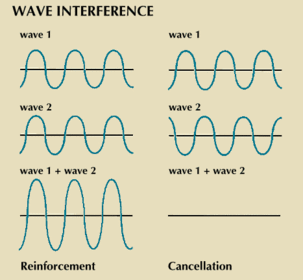
Stationary waves
These are created when 2 waves of the same amplitude, frequency and speed are superimposed.
They have nodes (points of no displacement) and antinodes (points of max displacement).
e.g. a guitar string
Stationary waves
- all points within 1 wavelength have the same phase
- all points in one loop are in antiphase with the next loop
- amplitude depends on position
- all points oscillate with the same frequency (except the nodes)
- energy remains in the system and does not travel
The electromagnetic spectrum:
Type Wavelength(x10^)Frequency (x10^)
Gamma -16 ➡️ -10 24 ➡️ 19
X-rays -12 ➡️ -8 24 ➡️ 18
Ultraviolet -10 ➡️ -7 19 ➡️ 16
Visible -8 ➡️ -6 16 ➡️ 13
Infrared -6 ➡️ -3 13 ➡️ 11
Microwaves -4 ➡️ -1 11 ➡️ 9
Radio waves -1 ➡️ 4 12 ➡️ 3
The Doppler Effect
When waves are emitted from a moving source/received by a moving boundary, the detected frequency differs from the emitted frequency. The shift in frequency is proportional to the relative speed of the motion.

Refraction
Waves refract when they travel into a different medium.
The refractive index is a measure of how much the velocity changes and therefore how much the direction changes.
Total Internal Reflection
It is possible that the wave reflects inside the denser medium, rather than refracting. This occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle C˚
Polarisation
Unpolarised waves have oscillations occurring in all planes. Waves can be polarised, and this means that oscillations occur in only one plane. These waves (transverse only) are said to be plane polarised.
Diffraction
When a waves encounters an obstacle or a gap, it diffracts, This means that the wave fronts spread out. Wave diffraction is greatest when the obstacle is of similar size to the wavelength

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes