Some key processes needed for AS Level Product Design
Pineado a
62
6
0
Sin etiquetas

|
Creado por Niamh Walsh
hace más de 9 años
|
|
Cerrar

|
Creado por Niamh Walsh
hace más de 9 años
|
|

PROCESSES
Steam bending
A process suitable for most woods, including laminates.
The timber is moistened in a steam chest, to the point where the timber is more pliable. The wood is then held in shape around a former until dried, after which it will retain its shape.
Uses include jewellery and ribs on boat hulls
Laminating
This is the process of layering materials to create a finished product.
For example, plywood is formed by layering hardwood veneer at 90˚ to each other and bonding with resin, forming warp-resistant board.
Laminate flooring and kitchen work surfaces are formed by layering chipboard/fibreboard with a hardwood veneer and a clear, hard-wearing resin on the top
Drop Iron Forging
Used where large numbers of similarly shaped objects are required. It is a refining process.
Large forces (the upper half of the mould half drops) on the metal blank force it into the shape of the die. This usually happens with many dies to achieve the products final shape.
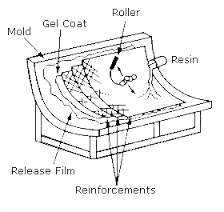
'Lay up' Resin techniques
The term used for processes involved with Glass Reinforced Plastic manufacture. A mould is required.
Die casting
The process used to cast metals with low melting points - alloys used are generally zinc or aluminium based.
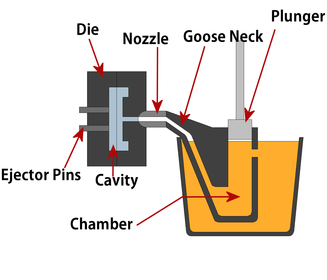
Industrial die casting
Usually hot chamber high pressure die casting.
More than one die is often used, so complex shapes can be achieved.
Uses include door locks and the internal components of electrical sockets
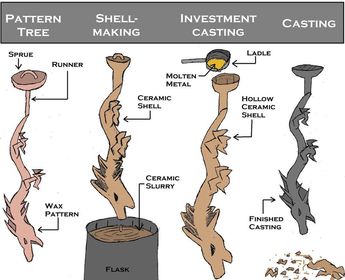
Investment casting
An extremely old process and not commonly used. Suitable for metals with a high melting point.
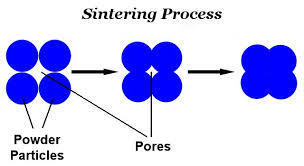
Sintering
Used for materials which are difficult to process in any other way.

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes